 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Detailed explanation of how to detect and upgrade Node dependencies in projects
Detailed explanation of how to detect and upgrade Node dependencies in projects
Detailed explanation of how to detect and upgrade Node dependencies in projects
This article will introduce you to the method of detecting and upgrading Node dependencies in the project. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

In modern front-end development, a project often relies on many third-party packages, ranging from dozens or even hundreds. So how to detect and upgrade these dependencies is became a problem. [Related recommendations: "nodejs Tutorial"]
npm outdated and npm update
Fortunately, npm provides us with npm outdated and npm update these two commands.
Enter an older react project and execute npm outdated. As expected, upgrade suggestions are given.
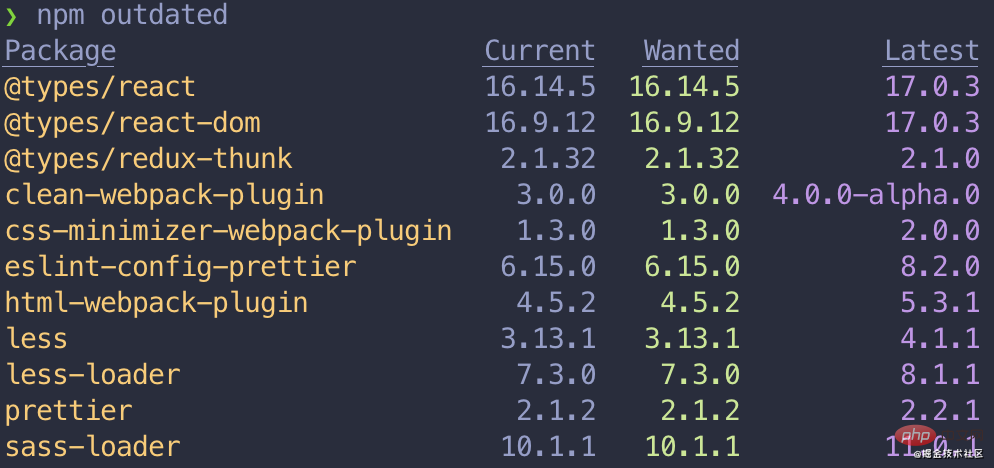
Then execute npm update to upgrade. No response ???
Looked at --help, maybe the posture is wrong? Try npm update less . No response 1
Continue trying npm update less --save, still no response.
The Wanted that appears in the picture belongs to Wanted, but I still want to upgrade to Latest
Then I checked the detailed log through npm update --dd, I found that there will always be some prompts like this in the end:
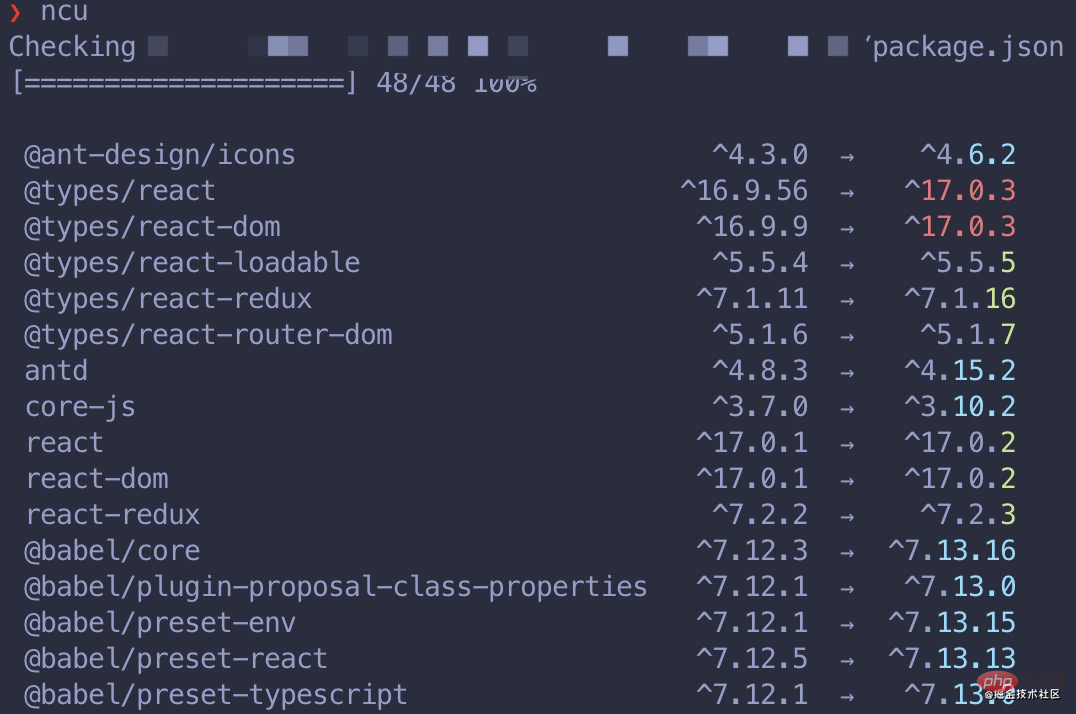
It seems that there is no hope of upgrading. The author thinks this may be for the sake of stability of the project? After all, upgrading across major versions is still very risky. But it doesn’t make sense that the minor version won’t be upgraded.
It seems npm update is hopeless.
So ncu is here!
神器ncu
ncu is npm-check-updates, which can detect and update## The dependent packages in #package.json are the latest latest versions. Let’s take a look at how to use it.
npm install -g npm-check-updates. Of course, you can also not install it and use npx to execute it. Here the author uses Global installation method.
npm-check-updates or quickly execute it through ncu.
Detecting upgradeable dependency packages
It is still the old react project just now, executencu for upgrade detection:

ncu can be upgraded with one click.
One-click upgrade
ncu provides us with the command parameters -u for one-click upgrade, execute ncu -u is enough.
Run npm install to install new versions.
package.json to check it out. It turns out that it is a powerful one, and everyone who can upgrade it will be upgraded to the latest version.
You need to be careful when performing one-click upgrade. After all,ncu -u
will not consider cross-version compatibility issues. Some packages may be incompatible when performing major version upgrades. You need to pay attention here. , be prepared to change the code.
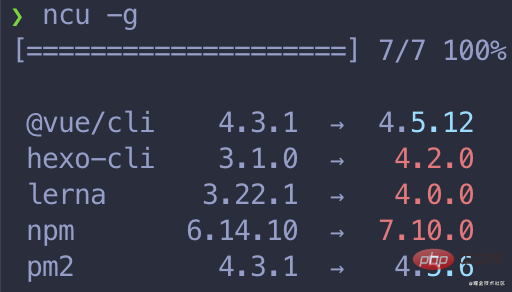
Global package detection, on-demand detection
Of coursencu You can also detect globally installed packages, execute ncu - g is enough:
# upgrade only mocha ncu mocha ncu -f mocha ncu --filter mocha # upgrade packages that start with "react-" ncu react-* ncu "/^react-.*$/" # upgrade everything except nodemon ncu \!nodemon ncu -x nodemon ncu --reject nodemon # upgrade only chalk, mocha, and react ncu chalk mocha react ncu chalk, mocha, react ncu -f "chalk mocha react" # upgrade packages that do not start with "react-". ncu \!react-* ncu '/^(?!react-).*$/' # mac/linux ncu "/^(?!react-).*$/" # windows
Configuration file mode
If you find it too troublesome to enter various filtering conditions on the command line, it is more convenient. The way to use it is to create a configuration file, such as.ncurc.json
{
"upgrade": true,
"reject": ["webpack", "antd"]
}- upgrade
: Do you need one-click upgrade? - #filter
: Which modules to upgrade only - reject
: Which modules to ignore
.ncurc.{json,yml,js}. Or customize the file name, and then use --configFileName and --configFilePath to specify the file.
API 调用
ncu 还对外暴露了 API,我们可以通过编程的方式检测并升级某个项目的依赖包。使用示例如下:
const ncu = require('npm-check-updates');
(async () => {
const upgraded = await ncu.run({
// Pass any cli option
packageFile: './package.json',
upgrade: true,
// Defaults:
// jsonUpgraded: true,
// silent: true,
});
console.log(upgraded); // { "mypackage": "^2.0.0", ... }
// `upgrade: false`:返回可升级的包及最新版本信息
// `upgrade: true`:返回已经升级的包及最新版本信息
})();目前,我们的脚手架里就用到了这个特性,通过脚手架来对项目依赖进行升级。
OK,以上就是关于 Node 依赖检测并升级的全部内容,你开始用 ncu 了吗?
更多编程相关知识,可访问:编程入门!!
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of how to detect and upgrade Node dependencies in projects. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 The difference between nodejs and tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:16 AM
The difference between nodejs and tomcat
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:16 AM
The main differences between Node.js and Tomcat are: Runtime: Node.js is based on JavaScript runtime, while Tomcat is a Java Servlet container. I/O model: Node.js uses an asynchronous non-blocking model, while Tomcat is synchronous blocking. Concurrency handling: Node.js handles concurrency through an event loop, while Tomcat uses a thread pool. Application scenarios: Node.js is suitable for real-time, data-intensive and high-concurrency applications, and Tomcat is suitable for traditional Java web applications.
 The difference between nodejs and vuejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:17 AM
The difference between nodejs and vuejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:17 AM
Node.js is a server-side JavaScript runtime, while Vue.js is a client-side JavaScript framework for creating interactive user interfaces. Node.js is used for server-side development, such as back-end service API development and data processing, while Vue.js is used for client-side development, such as single-page applications and responsive user interfaces.
 Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Node.js can be used as a backend framework as it offers features such as high performance, scalability, cross-platform support, rich ecosystem, and ease of development.
 What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
There are two npm-related files in the Node.js installation directory: npm and npm.cmd. The differences are as follows: different extensions: npm is an executable file, and npm.cmd is a command window shortcut. Windows users: npm.cmd can be used from the command prompt, npm can only be run from the command line. Compatibility: npm.cmd is specific to Windows systems, npm is available cross-platform. Usage recommendations: Windows users use npm.cmd, other operating systems use npm.
 What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
The following global variables exist in Node.js: Global object: global Core module: process, console, require Runtime environment variables: __dirname, __filename, __line, __column Constants: undefined, null, NaN, Infinity, -Infinity
 Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Yes, Node.js is a backend development language. It is used for back-end development, including handling server-side business logic, managing database connections, and providing APIs.
 Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
The main differences between Node.js and Java are design and features: Event-driven vs. thread-driven: Node.js is event-driven and Java is thread-driven. Single-threaded vs. multi-threaded: Node.js uses a single-threaded event loop, and Java uses a multi-threaded architecture. Runtime environment: Node.js runs on the V8 JavaScript engine, while Java runs on the JVM. Syntax: Node.js uses JavaScript syntax, while Java uses Java syntax. Purpose: Node.js is suitable for I/O-intensive tasks, while Java is suitable for large enterprise applications.
 How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Server deployment steps for a Node.js project: Prepare the deployment environment: obtain server access, install Node.js, set up a Git repository. Build the application: Use npm run build to generate deployable code and dependencies. Upload code to the server: via Git or File Transfer Protocol. Install dependencies: SSH into the server and use npm install to install application dependencies. Start the application: Use a command such as node index.js to start the application, or use a process manager such as pm2. Configure a reverse proxy (optional): Use a reverse proxy such as Nginx or Apache to route traffic to your application





