
This article will give you a detailed understanding of the various types of communication between components in Angular. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Three typical relationships between components: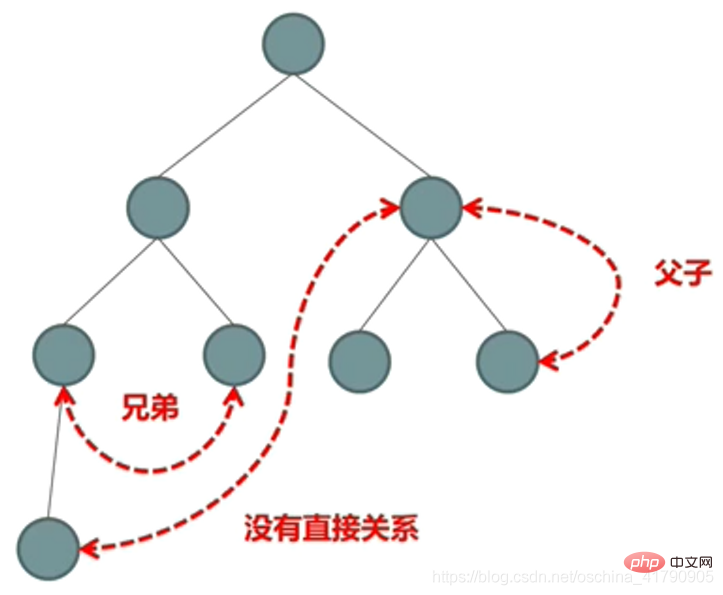
Interaction between parent components (@Input/@Output/template variable/@ViewChild)
Interaction between non-parent and child components ( Service/localStorage)
You can also use Session and routing parameters for communication, etc.
Recommended related tutorials: "angular tutorial 》
Writing of child components
@Component({
selector: 'app-child',
templateUrl: './child.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./child.component.css']
})
export class ChildComponent implements OnInit {
private _childTitle = '我是子组件';
@Input()
set childTitle(childTitle: string) {
this._childTitle = childTitle;
}
get childTitle(): string {
return this._childTitle;
}
@Output()
messageEvent: EventEmitter<string> = new EventEmitter<string>();
constructor() { }
ngOnInit(): void {
}
sendMessage(): void {
this.messageEvent.emit('我是子组件');
}
childFunction(): void {
console.log('子组件的名字是:' + this.childTitle);
}
}<div class="panel panel-primary">
<div class="panel-heading">{{childTitle}}</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<button (click)="sendMessage()" class="btn btn-success">给父组件发消息</button>
</div>
</div>Parent component
@Component({
selector: 'app-parent-and-child',
templateUrl: './parent-and-child.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./parent-and-child.component.css']
})
export class ParentAndChildComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit(): void {
}
doSomething(event: any): void {
alert(event);
}
}<div class="panel panel-primary">
<div class="panel-heading">父组件</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<app-child #child (messageEvent) = "doSomething($event)"></app-child>
<button (click)="child.childFunction()" class="btn btn-success">调用子组件的方法</button>
</div>
</div>@Input Property binding is one-way Yes, changes in the properties of the parent component will affect changes in the properties of the child component, but changes in the properties of the child component will not in turn affect changes in the properties of the parent component.
However, you can use @Input() and @Output() to achieve two-way binding of properties.
@Input() value: string; @Output() valueChange: EventEmitter<any> = new EventEmitter(); // 实现双向绑定 <input [(value)] = "newValue"></input>
Note: When using [()] for two-way binding, the output attribute name must be composed of the input attribute name and Change, in the form: xxxChange.
Use Service for interaction
/**
* 用于充当事件总线
*/
@Injectable()
export class EventBusService {
evnetBus: Subject<string> = new Subject<string>();
constructor() { }
}@Component({
selector: 'app-child1',
templateUrl: './child1.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./child1.component.css']
})
export class Child1Component implements OnInit {
constructor(private eventBusService: EventBusService) { }
ngOnInit(): void {
}
triggerEventBus(): void {
this.eventBusService.evnetBus.next('child1 触发的事件');
}
}<div class="panel panel-primary">
<div class="panel-heading">child1 组件</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<button (click)="triggerEventBus()" class="btn btn-success">触发事件</button>
</div>
</div>@Component({
selector: 'app-child2',
templateUrl: './child2.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./child2.component.css']
})
export class Child2Component implements OnInit {
events: Array<string> = new Array<string>();
constructor(private eventBusService: EventBusService) { }
ngOnInit(): void {
this.listenerEvent();
}
listenerEvent(): void {
this.eventBusService.evnetBus.subscribe( value => {
this.events.push(value);
});
}
}<div class="panel panel-primary">
<div class="panel-heading">child2 组件</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<p *ngFor="let event of events">{{event}}</p>
</div>
</div>@Component({
selector: 'app-brother',
templateUrl: './brother.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./brother.component.css']
})
export class BrotherComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit(): void {
}
}<div class="panel panel-primary">
<div class="panel-heading">第二种:没有父子关系的组件间通讯</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<app-child1></app-child1>
<app-child2></app-child2>
</div>
</div>Use localStorage to interact
@Component({
selector: 'app-local-child1',
templateUrl: './local-child1.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./local-child1.component.css']
})
export class LocalChild1Component implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit(): void {
}
writeData(): void {
window.localStorage.setItem('message', JSON.stringify({name: 'star', age: 22}));
}
}<div class="panel panel-primary">
<div class="panel-heading"> LocalChild1 组件</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<button class="btn btn-success" (click)="writeData()">写入数据</button>
</div>
</div>@Component({
selector: 'app-local-child2',
templateUrl: './local-child2.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./local-child2.component.css']
})
export class LocalChild2Component implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit(): void {
}
readData(): void {
const dataStr = window.localStorage.getItem('message');
const data = JSON.parse(dataStr);
console.log('name:' + data.name, 'age:' + data.age);
}
}<div class="panel panel-primary">
<div class="panel-heading">LocalChild2 组件</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<button class="btn btn-success" (click)="readData()">读取数据</button>
</div>
</div>@Component({
selector: 'app-local-storage',
templateUrl: './local-storage.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./local-storage.component.css']
})
export class LocalStorageComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit(): void {
}
}<div class="panel panel-primary">
<div class="panel-heading">第三种方案:利用 localStorge 通讯</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<app-local-child1></app-local-child1>
<app-local-child2></app-local-child2>
</div>
</div>Programming Video! !
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of several methods of communication between components in Angular. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!