Detailed explanation of the php7 environment built by vagrant

I have basically gone through the basic knowledge of vagrant before. I believe that as long as you follow the tutorial, you will have set up your own basic environment. Next, let’s talk about how to set up a development environment for php7.
Let me state that the box used here is the centos7 demonstrated earlier
The address is provided:
https://github.com/tommy-muehle/puppet-vagrant-boxes/ releases/download/1.1.0/centos-7.0-x86_64.box
Installing nginx
First you need to update some ngin-related sources.
$ rpm -Uvh http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/noarch/RPMS/nginx-release-centos-7-0.el7.ngx.noarch.rpm// 执行安装过程 $ yum install nginx
Recommended (free): PHP7
When you see the following interface, please wait. If you need to enter something, please press directly y Then press Enter. 
Start nginx and set it to start at boot
$ systemctl start nginx $ systemctl enable nginx
Install epel and remi sources
Installation epel, epel is a software warehouse project maintained by the Fedora team, providing RHEL/CentOS with software packages that they do not provide by default. When installing, you must pay attention to the version of your system.
$ rpm -ivh http://mirrors.opencas.cn/epel/7/x86_64/e/epel-release-7-5.noarch.rpm
Modified on 2016-10-22:
The source posted above recently cannot be used. Please find the corresponding version here
http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/
If you can’t pass the wall, please use domestic mirrors
http://mirrors.sohu.com/fedora- epel/7/x86_64/e/epel-release-7-8.noarch.rpm
remi source contains the latest php related information, such as: php7, mysql, etc., so in order to easily obtain php7 For the latest information, you also need to install this source.
$ rpm -ivh http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm
iptables firewall
Because I often use iptables before, I am not familiar with the firewalld firewall that comes with centos7, so I will turn off the firewalld that comes with centos7 and enable it myself. Be familiar with iptables.
First, turn off the built-in firewalld firewall
$ systemctl stop firewalld.service $ systemctl disable firewalld.service #防止开机启动
Install iptables
$ yum install iptables-services
The installation process is as shown in the figure below
Start iptables firewall
systemctl start iptables.service systemctl enable iptables.service #开机自动启动
Edit firewall configuration file
In order for us to have smooth access on our own host, we need to open the following ports,
vim /etc/sysconfig/iptables
Edit the firewall, set 80 (nginx) 3306 (mysql/mariadb) 6379 (redis) port, and the external network can access 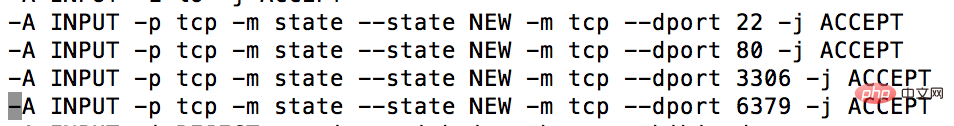
PHP7. 0 installation
View the installable php information in the remi source
$ yum list --enablerepo=remi --enablerepo=remi-php70 | grep php70
The list will list all the php module information that can be installed, install the modules you need from it, install it below Module is my own module selection situation. Some of them are required and some are optional. For example, php-fpm is necessary if you are using nginx.
$ yum install --enablerepo=remi --enablerepo=remi-php70 php php-opcache php-pecl-apcu php-devel php-mbstring php-mcrypt php-mysqlnd php-pecl-xdebug php-pdo php-pear php-fpm php-cli php-xml php-bcmath php-process php-gd php-common php-json php-imap php-pecl-redis php-pecl-memcached php-pecl-mongodb
After the installation is complete, enter php -v to view the currently installed php version information. 
Start php-fpm, because nginx needs it to parse the php program
$ systemctl start php-fpm$ systemctl enable php-fpm #设置开机自启动
Configure nginx to access php
Enter the nginx file configuration center,
$ cd /etc/nginx/conf.d/# 复制默认的配置文件 $ cp default.conf php.conf
First edit the default file through vim. Change the listening port to 8080, because our own php.conf will use port 80 later. 
Now let’s edit the copied php.conf file. You can directly copy the following content. As for the meaning of configuration, I will open an article to explain it separately later.
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
charset utf-8;
root /vagrant/www;# 自己的项目目录,也就是php项目所在目录
location / { # 请注意,一定要加index.php这项
index index.php index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php; # 注意此处变量的不同
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}After modifying the file, nginx must be restarted for the current configuration to take effect.
$ systemctl reload nginx
Test access
Create a new file index.php under /vagrant/www
<?php
phpinfo();Open it in the browser and access the corresponding ip , you can see the output php information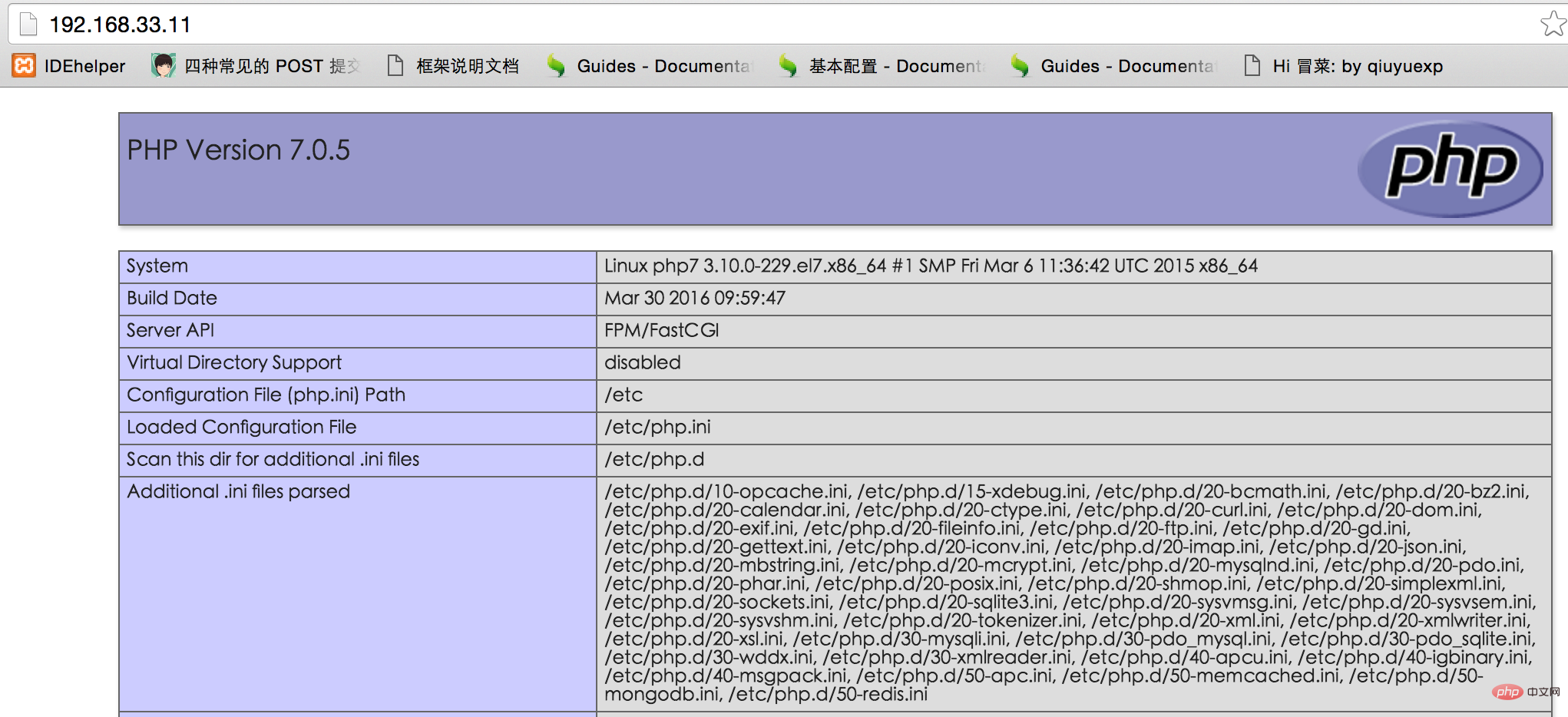
Note: If there are newly added php modules during use, you need to restart php-fpm
systemctl reload php-fpm
Mariadb installation
Many students here may have heard of mariadb for the first time, and they are mysql An important molecule of , or it can be understood as a replacement for mysql. Since mysql was controlled, the update speed has been too slow. There is basically no difference in usage between the two. You can find out for yourself what pitfalls there are in practice. Haha, don’t say I’m irresponsible.
# 安装$ yum install mariadb-server# 启动服务$ systemctl start mariadb# 开机启动$ systemctl enable mariadb
MariaDB security configuration
MariaDB default root password is empty, we need to set it and execute the script:
$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
这个脚本会经过一些列的交互问答来进行MariaDB的安全设置。
首先提示输入当前的root密码:
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
初始root密码为空,我们直接敲回车进行下一步。Set root password? [Y/n]
设置root密码,默认选项为Yes,我们直接回车,提示输入密码,在这里设置您的MariaDB的root账户密码。Remove anonymous users? [Y/n]
是否移除匿名用户,默认选项为Yes,建议按默认设置,回车继续。Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n]
是否禁止root用户远程登录?如果您只在本机内访问MariaDB,建议按默认设置,回车继续。 如果您还有其他云主机需要使用root账号访问该数据库,则需要选择n。Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n]
是否删除测试用的数据库和权限? 建议按照默认设置,回车继续。Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n]
是否重新加载权限表?因为我们上面更新了root的密码,这里需要重新加载,回车。
完成后你会看到Success!的提示,MariaDB的安全设置已经完成。我们可以使用以下命令登录MariaDB:
$ mysql -uroot -p
按提示输入root密码,就会进入MariaDB的交互界面,说明已经安装成功。 
最后我们将MariaDB设置为开机启动。
$ sudo systemctl enable mariadb
让外网可以进行链接
mysql> grant all on *.* to 'root'@'%' identified by 'root'; mysql> flush privileges;
安装composer
composer的大名,我就不想介绍了,如果你是一个phper,没用过,我也就不怪你,毕竟但是他现在才刚过1.0版,但是如果听都没听过,请面壁去……
安装说明
$ php -r “readfile(‘https://getcomposer.org/installer‘);” > composer-setup.php$ php composer-setup.php $ php -r “unlink(‘composer-setup.php’);”
上述 3 条命令的作用依次是:
- 下载安装脚本(composer-setup.php)到当前目录。
- 执行安装过程。
- 删除安装脚本 – composer-setup.php 。
全局安装composer
全局安装是将 Composer 安装到系统环境变量 PATH 所包含的路径下面,然后就能够在命令行窗口中直接执行 composer 命令了。
Mac 或 Linux 系统:打开命令行窗口并执行如下命令将前面下载的 composer.phar 文件移动到 /usr/local/bin/ 目录下面:
$ sudo mv composer.phar /usr/local/bin/composer
然后执行: composer -v 
由于composer的包都在国外,这里设置一下composer的配置,让其每次运行时,都使用国内的包
$ composer config -g repo.packagist composer https://packagist.phpcomposer.com
查看composer的配置文件
vim /root/.composer/config.json 
看到以上内容,表示配置成功!
至此,基本的php7环境搭建已经完成了。然后呢,下一次说一说用vagrant搭建redis吧。当然我不会仅仅只说redis的搭建额。到时候看啊吧!
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the php7 environment built by vagrant. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 How to Use Sessions Effectively in PHP 7?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:20 PM
How to Use Sessions Effectively in PHP 7?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:20 PM
This article details effective PHP 7 session management, covering core functionalities like session_start(), $_SESSION, session_destroy(), and secure cookie handling. It emphasizes security best practices including HTTPS, session ID regeneration, s
 How to Monitor PHP 7 Performance with Tools like New Relic?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:28 PM
How to Monitor PHP 7 Performance with Tools like New Relic?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:28 PM
This article explains how to monitor PHP 7 application performance using New Relic. It details New Relic's setup, key performance indicators (KPIs) like Apdex score and response time, bottleneck identification via transaction traces and error track
 How to Upgrade from PHP 5.6 to PHP 7?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:29 PM
How to Upgrade from PHP 5.6 to PHP 7?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:29 PM
This article details upgrading PHP 5.6 to PHP 7, emphasizing crucial steps like backing up, checking server compatibility, and choosing an upgrade method (package manager, compiling, control panel, or web server configuration). It addresses potentia
 How to Autoload Classes in PHP 7?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:20 PM
How to Autoload Classes in PHP 7?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:20 PM
This article explains PHP 7's autoloading, using spl_autoload_register() to load classes on demand. It details best practices like namespace-based autoloading and caching for performance optimization, addresses common issues (e.g., class not found
 How to Use Git for Version Control in PHP 7 Projects?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
How to Use Git for Version Control in PHP 7 Projects?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:27 PM
This article guides PHP 7 developers on using Git for version control. It covers initialization, staging, committing, ignoring files, remote repositories, branching, merging, conflict resolution, and essential Git commands. Best practices for effic
 How to Deploy a PHP 7 Application to a Web Server?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:28 PM
How to Deploy a PHP 7 Application to a Web Server?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:28 PM
This article details deploying PHP 7 applications, covering methods (FTP, SSH, deployment tools), server configuration (Apache/Nginx, PHP-FPM), database setup, and crucial security considerations. It highlights common challenges like server compatib
 How to Use Xdebug for Debugging PHP 7 Code?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:26 PM
How to Use Xdebug for Debugging PHP 7 Code?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:26 PM
This article explains how to use Xdebug for debugging PHP 7 code. It covers Xdebug configuration (installation, php.ini settings, IDE setup), breakpoint usage (conditional, function, remote), and troubleshooting connection issues. Effective debuggi
 How to Include and Require Files in PHP 7?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 02:52 PM
How to Include and Require Files in PHP 7?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 02:52 PM
This article explains PHP 7's include, include_once, require, and require_once file inclusion methods. It details their differences in error handling (warnings vs. fatal errors) and multiple inclusion prevention. Best practices for file organizatio




