
The directory where basic Linux commands are stored is "/bin". Bin is the abbreviation of binary. The "/bin" directory is a binary executable file directory. It is mainly used to place necessary executable files for the system, such as cat, cp, gzip, kill, ls, mkdir, more, mount, rm, etc.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.1 system, Dell G3 computer.
The directory where basic Linux commands are stored is "/bin".
bin:
bin is the abbreviation of binary, which mainly places the necessary executable files of the system, such as:
cat, cp, chmod df, dmesg, gzip, kill, ls, mkdir, more, mount, rm, su, tar, etc.

Tree directory structure:
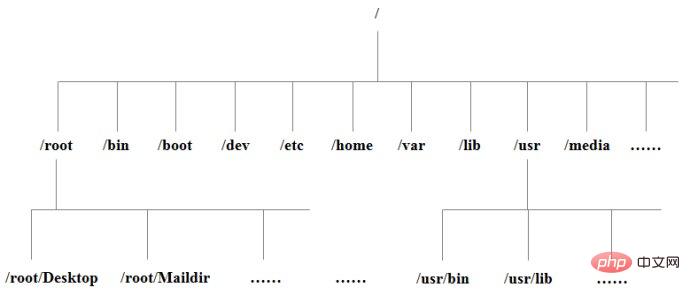
The following is an introduction to directory and file related commands, and by the way, we learned the directory organization structure :
List command: ls; parameter -l: detailed information, which is used to view what files are in the directory. I think the directory here is equivalent to the folder under windows. View the detailed command to also view the properties of these files. Linked files or file attributes called shortcuts start with l. If it is a directory, its file attributes begin with d;
View the current directory: pwd, used to view which directory it is currently in. When the Shell is first started, it is in the root directory. You can enter the root directory and use the ll command to view the directory structure.
1. /bin directory: bin is the abbreviation of Binary. This directory stores the most commonly used commands.
2. / boot directory:
1) Change directory [cd].
2) If you want to go to the root directory: [cd /]; and to go to the directory with an absolute path, [cd /boot] (absolute command).
3) You can view the files in the boot. To update the kernel, you need to update the files in the boot. vmlinuz-2.4.20-8 is the image of the kernel file;
In boot The grub directory stores the boot program, and grub.conf in the grub directory is the configuration file.
4) File printing (view file content): [cat]; such as [cat grub.conf].
3. /dev directory: [cd dev]; dev is the abbreviation of Device. Enter the device directory, which stores device files.
You need to care about this directory when making a driver.
What starts with b is a block device, and what starts with c is a character device; hdb2 represents the second partition of the second hard disk, and hda represents the first hard disk; (3, 66): 3 represents the major device number, Represents which type of equipment it is, 66 is the slave device number, and the identification is the number of this type of equipment.
4. /etc directory: [Return to the previous directory: [cd ..]; [cd etc] Enter the etc directory, which contains the system configuration files;
inittab File: Describes system startup settings at a certain run level. Run levels include halt, single user mode,
Full multiuser mode, X11 (graphical interface), reboot, etc.,
id: 5: Indicates starting with the graphical interface; the /etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit file configures the process started by the system. # respawn: The program behind it indicates that it will automatically restart after the process terminates unexpectedly;
rc.d: cd rc.d, the file name is green, which means it has execution permission;
12. /proc directory: the mapping of the system running process, view its contents, the number represents the ID number of the process, cd 1, enter process No. 1:
Memory usage, space mapping, status, etc. ;
cpuinfo: cpu related information, cat cpuinfo view;
devices: devices;
filesystems: supported file systems;
interrupts: Interrupts supported by the system;
iomem: memory mapping, the left side after cat viewing represents the address mapping;
ioports: io port mapping;
meminfo: memory information;
modules: module driver, there are two loading methods for Linux driver:
1) Directly compile the kernel;
2) After Linux is started, insert a separate module into the kernel;
partitions: partition;
pci: bus number, device number on the bus, interrupt number;
stat: status information;
version: version;
uptime: Indicates the running time of the entire system;
13. /root directory: The directory where the root user logs in
14. /sbin directory: System management tools;
15. /tmp directory: stores temporary files;
16. /usr directory: src directory stores kernel source code; include: writes header files needed for Linux;
17. /var directory: stores temporary variables;
Related recommendations: "Linux Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What is the directory where basic linux commands are stored?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!