The unicode character set uses several bytes to represent a character
The unicode character set uses 2 bytes to represent a character. Unicode sets a unified and unique binary encoding for each character in each language to meet the requirements for cross-language and cross-platform text conversion and processing; it can unify all texts in the world using 2 bytes coding.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
The unicode character set uses 2 bytes to represent a character.
Unicode (Unicode, Universal Code, Unicode) is a character encoding used on computers. It sets a unified and unique binary encoding for each character in each language to meet the requirements for cross-language and cross-platform text conversion and processing.
If various text encodings are described as dialects from various places, then Unicode is a language developed cooperatively by countries around the world.
In this language environment, there will be no more language encoding conflicts. Content in any language can be displayed on the same screen. This is the biggest benefit of Unicode. It means that all the text in the world is uniformly encoded using 2 bytes. In that way, with unified encoding like this, 2 bytes are enough to accommodate most text in all languages in the world.
The scientific name of Unicode is "Universal Multiple-Octet Coded Character Set", referred to as UCS.
The early Unicode standards were called UCS-2 and UCS-4. UCS-2 is encoded with two bytes, and UCS-4 is encoded with 4 bytes. What is currently used is UCS-2, which is a 2-byte encoding, and UCS-4 was developed to prevent 2 bytes from being insufficient in the future.
UCS-4 is divided into 2^7=128 groups according to the highest byte with the highest bit being 0. Each group is divided into 256 planes according to the next highest byte. Each plane is divided into 256 rows according to the third byte, and each row has 256 code points (cells). Plane 0 of group 0 is called BMP (Basic Multilingual Plane). UCS-2 is obtained by removing the first two zero bytes of UCS-4's BMP.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of The unicode character set uses several bytes to represent a character. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 1MB of storage capacity is equivalent to how many bytes
Mar 03, 2023 pm 05:42 PM
1MB of storage capacity is equivalent to how many bytes
Mar 03, 2023 pm 05:42 PM
1MB of storage capacity is equivalent to 2 to the 20th power bytes, or 1,048,576 bytes. MB is a storage unit in computers, pronounced as "mega"; because 1MB is equal to 1024KB, and 1KB is equal to 1024B (bytes), so 1MB is equal to 1048576 (1024 *1024) bytes.
 How many bytes does 128mb mean?
Nov 29, 2022 am 10:35 AM
How many bytes does 128mb mean?
Nov 29, 2022 am 10:35 AM
128mb refers to 134217728 bytes; the byte conversion formula is "1MB=1024KB=1048576B=8388608bit", which means that 1048576 English letters and 524288 Chinese characters can be saved; the traffic unit conversion formula is 1GB=1024MB, 1MB=1024KB, 1KB= 1024B.
 1 bit equals how many bytes
Mar 09, 2023 pm 03:11 PM
1 bit equals how many bytes
Mar 09, 2023 pm 03:11 PM
1 bit is equal to one-eighth of a byte. In the binary number system, each 0 or 1 is a bit (bit), and a bit is the smallest unit of data storage; every 8 bits (bit, abbreviated as b) constitute a byte (Byte), so "1 byte ( Byte) = 8 bits”. In most computer systems, a byte is an 8-bit (bit) long data unit. Most computers use a byte to represent a character, number, or other character.
 How many bytes does one ascii character occupy?
Mar 09, 2023 pm 03:49 PM
How many bytes does one ascii character occupy?
Mar 09, 2023 pm 03:49 PM
One ascii character occupies 1 byte. ASCII code characters are represented by 7-bit or 8-bit binary encoding in the computer and are stored in one byte, that is, one ASCII code occupies one byte. ASCII code can be divided into standard ASCII code and extended ASCII code. Standard ASCII code is also called basic ASCII code. It uses 7-bit binary numbers (the remaining 1 binary digit is 0) to represent all uppercase and lowercase letters, and the numbers 0 to 9. Punctuation marks, and special control characters used in American English.
 Use java's Character.isDigit() function to determine whether a character is a number
Jul 27, 2023 am 09:32 AM
Use java's Character.isDigit() function to determine whether a character is a number
Jul 27, 2023 am 09:32 AM
Use Java's Character.isDigit() function to determine whether a character is a numeric character. Characters are represented in the form of ASCII codes internally in the computer. Each character has a corresponding ASCII code. Among them, the ASCII code values corresponding to the numeric characters 0 to 9 are 48 to 57 respectively. To determine whether a character is a number, you can use the isDigit() method provided by the Character class in Java. The isDigit() method is of the Character class
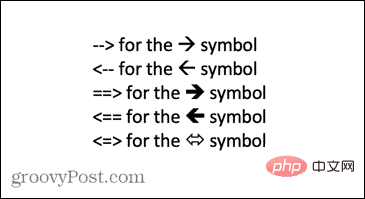 How to type arrows in Word
Apr 16, 2023 pm 11:37 PM
How to type arrows in Word
Apr 16, 2023 pm 11:37 PM
How to use AutoCorrect to type arrows in Word One of the fastest ways to type arrows in Word is to use the predefined AutoCorrect shortcuts. If you type a specific sequence of characters, Word automatically converts those characters into arrow symbols. You can draw many different arrow styles using this method. To type an arrow in Word using AutoCorrect: Move your cursor to the location in the document where you want the arrow to appear. Type one of the following character combinations: If you don't want what you type to be corrected to an arrow symbol, press the backspace key on your keyboard to
 How many bytes do utf8 encoded Chinese characters occupy?
Feb 21, 2023 am 11:40 AM
How many bytes do utf8 encoded Chinese characters occupy?
Feb 21, 2023 am 11:40 AM
UTF8 encoded Chinese characters occupy 3 bytes. In UTF-8 encoding, one Chinese character is equal to three bytes, and one Chinese punctuation mark occupies three bytes; while in Unicode encoding, one Chinese character (including traditional Chinese) is equal to two bytes. UTF-8 uses 1~4 bytes to encode each character. One US-ASCIl character only needs 1 byte to encode. Latin, Greek, Cyrillic, Armenian, and Hebrew with diacritical marks. , Arabic, Syriac and other letters require 2-byte encoding.
 How many bytes does an ascii code occupy?
Sep 07, 2023 pm 04:03 PM
How many bytes does an ascii code occupy?
Sep 07, 2023 pm 04:03 PM
An ASCII code occupies one byte. ASCII code is a coding standard used to represent characters. It uses 7-bit binary numbers to represent 128 different characters, including letters, numbers, punctuation marks, special characters, etc. A byte is the basic unit of computer storage unit. It consists of 8 binary bits. Each binary bit can be 0 or 1. One byte can represent 256 different values, so it can represent all characters in the ASCII code.



