A brief discussion on the defects of RDB and AOF persistence modes in Redis
This article will introduce to you the shortcomings of Redis's two persistence modes (RDB and AOF). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

[Related recommendations: Redis video tutorial]
1. RDB persistence mode defects
1. Problem description:
There are 200 concurrent routes, and the simulation continues to write to Redis. After 4 hours, a large number of interface calls begin to fail. The error message is as follows:
{"data":{"sendResult":null},"base":{"returncode":"99999","returndesc":"系统异常:MISCONF Redis is configured to save RDB snapshots, but is currently not able to persist on disk. Commands that may modify the data set are disabled. Please check Redis logs for details about the error."},"qrybase":{"total":0,"count":0,"start":0}}2. Reason Analysis:
Interpreted the error message and thought it was caused by insufficient disk space. It was found that 42% of the disk was left, as shown below:
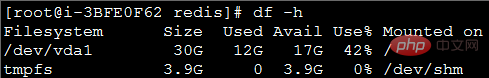
So based on the error message It prompts to turn on the Redis log and continue the stress test. The interface still reports an error, but from the Redis log information
Can't save in background: fork: Cannot allocate memory
It is related to the improper use of memory by the process. Check the memory occupied by the main process of Redis as follows: occupying nearly 55%*4G of memory
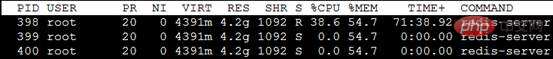
Specific reason: In order to avoid the main process suspended animation when Redis saves data to the hard disk, it needs to Fork a copy The main process, and then completes the data saving to the hard disk in the Fork process. If the main process uses 2.2GB of memory, an additional 2.2GB is needed when Fork the child process. At this time, the memory is not enough, Fork fails, and the data is saved. The hard drive also failed.
3. Mitigation plan (cannot fundamentally solve the problem):
3.1 Modify the configuration item stop-writes-on-bgsave-error no in the redis.conf file (the default value is yes), that is When an error occurs in the bgsave snapshot operation, stop writing data to the disk. In this way, any subsequent write errors will fail. In order not to affect subsequent write operations, you need to change this value to no
3.2 Modify the kernel parameters (3 below) method), but requires root permissions:
(1) 编辑/etc/sysctl.conf ,改vm.overcommit_memory=1,然后sysctl -p 使配置文件生效 (2)sysctl vm.overcommit_memory=1 (3)echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/overcommit_memory
2. AOF persistence mode defects
1. Problem 1 description:
Redis master-slave All nodes turned on AOF mode, with 200 concurrent connections, simulating continuous writing to Redis. After 15 minutes, a large number of interface calls began to fail, and the Linux virtual server where Redis was located hung.
The interface error is as follows:
{"data":null,"base":{"returndesc":"系统异常","returncode":"999999"},"qrybase":null}
Biz(dubbo)接口报错如下:
2015-06-05 11:28:28.760 [DubboServerHandler-X.X.X.X:20882-thread-173] ERROR - error while validate jedis!
redis.clients.jedis.exceptions.JedisConnectionException: java.net.SocketTimeoutException: Read timed outCause analysis:
From the dubbo interface error message, it is caused by the interface API operation Redis timeout. Judging from the system logs and IO monitoring, it is shown that the above problems are caused by IO bottlenecks (system IO is too busy), as shown below:

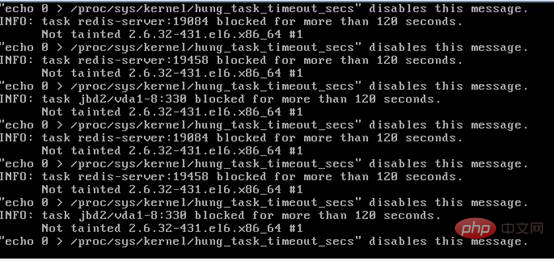
It can also be seen from the system log that the IO blocking time exceeds 120 seconds, and the machine hangs due to the system security mechanism.
Summary
The test results prove that the AOF mode has the most obvious flaw, that is, IO will become a performance bottleneck when access pressure is high, resulting in service unavailability.
3. Mitigation plan (cannot fundamentally solve the problem)
Edit /etc/sysctl.conf and add the following configuration:
vm.dirty_background_ratio = 5 vm.dirty_ratio = 10
Then sysctl -p makes the configuration file take effect.
Description of Problem 2:
Whether AOF mode or RDB (snapshot mode) is used, when the size of the two files (.aof or .rdb) exceeds 80% of the system memory, the Redis process will be killed by the system down, causing the service to become unavailable.
Summary
The above problems indicate that we need to plan the system memory capacity in advance when using Redis, because once Redis crashes, a large amount of data will be lost and it is unrecoverable.
For more programming related knowledge, please visit: Programming Video! !
The above is the detailed content of A brief discussion on the defects of RDB and AOF persistence modes in Redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.




