 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 How to use Nodejs to connect to Mysql and implement basic add, delete, modify and query operations
How to use Nodejs to connect to Mysql and implement basic add, delete, modify and query operations
How to use Nodejs to connect to Mysql and implement basic add, delete, modify and query operations
This article will introduce to you how to use Nodejs to connect to Mysql and implement basic CRUD operations. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

[Recommended study: "nodejs Tutorial"]
The main technical points of the following sample code Includes
-
Basic framework
Koa
Koa-router
koa-nunjucks-2
- ##Mysql connection package
- mysqljs
0. Prerequisites
- Install mysql database And start
- Install Nodejs (there should be no problems with this)
1. Node connects to the database
- Create an empty folder
- Execute
yarn add koa koa-router mysql
- Create a js (test.js) file in the root directory to test the database connection operation
- Let’s first write a paragraph in test.js Code, output hello, ensure that the startup program does not report an error
const Koa = require("koa") // 导入koa const Router = require("koa-router") //导入koa-router const mysql = require("mysql") // 导入mysql,连接mysql 需要用到 const app = new Koa(); // 实例化koa const router = new Router(); // 实例化路由 // 创建一个路径为/hello的get请求 router.get("/hello", async ctx => { // 返回 字符串 hello ctx.body = "hello" }) // koa注册路由相关 app .use(router.routes()) .use(router.allowedMethods()) // 监听端口 .listen(3333,()=>{ console.log("server running port:" + 3333); })Copy after login- Execute
node test.js
ornodemon test.jsin the project root directory Starting the project - Using
nodemon
Starting the project requires global installationyarn global add nodemonornpm i -g nodemon - Use
nodemon
to start the project,nodemonwill monitor the files in the startup directory, if any files change,nodemonThe node application will be automatically restarted. It is strongly recommended to usenodemonto start the node project - After the project is started, we enter
http:// in the browser localhost:3333/hello
, you can see the text hello output on the page
- After this interface appears, it proves that there is no problem with the startup of our project
- Next we will use node to connect to the mysql database
- Execute
- Let’s prepare a wave of data first
CREATE DATABASE db1; USE db1; CREATE TABLE user ( id INT PRIMARY KEY auto_increment, NAME VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, age INT NOT NULL ); INSERT INTO user VALUES (null, "张三", 23), (null, "李四", 24), (null, "王五", 25), (null, "赵六", 26);Copy after login
2. Connect to the mysql database to implement the table display function
- Next we will test.js Write the code to connect to mysql
const Koa = require("koa") // 导入koa const Router = require("koa-router") //导入koa-router const mysql = require("mysql") // 导入mysql,连接mysql 需要用到 const app = new Koa(); // 实例化koa const router = new Router(); -- 实例化路由 // mysqljs 连接 mysql数据库 let connection = mysql.createConnection({ host: '127.0.0.1', // mysql所在的主机,本地的话就是 127.0.0.1 或者 localhost, 如果数据库在服务器上,就写服务器的ip user: 'root', // mysql的用户名 password: '密码', // mysql的密码 database: 'db1' // 你要连接那个数据库 }) // 连接 mysql connection.connect(err=>{ // err代表失败 if(err) { console.log("数据库初始化失败"); }else { console.log("数据库初始化成功"); } }) // 创建一个路径为/hello的get请求 router.get("/hello", async ctx => { // 返回 字符串 hello ctx.body = "hello" }) // koa注册路由相关 app .use(router.routes()) .use(router.allowedMethods()) // 监听端口 .listen(3333,()=>{ console.log("server running port:" + 3333); })Copy after login

- ## Terminal output
- Database initialization successful
text means that the database connection is successful
Just now we have prepared four pieces of data in the db1 database, and then we can put the data The query is displayed and displayed on the console
We add this query code under the connection.connect method- Database initialization successful
- The first parameter of the connection.query method is a
- sql
statement of string type. The second parameter is optional. As will be mentioned later, the last parameter is a parameter that contains error information and correct response result data. Method
<div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false"> const selectSql = "SELECT * FROM user" connection.query(selectSql, (err,res) => { if(err) console.log(err); console.log(res); })</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>
The data returned is like this- sql

- At this time, the data in the database has been queried, then we can return the data to the front end in JSON format
By adding this paragraph The code returns the data to the browser in JSON format // 因为 mysqljs不支持 Promise方式CRUD数据 // 所以我们做一个简单的封装 function resDb(sql) { return new Promise((resolve,reject) => { connection.query(sql, (err,res) => { if(err) { reject(err) }else { resolve(res) } }) }) } //请求 /userAll 的时候返回数据 router.get("/userAll", async ctx => { ctx.body = await resDb("SELECT * FROM user") })Copy after login
- This data is what we need, uh uh uh, the data is returned , we are doing the front-end, how can we not have a page? First add a table page to display data. The
- nunjucks
template engine is used here. Let’s install it first
yarn add koa-nunjucks-2
Add this code to test.js - nunjucks
const koaNunjucks = require('koa-nunjucks-2'); const path = require('path'); // 注入 nunjucks 模板引擎 app.use(koaNunjucks({ ext: 'html', // html文件的后缀名 path: path.join(__dirname, 'views'), // 视图文件放在哪个文件夹下 nunjucksConfig: { trimBlocks: true // 自动去除 block/tag 后面的换行符 } })); //在 /userAll这个路由中我们不直接返回数据了,我们返回table.html页面 router.get("/userAll", async ctx => { const userAll = await resDb("SELECT * FROM user") await ctx.render("table",{userAll}) })Copy after login
- By nunjucks Template engine, we put all html files in the views folder in the root directory, then we need to create a views folder in the root directory, and create the table.html file in the folder. The file code is as follows
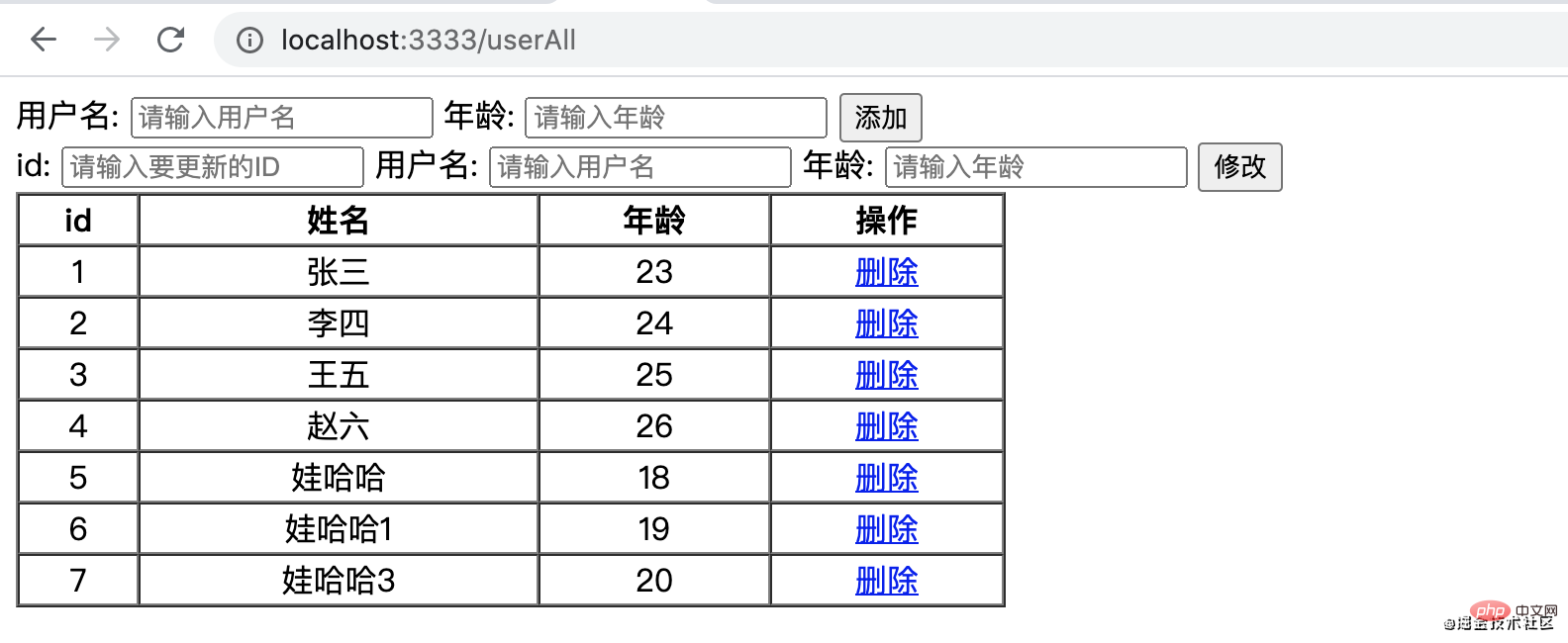
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <style> .table{ width: 500px; } td{ text-align: center; } </style> </head> <body> <table border="1" cellspacing="0"> <thead> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>姓名</th> <th>年龄</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {% for user in userAll %} <tr > <td>{{user.id}}</td> <td>{{user.NAME}}</td> <td>{{user.age}}</td> </tr> {% endfor %} </tbody> </table> </body> </html>Copy after loginAfter restarting the server, visit - http://localhost:3333/userAll
The query function is completed, and then we can implement the new functions ##this page After it comes out, the display part is done
##this page After it comes out, the display part is done
3、 添加数据到mysql数据库中
我们先把table.html页面的添加部分写完
<form action="/addUser"> <label for="name"> 用户名: <input type="text" name="name" placeholder="请输入用户名"> </label> <label for="age"> 年龄: <input type="number" name="age" min="0" placeholder="请输入年龄"> </label> <input type="submit" value="添加"> </form>Copy after login这个时候页面是长这样的

当我们输入完用户名和年龄点击添加按钮后,浏览器会通过 get请求 把数据发送到
/addUser这个路由中,接下来,我们在test.js中接收一下前端传的参数,并且把参数保存到数据库中。然后刷新页面//请求 /addUser 接受前端传过来的数据,并且把数据持久化到数据库中 router.get("/addUser", async ctx => { const { name, age } = ctx.query // 判断 name 和 age是否有值,都有值时,数据存入数据库,刷新表格页面 // 否则直接返回到表格页面 if(name && age) { await resDb("INSERT INTO user values(null,?,?)",[name, age]) } //重定向路由,到 userAll ctx.redirect("/userAll") })Copy after login为了提高
resDb的健壮性,我们对这个方法进行了升级function resDb(sql, params) { return new Promise((resolve,reject) => { let sqlParamsList = [sql] if(params) { sqlParamsList.push(params) } connection.query(...sqlParamsList, (err,res) => { if(err) { reject(err) }else { resolve(res) } }) }) }Copy after login升级之后的这个方法适合 CRUD的 promise 化了,当然 修改和删除功能下边我们会说
到这个时候,我们的新增功能就完成了,那么我们来看一波截图,并且理一下逻辑


4、 通过id更新数据
更新数据的前端部分,我们就不写模态框了,直接写个类似新增的表单,实现更新的操作吧,其实新增和更新功能非常类似,有差别的地方只是sql的写法
我们先把table.html页面改造一下
<form action="/updateUser"> <label for="id"> id: <input type="number" name="id" placeholder="请输入要更新的ID"> </label> <label for="name"> 用户名: <input type="text" name="name" placeholder="请输入用户名"> </label> <label for="age"> 年龄: <input type="number" name="age" min="0" placeholder="请输入年龄"> </label> <input type="submit" value="修改"> </form>Copy after login下面我们看下后台的代码
//请求 /updateUser 接受前端传过来的数据,并且把数据持久化到数据库中 router.get("/updateUser", async ctx => { const { id, name, age } = ctx.query // 判断 id, name 和 age是否有值,都有值时,更新数据库中的数据,刷新表格页面 // 否则直接返回到表格页面 if(id, name && age) { await resDb("UPDATE user SET name=?, age=? WHERE id=?",[name, age, id]) } //重定向路由,到 userAll ctx.redirect("/userAll") })Copy after login代码逻辑和新增部分的逻辑是一样的,
刚才在写新增和更新的sql代码,大家会看到sql语句中有
?占位符,第二个参数数组是?占位符对应的内容。那么这个时候大家肯定会有这样一个疑问,为啥我们不直接把前端传过来的参数拼进去。非得这么麻烦。其实这样通过占位符的方式写
sql是为了防止sql注入,有关sql注入的文章大家可以参考这篇 sql注入原理及防范
5、通过id删除单条数据
老规矩我们先把table.html页面改造一下
<table class="table" border="1" cellspacing="0"> <thead> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>姓名</th> <th>年龄</th> <th>操作</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {% for user in userAll %} <tr > <td>{{user.id}}</td> <td>{{user.NAME}}</td> <td>{{user.age}}</td> <td> <a href={{'/delete/'+user.id}}>删除</a> </td> </tr> {% endfor %} </tbody> </table>Copy after login看下页面效果

老规矩,下面我们来看看后台的代码
//请求/delete/:id 接受前端传过来的数据,并且把对应的id的数据删掉 router.get("/delete/:id", async ctx => { const { id } = ctx.params // 判断 id否有值,有值时,根据id删除数据库中的数据,刷新表格页面 // 否则直接返回到表格页面 if(id) { await resDb("DELETE FROM user WHERE id=?",[id]) } //重定向路由,到 userAll ctx.redirect("/userAll") })Copy after login到目前为止对表格的增删改查(CRUD),就都已经写完了。
6、 完整代码
目录结构
package.json
{ "koa": "^2.13.1", "koa-nunjucks-2": "^3.0.2", "koa-router": "^10.0.0", "mysql": "^2.18.1" }Copy after logintest.js
const Koa = require("koa")
const Router = require("koa-router")
const mysql = require("mysql")
const koaNunjucks = require('koa-nunjucks-2');
const path = require('path');
const app = new Koa();
const router = new Router();
// mysqljs 连接 mysql数据库
let connection = mysql.createConnection({
host: '127.0.0.1', // mysql所在的主机,本地的话就是 127.0.0.1 或者 localhost, 如果数据库在服务器上,就写服务器的ip
user: 'root', // mysql的用户名 默认root
password: 'mysql密码', // mysql的密码
database: 'db1' // 你要连接那个数据库
})
// 连接 mysql
connection.connect(err=>{
// err代表失败
if(err) {
console.log("数据库初始化失败");
}else {
console.log("数据库初始化成功");
}
})
// 因为 mysqljs不支持 Promise方式CRUD数据
// 所以我们做一个简单的封装
function resDb(sql, params) {
return new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
let sqlParamsList = [sql]
if(params) {
sqlParamsList.push(params)
}
connection.query(...sqlParamsList, (err,res) => {
if(err) {
reject(err)
}else {
resolve(res)
}
})
})
}
// 注入 nunjucks 模板引擎
app.use(koaNunjucks({
ext: 'html', // html文件的后缀名
path: path.join(__dirname, 'views'), // 视图文件放在哪个文件夹下
nunjucksConfig: {
trimBlocks: true // 自动去除 block/tag 后面的换行符
}
}));
//请求 /userAll 的时候返回数据
router.get("/userAll", async ctx => {
const userAll = await resDb("SELECT * FROM user")
await ctx.render("table",{userAll})
})
//请求 /addUser 接受前端传过来的数据,并且把数据持久化到数据库中
router.get("/addUser", async ctx => {
const { name, age } = ctx.query
// 判断 name 和 age是否有值,都有值时,数据存入数据库,刷新表格页面
// 否则直接返回到表格页面
if(name && age) {
await resDb("INSERT INTO user values(null,?,?)",[name, age])
}
//重定向路由,到 userAll
ctx.redirect("/userAll")
})
//请求 /updateUser 接受前端传过来的数据,并且把数据持久化到数据库中
router.get("/updateUser", async ctx => {
const { id, name, age } = ctx.query
// 判断 id, name 和 age是否有值,都有值时,更新数据库中的数据,刷新表格页面
// 否则直接返回到表格页面
if(id, name && age) {
await resDb("UPDATE user SET name=?, age=? WHERE id=?",[name, age, id])
}
//重定向路由,到 userAll
ctx.redirect("/userAll")
})
//请求/delete/:id 接受前端传过来的数据,并且把对应的id的数据删掉
router.get("/delete/:id", async ctx => {
const { id } = ctx.params
// 判断 id否有值,有值时,根据id删除数据库中的数据,刷新表格页面
// 否则直接返回到表格页面
if(id) {
await resDb("DELETE FROM user WHERE id=?",[id])
}
//重定向路由,到 userAll
ctx.redirect("/userAll")
})
//测试代码
router.get("/hello", ctx => {
ctx.body = "hello"
})
app
.use(router.routes())
.use(router.allowedMethods())
.listen(3333,()=>{
console.log("server running port:" + 3333);
})views/table.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <style> .table { width: 500px; } td { text-align: center; } </style> </head> <body> <form action="/addUser" autocomplete="off"> <label for="name"> 用户名: <input type="text" name="name" placeholder="请输入用户名"> </label> <label for="age"> 年龄: <input type="number" name="age" min="0" placeholder="请输入年龄"> </label> <input type="submit" value="添加"> </form> <form action="/updateUser" autocomplete="off"> <label for="id"> id: <input type="number" name="id" placeholder="请输入要更新的ID"> </label> <label for="name"> 用户名: <input type="text" name="name" placeholder="请输入用户名"> </label> <label for="age"> 年龄: <input type="number" name="age" min="0" placeholder="请输入年龄"> </label> <input type="submit" value="修改"> </form> <table border="1" cellspacing="0"> <thead> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>姓名</th> <th>年龄</th> <th>操作</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {% for user in userAll %} <tr> <td>{{user.id}}</td> <td>{{user.NAME}}</td> <td>{{user.age}}</td> <td> <a href={{'/delete/'+user.id}}>删除</a> </td> </tr> {% endfor %} </tbody> </table> </body> </html>Copy after login
7、写在最后
当你看到这里的时候,首先你是个很有毅力的人,这篇文章没有插图,全都是代码实现以及页面截图,从头看到尾的话给自己点个赞吧
这篇文章详细的介绍了nodejs连接mysql数据库,并且实现基于模板引擎的
增删改查功能,以及对数据库返回结果简单的做了一个promise封装,也对koa及其实例中用到的插件做了相关的介绍
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
The above is the detailed content of How to use Nodejs to connect to Mysql and implement basic add, delete, modify and query operations. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1390
1390
 52
52
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's position in databases and programming is very important. It is an open source relational database management system that is widely used in various application scenarios. 1) MySQL provides efficient data storage, organization and retrieval functions, supporting Web, mobile and enterprise-level systems. 2) It uses a client-server architecture, supports multiple storage engines and index optimization. 3) Basic usages include creating tables and inserting data, and advanced usages involve multi-table JOINs and complex queries. 4) Frequently asked questions such as SQL syntax errors and performance issues can be debugged through the EXPLAIN command and slow query log. 5) Performance optimization methods include rational use of indexes, optimized query and use of caches. Best practices include using transactions and PreparedStatemen
 Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL is chosen for its performance, reliability, ease of use, and community support. 1.MySQL provides efficient data storage and retrieval functions, supporting multiple data types and advanced query operations. 2. Adopt client-server architecture and multiple storage engines to support transaction and query optimization. 3. Easy to use, supports a variety of operating systems and programming languages. 4. Have strong community support and provide rich resources and solutions.
 How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Apache connects to a database requires the following steps: Install the database driver. Configure the web.xml file to create a connection pool. Create a JDBC data source and specify the connection settings. Use the JDBC API to access the database from Java code, including getting connections, creating statements, binding parameters, executing queries or updates, and processing results.
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Installing MySQL on CentOS involves the following steps: Adding the appropriate MySQL yum source. Execute the yum install mysql-server command to install the MySQL server. Use the mysql_secure_installation command to make security settings, such as setting the root user password. Customize the MySQL configuration file as needed. Tune MySQL parameters and optimize databases for performance.




