1mb equals how many bytes
1MB is equal to 2^20 bytes. MB, the full name is "MByte", a storage unit in computers. Byte is a unit of measurement used by computer information technology to measure storage capacity. It is a string of binary digits processed as a unit and is a small unit that constitutes information.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
1MB is equal to 2^20 bytes.
1MB=1024KB= 2^20 B.
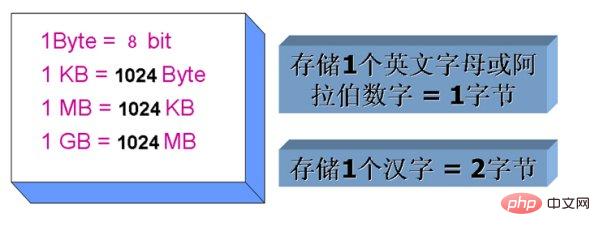
1. Byte (Byte) is a unit of measurement used by computer information technology to measure storage capacity. A string of binary digits processed as a unit is a small unit that constitutes information. The most commonly used byte is an octet, that is, it contains an eight-bit binary number.
2. KB kilobytes (Kbytes), a unit of computer storage capacity, also commonly expressed in KB. 1KB=1024 bytes.
Kilobyte (Kilobyte), often written as kB, KB or K, is a unit of information measurement that is commonly used today to indicate the storage capacity of storage media with general capacity such as memory.
This unit of measurement is easily confused with KiB. According to the IEC naming standard, the binary standard naming is KiB, MiB, etc. Linux and macOS X have adopted decimal standard naming. However, Windows still incorrectly labels KiB as KB.
3. MB, English abbreviation, a storage unit in computers, full name MByte.
MB (full name MByte): A storage unit in computers, pronounced as "mega".
The data units MB and Mb (note the capitalization of the B letter) are often mistaken for the same meaning. In fact, MByte means "megabyte" and Mbit means "megabit". MByte refers to the number of bytes, and Mbit refers to the number of bits.
Although the "Byte" in MByte is translated the same as the "bit" in Mbit, both are bits and are units of data measurement, but they are completely different. Byte is the "number of bytes" and bit is the "number of bits". In computers, every eight bits is one byte, that is, 1Byte=8bit, which is a 1:8 correspondence. Therefore, when writing units, be sure to pay attention to the capitalization and meaning of the letter B.
Extended information:
Gigabyte (GB, Gigabyte, also known as Jigabyte or Jinggabyte in China byte or gigabyte or halberd), often abbreviated as G.
GB is a decimal unit of information measurement. Gigabyte is often confused with Gibibyte, the binary unit of information measurement. It is often used to indicate the storage capacity of storage media with larger capacity such as hard drives and memories.
1GB (Gigabyte, gigabyte, billion bytes, also known as "gigabyte") = 1024MB = 2^30 B.
For more computer-related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of 1mb equals how many bytes. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 1MB of storage capacity is equivalent to how many bytes
Mar 03, 2023 pm 05:42 PM
1MB of storage capacity is equivalent to how many bytes
Mar 03, 2023 pm 05:42 PM
1MB of storage capacity is equivalent to 2 to the 20th power bytes, or 1,048,576 bytes. MB is a storage unit in computers, pronounced as "mega"; because 1MB is equal to 1024KB, and 1KB is equal to 1024B (bytes), so 1MB is equal to 1048576 (1024 *1024) bytes.
 How many bytes does 128mb mean?
Nov 29, 2022 am 10:35 AM
How many bytes does 128mb mean?
Nov 29, 2022 am 10:35 AM
128mb refers to 134217728 bytes; the byte conversion formula is "1MB=1024KB=1048576B=8388608bit", which means that 1048576 English letters and 524288 Chinese characters can be saved; the traffic unit conversion formula is 1GB=1024MB, 1MB=1024KB, 1KB= 1024B.
 1 bit equals how many bytes
Mar 09, 2023 pm 03:11 PM
1 bit equals how many bytes
Mar 09, 2023 pm 03:11 PM
1 bit is equal to one-eighth of a byte. In the binary number system, each 0 or 1 is a bit (bit), and a bit is the smallest unit of data storage; every 8 bits (bit, abbreviated as b) constitute a byte (Byte), so "1 byte ( Byte) = 8 bits”. In most computer systems, a byte is an 8-bit (bit) long data unit. Most computers use a byte to represent a character, number, or other character.
 How many bytes does one ascii character occupy?
Mar 09, 2023 pm 03:49 PM
How many bytes does one ascii character occupy?
Mar 09, 2023 pm 03:49 PM
One ascii character occupies 1 byte. ASCII code characters are represented by 7-bit or 8-bit binary encoding in the computer and are stored in one byte, that is, one ASCII code occupies one byte. ASCII code can be divided into standard ASCII code and extended ASCII code. Standard ASCII code is also called basic ASCII code. It uses 7-bit binary numbers (the remaining 1 binary digit is 0) to represent all uppercase and lowercase letters, and the numbers 0 to 9. Punctuation marks, and special control characters used in American English.
 How many bytes do utf8 encoded Chinese characters occupy?
Feb 21, 2023 am 11:40 AM
How many bytes do utf8 encoded Chinese characters occupy?
Feb 21, 2023 am 11:40 AM
UTF8 encoded Chinese characters occupy 3 bytes. In UTF-8 encoding, one Chinese character is equal to three bytes, and one Chinese punctuation mark occupies three bytes; while in Unicode encoding, one Chinese character (including traditional Chinese) is equal to two bytes. UTF-8 uses 1~4 bytes to encode each character. One US-ASCIl character only needs 1 byte to encode. Latin, Greek, Cyrillic, Armenian, and Hebrew with diacritical marks. , Arabic, Syriac and other letters require 2-byte encoding.
 How many bytes does an ascii code occupy?
Sep 07, 2023 pm 04:03 PM
How many bytes does an ascii code occupy?
Sep 07, 2023 pm 04:03 PM
An ASCII code occupies one byte. ASCII code is a coding standard used to represent characters. It uses 7-bit binary numbers to represent 128 different characters, including letters, numbers, punctuation marks, special characters, etc. A byte is the basic unit of computer storage unit. It consists of 8 binary bits. Each binary bit can be 0 or 1. One byte can represent 256 different values, so it can represent all characters in the ASCII code.
 Detailed explanation of the method of converting int type to bytes in PHP
Mar 06, 2024 pm 06:18 PM
Detailed explanation of the method of converting int type to bytes in PHP
Mar 06, 2024 pm 06:18 PM
Detailed explanation of the method of converting int type to byte in PHP In PHP, we often need to convert the integer type (int) to the byte (Byte) type, such as when dealing with network data transmission, file processing, or encryption algorithms. This article will introduce in detail how to convert the int type to the byte type and provide specific code examples. 1. The relationship between int type and byte In the computer field, the basic data type int represents an integer, while byte (Byte) is a computer storage unit, usually 8-bit binary data
 4kb indicates how many bytes there are in the storage unit
Feb 28, 2023 pm 12:12 PM
4kb indicates how many bytes there are in the storage unit
Feb 28, 2023 pm 12:12 PM
4KB means that the storage unit is 4096 bytes. KB refers to kilobyte, which is a multiple form of computer data storage unit byte. A kilobyte is based on the power of 2, that is, a kilobyte (1KB) is equal to 1024 bytes (B ); therefore "4KB=4*1024B=4096B", that is, 4KB represents 4096 bytes.



