How to install php script language under linux
Method: 1. Install libtool and libtool-ltdl; 2. Modify the gd library file; 3. Execute the "make install" command to compile and install the PHP source code package; 4. Create a PHP configuration file; 5. Allow apache to Identify the ".php" extension; 6. Restart the Apache server.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, PHP version 5.4.25, DELL G3 computer
How to install php under linux
1) Install libtool and libtool-ltdl
[root@localhost mysql]# yum -y install "libtool*" [root@localhost mysql]# yum -y install "libtool-ltdl*"
2) Manually modify the gd library file
PHP 5.4 also has some bugs. When detecting the gd library, an error will be reported and we need to modify it manually. The command is as follows:
[root@localhost mysql]# vi /usr/local/gd2/include/gd_io.h
#修改gd_io.h头文件
typedef struct gdIOCtx
{
…
void (*data);
#在此程序段中加入此句
}3) Compile and install the PHP source package
The command is as follows:
[root@localhost mysql]# cd /usr/local/src/ php-5.4.25 [root@localhost php-5.4.25]# ./configure \ #编译前配置 --prefix=/usr/local/php/ \ #指定安装位置 --with-config-file-path=/usr/local/php/etc/ \ #指定PHP配置文件位置 --with-apxs2=/usr/local/apache2/bin/apxs \ #调用apache2 --with-mysql=/usr/local/mysql/ \ #调用mysql --with-libxml-dir=/usr/local/libxml2/ \ #调用libxml2库 --with-jpeg-dir=/usr/local/jpeg6/ \ #调用jpeg库 --with-png-dir=/usr/local/libpng/ \ #调用libpng库 --with-freetype-dir=/usr/local/freetype/ \ #调用freetype库 --with-gd=/usr/local/gd2/ \ #调用gd库 --with-mcrypt=/usr/local/libmcrypt/ \ #调用libmcrypt库 --with-mysqli=/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql_config \#增加MysqlLi功能 --enable-soap \ #支持SOAP和Web Services --enable-mbstring=all \ #支持多字节字符串 --enable-sockets #支持socket(套接字)通信 --with-pdo-mysql=/usr/local/mysql #启用mysql的pdo模块支持 [root@localhost php-5.4.25]# make #编译 [root@localhost php-5.4.25]# make install #编译安装
4) Create a PHP configuration file
The same as MySQL, this configuration file does not need to be created manually, there is also a template file, we only need to copy it. The command is as follows:
[root@localhost php-5.4.25]# cp /usr/local/src/ php-5.4.25/php.ini-production /usr/local/php/etc/php.ini
5) Let apache recognize the ".php" extension
When installing PHP, use - in the ./configure command -with-apxs2=/usr/local/apache2/bin/apxs option, PHP has been recognized by apache as a module. However, apache does not know which extension files need to be parsed by calling the PHP module (if it is an extension that apache does not recognize, then when the client accesses it, apache will not try to parse it, but will prompt the client to download it), so we You need to modify the apache configuration file so that apache can recognize the extension of the PHP script.
For example, if we want apache to call the PHP module to parse the contents of these files when it encounters the ".php" and ".phps" extensions, then we only need to execute the following command:
[root@localhost php-5.4.25]# vi /usr/local/apache2/etc/httpd.conf #修改apache配置文件,加入如下内容 AddType application/x-httpd-php.php.phps
#This sentence means: If the .php and .phps extensions are encountered, the PHP module is called to parse the content of this file
This sentence is loaded in the apache configuration file Any location is acceptable, but there is a similar statement AddType application/x-gzip.gz.tgz in the system, so we generally load it after this sentence. The command is as follows:
[root@localhost php-5.4.25]# vi /usr/local/apache2/etc/httpd.conf …省略部分输出… # If the AddEncoding directives above are commented-out, then you probably should define those extensions to indicate media types: # AddType application/x-compress .Z AddType application/x-gzip .gz .tgz AddType application/x-httpd-php .php .phps #加载到此位置 …省略部分输出…
As for the extension of the PHP file, it can be freely defined.
6) Restart the Apache server
We have modified the apache configuration file. If you want this modification to take effect, you must restart the Apache server. The restart command is as follows:
[root@localhost php-5.4.25]# /usr/local/apache2/bin/apachectl stop [root@localhost php-5.4.25]# /usr/local/apache2/bin/apachectl start
It is best not to use the restart parameter here, because for the apache startup command of the source code package, the restart parameter sometimes does not work.
Supplement: Test whether the PHP environment is normal
For apache installed in the source code package, the default storage location of the web page is /usr/local/apache2/ htdocs/ directory. In order to test whether the PHP environment is normal, we need to create a PHP file in this directory to see if the file can be displayed normally. The command is as follows:
[root@localhost php-5.4.25]# vi /usr/local/apache2/htdocs/index.php <?php phpinfo(); ?>
Here we use the phpinfo() function. The main function of this function is to display PHP-related information. This information includes PHP compilation information, PHP version, server information and environment. , PHP environment, operating system information, paths, main configuration options, HTTP header information and PHP permissions, etc. We generally use this function to test whether PHP is installed successfully, and then enter "http://serverIP/index.php" in the browser to execute the file, as shown in the figure below.
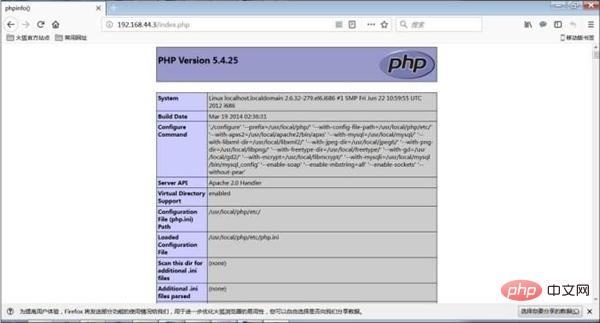
If you can see the picture above, congratulations, PHP is installed successfully.
Recommended learning: "PHP Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of How to install php script language under linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 PHP: Handling Databases and Server-Side Logic
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP: Handling Databases and Server-Side Logic
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP uses MySQLi and PDO extensions to interact in database operations and server-side logic processing, and processes server-side logic through functions such as session management. 1) Use MySQLi or PDO to connect to the database and execute SQL queries. 2) Handle HTTP requests and user status through session management and other functions. 3) Use transactions to ensure the atomicity of database operations. 4) Prevent SQL injection, use exception handling and closing connections for debugging. 5) Optimize performance through indexing and cache, write highly readable code and perform error handling.
 PHP's Purpose: Building Dynamic Websites
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP's Purpose: Building Dynamic Websites
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP is used to build dynamic websites, and its core functions include: 1. Generate dynamic content and generate web pages in real time by connecting with the database; 2. Process user interaction and form submissions, verify inputs and respond to operations; 3. Manage sessions and user authentication to provide a personalized experience; 4. Optimize performance and follow best practices to improve website efficiency and security.
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning.
 Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
CentOS will be shut down in 2024 because its upstream distribution, RHEL 8, has been shut down. This shutdown will affect the CentOS 8 system, preventing it from continuing to receive updates. Users should plan for migration, and recommended options include CentOS Stream, AlmaLinux, and Rocky Linux to keep the system safe and stable.
 How to install centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
How to install centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
CentOS installation steps: Download the ISO image and burn bootable media; boot and select the installation source; select the language and keyboard layout; configure the network; partition the hard disk; set the system clock; create the root user; select the software package; start the installation; restart and boot from the hard disk after the installation is completed.
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use Docker Desktop? Docker Desktop is a tool for running Docker containers on local machines. The steps to use include: 1. Install Docker Desktop; 2. Start Docker Desktop; 3. Create Docker image (using Dockerfile); 4. Build Docker image (using docker build); 5. Run Docker container (using docker run).




