 Backend Development
Backend Development
 PHP Tutorial
PHP Tutorial
 Based on PHP Laravel, let's talk about ways to write less 'bad” PHP code! !
Based on PHP Laravel, let's talk about ways to write less 'bad” PHP code! !
Based on PHP Laravel, let's talk about ways to write less 'bad” PHP code! !
This article will give you a detailed introduction on how to write less "bad" PHP code! ! It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Written to children who are newborn calves and are not afraid of tigers, you can read it at will This chapter is based on PHP Laravel
Preface
People often ask
- How to design the directory better?
- How to distribute the code well?
- How to write a maintainable project?
I also write about "bad" projects. The following is based on the summary of articles and personal development experience of major Internet experts.
Controller
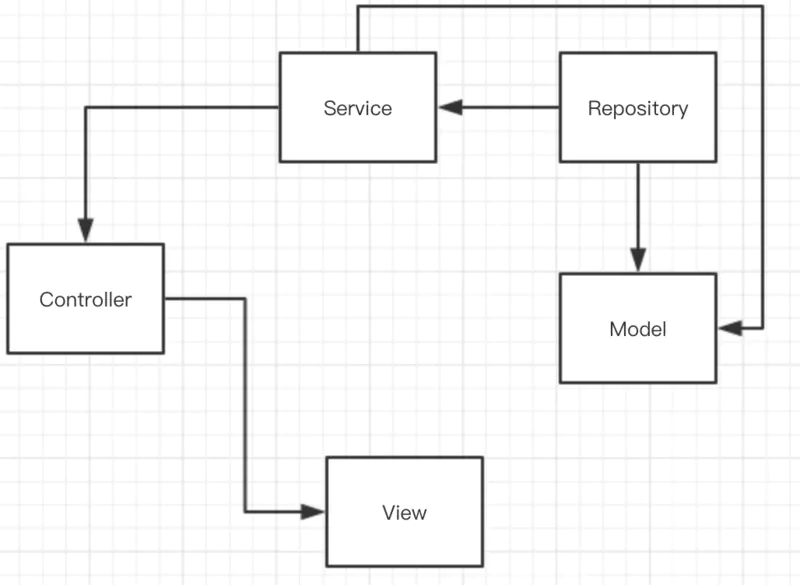
Controller, as the name suggests, is a controller. When you get started with PHP, you know that Controller represents the C layer in MVC. The concept of MVC itself is code separation, which teaches you how to separate businesses. However, as the business continues to develop, the complexity of the code also increases, and the links between functions are intricate. In the end, your MVC becomes As shown in the figure below, relying solely on the MVC design idea can no longer support the growing business.
Now we redefine the tasks and capabilities of the Controller. The controller only controls Http Reqeust requests, which complies with the SOLID single function principle.

Writing the business code directly in the Controller will make the code extremely bloated and difficult to maintain and expand.
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controller;
class UserController extends Controller{
public function register(Request $request){
$user = new User();
$user->username = $request->input('username');
$user->password = $request->input('password');
$result = $user->save();
return $result;
}
}At this time, we should think about how to separate the business code. We introduce the concept of Service
Service
Service itself is translated as service
- Inject external methods and public methods into Service
- Inject Service into the controller

Like the picture above
UserController
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controller;
class UserController extends Controller{
public $request;
protected $userService;
public function __construct(Request $request, UserService $userService)
{
$this->request = $request;
$this->userService = $userService;
}
public function register()
{
//... validation
return $this->userService->register ($this->request->all());
}
}UserService
<?php
namespace App\Service;
class UserService{
public function register($data)
{
$username = $data['username'];
$password = $data['password'];
$password = encrypt ($password);
$user = new User();
$user->username = $username;
$user->password = $password;
$result = $user->save();
return $result;
}
}Until now, we have at least completely separated the business from the request. But it is still unsatisfactory. If all business and CURD are written in Service, it will just transfer the bloat of Controller to Service, and then Service will have no meaning in existence. Therefore, we need to continue to divide the Service and separate the R operations of the database, because the operations of CUD are basically the same, while the R operations become more colorful according to the complexity of the business. So standalone R operation. At this time we refer to the concept of Repository.
Repository
We use Repository auxiliary Model to encapsulate relevant query logic into different repositories to facilitate the maintenance of logic code
- Conforming to the single principle of SOLID
- Conforming to SOLID dependency inversion

##UserController<?php
namespace App\Http\Controller;
class UserController extends Controller{
public $request;
protected $userService;
public function __construct(Request $request, UserService $userService)
{
$this->request = $request;
$this->userService = $userService;
}
public function getUserInfo()
{
//... validation
return $this->userService->getUserInfo ($this->request->all());
}
}Copy after login
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controller;
class UserController extends Controller{
public $request;
protected $userService;
public function __construct(Request $request, UserService $userService)
{
$this->request = $request;
$this->userService = $userService;
}
public function getUserInfo()
{
//... validation
return $this->userService->getUserInfo ($this->request->all());
}
}UserService<?php
namespace App\Service;
class UserService{
public $userRepository;
public function __construct(UserRepository $userRepository){
$this->userRepository = $userRepository;
}
public function getUserInfo()
{
return $this->userRepository->getUserInfo($data);
}
}Copy after login
<?php
namespace App\Service;
class UserService{
public $userRepository;
public function __construct(UserRepository $userRepository){
$this->userRepository = $userRepository;
}
public function getUserInfo()
{
return $this->userRepository->getUserInfo($data);
}
}UserRepository<?php
namespace App\Repository;
class UserRepository{
public function getUserInfo($data)
{
$userId = $data['user_id'];
$result = User::where('id',$userId)->first();
return $result;
}
}Copy after login
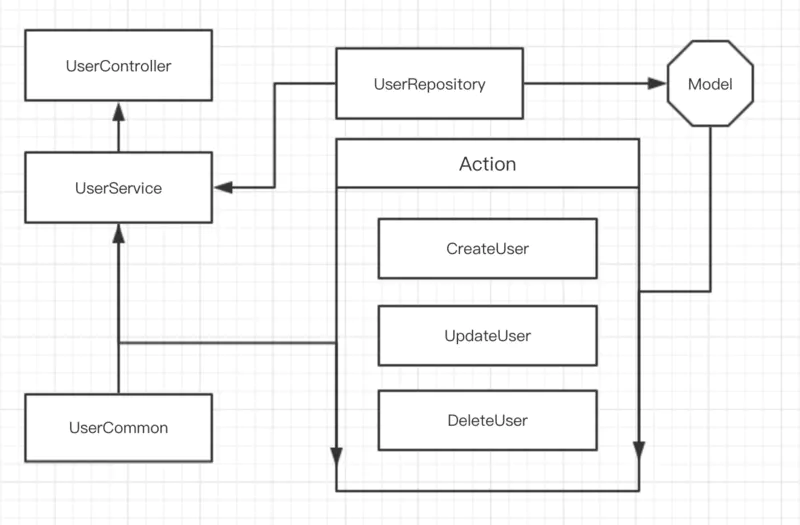
After solving the problem of R, someone asked, can it be put together because CUD is relatively unified and simple? Yet? The answer is NO, we quote a new noun Action. <?php
namespace App\Repository;
class UserRepository{
public function getUserInfo($data)
{
$userId = $data['user_id'];
$result = User::where('id',$userId)->first();
return $result;
}
}Action
This is what I learned after reading @Charlie_Jade’s articleIndependent of each operation file, such as CreateUser ,DeleteUser,UpdateUser
- Conforms to the single principle of SOLID
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controller;
class UserController extends Controller{
public $request;
protected $userService;
public function __construct(Request $request, UserService $userService)
{$this->request = $request;$this->userService = $userService;
}
public function register(){
//... validation return $this->userService->register($this->request->all());
}
public function getUserInfo()
{return $this->userService->getUserInfo ($this->request->all());
}
}Copy after login
UserService<?php
namespace App\Http\Controller;
class UserController extends Controller{
public $request;
protected $userService;
public function __construct(Request $request, UserService $userService)
{$this->request = $request;$this->userService = $userService;
}
public function register(){
//... validation return $this->userService->register($this->request->all());
}
public function getUserInfo()
{return $this->userService->getUserInfo ($this->request->all());
}
}<?php
namespace App\Service;
class UserService{
public function getUserInfo(UserRepository $userRepository)
{ return $this->userRepository->getUserInfo($data);
}
public function register(){ $result = (new CreateUser())->execute($this->request->all());
return $result;
}
}Copy after login
UserRepository<?php
namespace App\Service;
class UserService{
public function getUserInfo(UserRepository $userRepository)
{ return $this->userRepository->getUserInfo($data);
}
public function register(){ $result = (new CreateUser())->execute($this->request->all());
return $result;
}
}<?php
namespace App\Repository;
class UserRepository{
public function getUserInfo($data)
{ $userId = $data['user_id']; $result = User::where('id',$userId)->first();return $result;
}
}Copy after login
CreateUser<?php
namespace App\Repository;
class UserRepository{
public function getUserInfo($data)
{ $userId = $data['user_id']; $result = User::where('id',$userId)->first();return $result;
}
}<?php
namespace App\Action;
use App\Model\Member;
class CreateUser extends CreateUserWallet
{
public function execute(array $data)
{$models = new Member();$models->tel = $data['tel'];$models->password = $data['password'];$result = $models->save ();return $result;
}
}Copy after loginThe above code logic is shown in the figure below
 In addition to templates (V) and other HTML, JS, etc., some other rules, or methods, are needed to achieve decoupling of some codes. No code examples are provided below.
In addition to templates (V) and other HTML, JS, etc., some other rules, or methods, are needed to achieve decoupling of some codes. No code examples are provided below.
Common
is translated as public, commonly used. In some development, you may need some public methods (not public classes, such as email sending, etc.) It is not appropriate to use it), such as checking the user's balance, checking whether the user is registered or online, generating an order number, etc. Using Common is even simpler. It looks more like a public function library
Event
You can choose to use it when you don’t care about the execution results, but Event’s Listen also provides a queue.
Exception
Don’t use Return to return all your error messages. In many cases, your return may not be your return
Recommended learning: "PHP Video Tutorial》
The above is the detailed content of Based on PHP Laravel, let's talk about ways to write less 'bad” PHP code! !. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
<?php
namespace App\Action;
use App\Model\Member;
class CreateUser extends CreateUserWallet
{
public function execute(array $data)
{$models = new Member();$models->tel = $data['tel'];$models->password = $data['password'];$result = $models->save ();return $result;
}
} In addition to templates (V) and other HTML, JS, etc., some other rules, or methods, are needed to achieve decoupling of some codes. No code examples are provided below.
In addition to templates (V) and other HTML, JS, etc., some other rules, or methods, are needed to achieve decoupling of some codes. No code examples are provided below. 
Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP's Current Status: A Look at Web Development Trends
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
PHP's Current Status: A Look at Web Development Trends
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
PHP remains important in modern web development, especially in content management and e-commerce platforms. 1) PHP has a rich ecosystem and strong framework support, such as Laravel and Symfony. 2) Performance optimization can be achieved through OPcache and Nginx. 3) PHP8.0 introduces JIT compiler to improve performance. 4) Cloud-native applications are deployed through Docker and Kubernetes to improve flexibility and scalability.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
PHP is still dynamic and still occupies an important position in the field of modern programming. 1) PHP's simplicity and powerful community support make it widely used in web development; 2) Its flexibility and stability make it outstanding in handling web forms, database operations and file processing; 3) PHP is constantly evolving and optimizing, suitable for beginners and experienced developers.
 PHP's Purpose: Building Dynamic Websites
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP's Purpose: Building Dynamic Websites
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP is used to build dynamic websites, and its core functions include: 1. Generate dynamic content and generate web pages in real time by connecting with the database; 2. Process user interaction and form submissions, verify inputs and respond to operations; 3. Manage sessions and user authentication to provide a personalized experience; 4. Optimize performance and follow best practices to improve website efficiency and security.
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.





