An in-depth analysis of asynchrony in Node.js
This article will give you a detailed introduction to asynchronous in Node.js. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

About Node.js Asynchrony, two points cannot be avoided: Non-blocking I/O and Event loop . It is precisely because of these two points that Node.js can be called high-performance and be used in online environments. So let’s learn about the asynchronous mechanism and usage of Node.js! [Recommended learning: "nodejs Tutorial"]
Non-blocking I/O of Node.js
- ##I/O is
- Input
/Output, theinput and output of a system. The difference between blocking I/O and non-blocking I/O lies in whether - the system can receive other input during the period from input to output.
accepted the other dishes before serving them to you. Human order, then this is non-blocking I/O. The key to understanding non-blocking I/O is to
Determine a system for- Input
- /Output
.Think about whether other I/O can be performed during the I/O process. - In the example of ordering food, a system that performs Input
Output is ordering - processing by the kitchen (aunt) - serving Such a system that allows you to eat; ordering food is Input, and serving food is Output. In this example, the key to judging whether the two are non-blocking or blocking is During the process of ordering and serving, can I accept other orders and be served? It's like if you order a Buddha Jumps Over the Wall, it may take a long time to wait for the food to be served. Then the people who come will order some simple dishes, the kind of stir-fried noodles that can be fried in one minute. Maybe after a few waves of people come and go, I haven't been able to serve you food yet. Node.js is used to control the computer. Some operations such as reading files are very time-consuming. If other I/O cannot be performed, the processing efficiency will be very low. Yes, this is one reason why Node.js is non-blocking I/O.
Event loop of Node.js
Node.js will initialize the event loop
provided by libuv when it is started. Each event loop They all contain 6 stages. These 6 stages will be executed repeatedly in each event loop in the order shown in the figure below, as shown below:
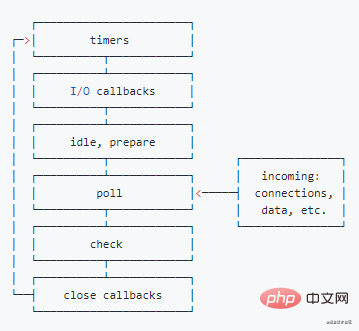
- Phase: This phase executes the callbacks of
- timer
(setTimeout,setInterval)I/Ocallbacks Phase: Handle some unexecuted I/O callbacks from the previous cycle -
idle, - prepare
Phase: Only used internally by Nodepoll Stage: Get new I/O events, Node will block here under appropriate conditions -
check Stage: Execute - setImmediate( )
's callbackclose callbacks Stage: Execute - socket
'scloseevent callbackEach stage has a first-in-first-out (FIFO) queue for executing callbacks. When the event loop runs to each stage, the callback function will be taken out from the corresponding callback queue for execution until the contents of the queue are consumed. exhausted, or the number of callbacks executed reached the maximum
Then the event loop will enter the next stage, and then the callback function will be taken out from the queue corresponding to the next stage and executed, and this will be repeated until the last stage of the event loop. The event loop will also be executed one by one until the process ends.
The relationship between the six macro queues and micro queues in the event loop is as follows: Micro queue (microtask
) is executed between various stages of the event loop, or in each stage of the event loop Executed between corresponding macro queues (macrotask).
Here is a particularly confusing version change: 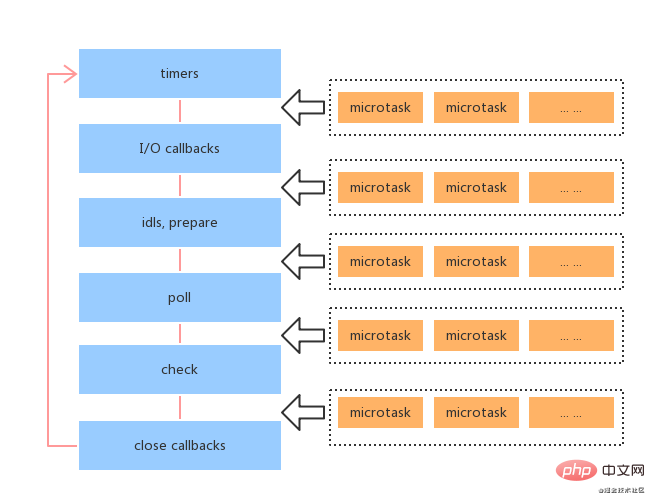
- If it is Node10 and previous versions: There are several macro tasks in the macro queue, and the micro tasks in the micro queue will not be executed until all macro tasks in the macro queue are completed.
- If it is Node11 and later versions: Once a macro task in the corresponding macro queue in a stage is executed (
setTimeout,setIntervalandsetImmediateamong the three (excluding I/O), execute the microtask queue immediately, execute all the microtasks in the microqueue, and then return to the macroqueue to execute the next macrotask. This is consistent with the browser-side operation.
Node.js Asynchronous Programming - callback
- Callback function format specification
error-first callbacknode-style callback
##The first parameter is - error
, followed by Parameters are the result.
// 第一个参数是错误捕获
interview(function (err, res) {
if (err) {
console.log('cry')
return;
}
console.log('smile')
})
function interview(callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
if (Math.random() > 0.2) {
callback(null, 'success')
} else {
callback(new Error('fail'))
}
}, 500)
}- npm
:async.js; can be passedasync.jsTo control asynchronous processes - thunk
: A programming method
Node.js asynchronous programming – Promise
- can be understood literally,
- Promise
means promise; the current event loop cannot get the result, but the future event loop It will give you the result It is a state machine. Once the state is determined to be - resolved
orrejectedit will not change- pending
: Initial state, the state that has not yet obtained the result - fulfilled
/resolved: Successful state - rejected
: Failure status
- pending
.then and .catch
- resolved
ThePromiseof the state will call back the first.then - rejected
of the statePromiseWill call back the first.catch of any - rejected
status and noPromise## followed by.catch#, will cause a global error in the browser/Node environment// promise的状态转换以及通过then获取内容 const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(function () { resolve(3); // reject(new Error(4)) }, 500) }) promise.then(function (result) { console.log(result) }).catch(function (err) { console.log(err) }) setTimeout(() => { console.log(promise) }, 800)Copy after loginExecuting
and catch will return a new Promise, The Promise final state is determined based on the execution results of the then and catch callback functions
- throw
- , the
PromiseisrejectedstatusIf the callback function eventually isreturn - , the
PromiseisresolvedStatusBut if the callback function finallyreturn - returns a
Promise, thePromisewill be the same as the callback functionreturn’sPromisestate remains consistent
async/await
- async function
- is the syntactic sugar encapsulation of
PromiseThe ultimate solution for asynchronous programming – writing asynchronously in a synchronous manner - await
- The keyword can "pause" the execution of
async functionawait - The keyword can be obtained in a synchronous way# The execution result of ##Promise
try-catch can obtain the error obtained by - await
(async function () { await findJob() console.log('trip') })() async function findJob() { try { // 进行三轮面试 await interview(1); await interview(2); await interview(3); console.log('smile') } catch (e) { console.log('cry at ' + e.round) } } // 进行第round轮面试 function interview(round) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { if (Math.random() < 0.2) { const error = new Error('failed'); error.round = round; reject(error); } else { resolve('success'); } }, 500) }) }Copy after loginSummaryUnderstanding non-blocking I/O mainly lies in
determining a system that performs I/O, and then thinking about whether other I/O can be performed /O- .
- Node.js’ Event loop In Node11 version and later, it runs the same as the browser’s event loop, so please pay attention to the distinction.
- Node.js asynchronous programming specification is that the first parameter is error , and the following is the result.
-
Promise is a - state machine
, the initial state ispending, once the state is determined to be resolvedorrejectedwill not change, and chain calls can be made through.thenand.catch.async/ - await
in a synchronous way is the ultimate solution to asynchronous programming.For more programming related knowledge, please visit: Programming Video
The above is the detailed content of An in-depth analysis of asynchrony in Node.js. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
- The keyword can "pause" the execution of

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 An article about memory control in Node
Apr 26, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
An article about memory control in Node
Apr 26, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
The Node service built based on non-blocking and event-driven has the advantage of low memory consumption and is very suitable for handling massive network requests. Under the premise of massive requests, issues related to "memory control" need to be considered. 1. V8’s garbage collection mechanism and memory limitations Js is controlled by the garbage collection machine
 Quick Application: Practical Development Case Analysis of PHP Asynchronous HTTP Download of Multiple Files
Sep 12, 2023 pm 01:15 PM
Quick Application: Practical Development Case Analysis of PHP Asynchronous HTTP Download of Multiple Files
Sep 12, 2023 pm 01:15 PM
Quick Application: Practical Development Case Analysis of PHP Asynchronous HTTP Download of Multiple Files With the development of the Internet, the file download function has become one of the basic needs of many websites and applications. For scenarios where multiple files need to be downloaded at the same time, the traditional synchronous download method is often inefficient and time-consuming. For this reason, using PHP to download multiple files asynchronously over HTTP has become an increasingly common solution. This article will analyze in detail how to use PHP asynchronous HTTP through an actual development case.
 Learn more about Buffers in Node
Apr 25, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
Learn more about Buffers in Node
Apr 25, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
At the beginning, JS only ran on the browser side. It was easy to process Unicode-encoded strings, but it was difficult to process binary and non-Unicode-encoded strings. And binary is the lowest level data format of the computer, video/audio/program/network package
 How Swoole supports asynchronous SMTP operations
Jun 25, 2023 pm 12:24 PM
How Swoole supports asynchronous SMTP operations
Jun 25, 2023 pm 12:24 PM
With the continuous development and popularization of the Internet, email has become an indispensable part of people's lives and work, and SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is one of the important protocols for email sending. As an asynchronous network communication framework for PHP, Swoole can well support asynchronous SMTP operations, making email sending more efficient and stable. This article will introduce how Swoole supports asynchronous SMTP operations, including using sync
 How Swoole supports asynchronous AMQP operations
Jun 25, 2023 am 08:22 AM
How Swoole supports asynchronous AMQP operations
Jun 25, 2023 am 08:22 AM
As the volume of Internet business continues to grow, the demand for high concurrency and high performance is getting higher and higher, and Swoole, as a network communication framework for PHP, is increasingly favored by developers. Among them, Swoole supports asynchronous AMQP, which is one of the more common application scenarios. So let's take a look at how Swoole supports asynchronous AMQP operations. First, we need to clarify what AMQP is. AMQP (AdvancedMessageQueuingProtocol) Advanced
 Advanced Guide to Python asyncio: From Beginner to Expert
Mar 04, 2024 am 09:43 AM
Advanced Guide to Python asyncio: From Beginner to Expert
Mar 04, 2024 am 09:43 AM
Concurrent and Asynchronous Programming Concurrent programming deals with multiple tasks executing simultaneously, asynchronous programming is a type of concurrent programming in which tasks do not block threads. asyncio is a library for asynchronous programming in python, which allows programs to perform I/O operations without blocking the main thread. Event loop The core of asyncio is the event loop, which monitors I/O events and schedules corresponding tasks. When a coroutine is ready, the event loop executes it until it waits for I/O operations. It then pauses the coroutine and continues executing other coroutines. Coroutines Coroutines are functions that can pause and resume execution. The asyncdef keyword is used to create coroutines. The coroutine uses the await keyword to wait for the I/O operation to complete. The following basics of asyncio
 How to use the asynchronous request function in the Vue documentation
Jun 20, 2023 pm 05:55 PM
How to use the asynchronous request function in the Vue documentation
Jun 20, 2023 pm 05:55 PM
Vue.js is a popular front-end JavaScript framework that provides a way to build user interfaces in your applications. In the Vue.js documentation, we can find a lot of useful information, especially about how to use asynchronous request functions. Asynchronous request functions are a way to perform asynchronous tasks in an application. They are used to get data from the server, process input, validate forms, etc. Generally speaking, asynchronous request functions need to be combined with Java functions such as Promise, async and await.
 Asynchronous and non-blocking technology in Java exception handling
May 01, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Asynchronous and non-blocking technology in Java exception handling
May 01, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
Asynchronous and non-blocking techniques can be used to complement traditional exception handling, allowing the creation of more responsive and efficient Java applications: Asynchronous exception handling: Handling exceptions in another thread or process, allowing the main thread to continue executing, avoiding blocking. Non-blocking exception handling: involves event-driven exception handling when an I/O operation goes wrong, avoiding blocking threads and allowing the event loop to handle exceptions.




