
The tcp/ip protocol adopts a 4-layer hierarchical structure: 1. Network interface layer (host-network layer); 2. Internet layer, providing simple and flexible, connectionless, best-effort datagram delivery Services; 3. Transport layer, which provides end-to-end logical communication between application processes; 4. Application layer, which provides applications for users.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
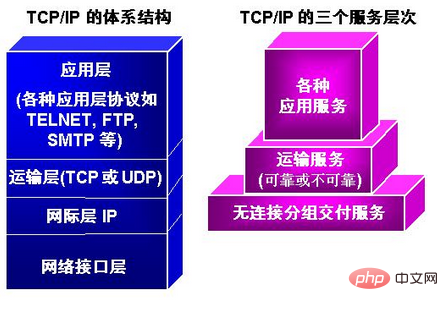
In the TCP/IP protocol, the network interface layer is located on the fourth layer. Since the network interface layer merges the physical layer and the data link layer, the network interface layer is not only the physical medium for transmitting data, but also provides an accurate line for the network layer.
The physical layer defines some characteristics related to the interface of the transmission media, namely mechanical characteristics, electrical characteristics, functional characteristics, process characteristics, and needs to complete the conversion between parallel transmission and serial transmission.
The data link layer provides transparent and reliable data transmission services to users of this layer. Transparency means that there are no restrictions on the content, format and encoding of data transmitted on this layer, and there is no need to explain the meaning of the information structure; reliability means that during the transmission process, the physical connections that may be faulty provided by the physical layer are transformed into logical The specific methods of error-free data links include frame synchronization, error control, flow control, and link management.
The main broadband access technologies in the physical layer include CD protocol, Ethernet 802.3.
2. Internet layerThe main protocols in the Internet layer include IP protocol, Address Resolution Protocol ARP and Reverse Address Resolution Protocol RARP, and Internet Control Message Protocol ICMP.
The IP protocol is the core of the Internet layer. Through routing, the next hop IP is encapsulated and handed over to the network interface layer. IP datagrams are a connectionless service.
ICMP is a supplement to the Internet layer and can send back messages. Used to check whether the network is smooth (use the ping command).
ARP is to find the MAC address of the host through a known IP.
RARP determines the IP address through the MAC address.
3. Transport layerThe main protocols in the transport layer are User Datagram Protocol UDP and Transmission Control Protocol TCP
4. Application layerThe main protocols in the application layer include Domain Name System DNS, File Transfer Protocol FTP, Remote Terminal Protocol TELNET, Hypertext Transfer Protocol HTTP, Simple Mail Transfer Protocol SMTP, Mail Reading Protocol POP3 and IMAP, and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP, Simple Network Management Protocol SNMP.
DNS: Provided Domain name resolution service, providing conversion between domain names and IP addresses, using port 53
FTP: transferring files between any computers in heterogeneous networks, using port 21
TELNET: providing users Remote login service, using port 23, using clear code transmission, poor confidentiality, simple and convenient
HTTP: used to realize various links on the World Wide Web, that is, the connection between the World Wide Web client program and the World Wide Web server, using port 80
SMTP/POP3, IMAP: Provides email transmission and is used to control the sending and transfer of letters. /Read mail from the mail server.
DHCP: Automatically assign IP addresses to computers newly added to the network.
SNMP: Managing software and hardware platforms produced by many manufacturers on the Internet
For more related knowledge, please visit the
FAQThe above is the detailed content of What layers does the tcp/ip protocol contain?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 What is the use of java
What is the use of java
 Domestic Bitcoin buying and selling platform
Domestic Bitcoin buying and selling platform
 psrpc.dll not found solution
psrpc.dll not found solution
 Three mainstream frameworks for web front-end
Three mainstream frameworks for web front-end
 The difference between indexof and includes
The difference between indexof and includes
 How to calculate the factorial of a number in python
How to calculate the factorial of a number in python
 Computer system vulnerability repair methods
Computer system vulnerability repair methods
 How to solve the problem of access denied when booting up Windows 10
How to solve the problem of access denied when booting up Windows 10
 Latest ranking of digital currency exchanges
Latest ranking of digital currency exchanges