Analyzing variables in PHP's underlying kernel source code (3)
This article introduces to you "Analysis of Variables in PHP's Underlying Kernel Source Code (3)". It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.
Recommended related articles: "Analysis of variables in PHP's underlying kernel source code (1)" "Analysis of variables in PHP's underlying kernel source code (2) zend_string"
The source code of the zend_string structure has been read through above.
struct _zend_string {
zend_refcounted_h gc; //占用8个字节 用于gc的计数和字符串类型的记录
zend_ulong h; // 占用8个字节 用于记录 字符串的哈希值
size_t len; //占用8个字节 字符串的长度
char val[1]; //占用1个字节 字符串的值存储位置
};The len variable enables zend_string to have binary security features
gc, that is, the zend_refcounted_h structure can realize the copy-on-write function
typedef struct _zend_refcounted_h {
uint32_t refcount;//引用数
union {
uint32_t type_info; //字符串所属的变量类别
} u;
} zend_refcounted_h;copy-on-write technology is widely used in redis and the Linux kernel
For example, Redis needs to create a child process of the current server process, and most operating systems use copy-on-write (copy-on-write). on-write) to optimize the usage efficiency of the child process, so during the existence of the child process, the server will increase the threshold of the load factor, thereby avoiding hash table expansion operations and unnecessary memory write operations during the existence of the child process. Save memory as much as possible.
PHP 7 also uses copy-on-write to save memory during assignment operations. When a string is assigned, it does not directly copy a copy of the data, but instead copies the data in _zend_refcounted_h in the zend_string structure. The refcount is calculated as 1, and when the string is destroyed, the refcount in _zend_refcounted_h in the zend_string structure is calculated as -1.
If you have read the book "PHP Underlying Source Code Design and Implementation" written by Chen Lei, you may find that it is slightly different because my version is PHP7.4. The version in the book is different from the one I installed locally. I guess Probably for unified memory management.
The gc.u.flags field in the zend_string structure, gc.u.flags has a total of 8 bits, one for each category, and can be labeled repeatedly. In theory, up to 8 kinds of labels can be printed. The current PHP 7 source code mainly involves the following categories: 1) For temporary ordinary strings, the flags field is identified as 0. 2) For internal strings, used to store literals, identifiers, etc. in PHP code, the flags field is Identified as IS_STR_PERSISTENT |IS_STR_INTERNED. 3) For PHP known strings, the flags field will be identified as IS_STR_PERSISTENT|IS_STR_INTERNED|IS_STR_PERMANENT.
--------Excerpted from "Design and Implementation of PHP Underlying Source Code"
At the bottom of PHP7.4 source code, variables will be classified to facilitate memory management, which relies on the zend_zval structure The u1.v.type_flags field
struct _zval_struct {
197 zend_value value; //变量
198 union {
199 struct {
200 ZEND_ENDIAN_LOHI_3(
201 zend_uchar type, //变量类型
202 zend_uchar type_flags,//可以用于变量的分类
203 union {
204 uint16_t extra; /* not further specified */
205 } u)
206 } v;
207 uint32_t type_info;//变量类型
208 } u1;
209 u2;
222 };has the following code on line 555
/* zval.u1.v.type_flags */ #define IS_TYPE_REFCOUNTED(1<<0) //REFCOUNTED 可以计数的 #define IS_TYPE_COLLECTABLE(1<<1) // TYPE_COLLECTABLE可收集的 #if 1 /* This optimized version assumes that we have a single "type_flag" */ /* IS_TYPE_COLLECTABLE may be used only with IS_TYPE_REFCOUNTED */ /*优化后的版本假设我们有一个单一的"type_flag" */ /* IS_TYPE_COLLECTABLE只能与IS_TYPE_REFCOUNTED一起使用*/ # define Z_TYPE_INFO_REFCOUNTED(t)(((t) & Z_TYPE_FLAGS_MASK) != 0) #else # define Z_TYPE_INFO_REFCOUNTED(t)(((t) & (IS_TYPE_REFCOUNTED << Z_TYPE_FLAGS_SHIFT)) != 0) #endif
So in the PHP7.4 version, zval.u1.v.type_flags has only two types: 0 or 1. At the same time, I I also looked at the latest PHP8 version code and the same is true
In order to better understand the source code, we will also put the previous two sections together. We installed gdb to debug PHP
GDB (GNU symbolic debugger ) is simply a debugging tool. It is a free software protected by the General Public License, the GPL. Like all debuggers, GDB allows you to debug a program, including stopping the program where you want it, at which time you can view variables, registers, memory, and the stack. Furthermore you can modify variables and memory values. GDB is a very powerful debugger that can debug multiple languages. Here we only cover C and C debugging, not other languages. Another point to note is that GDB is a debugger, unlike VC which is an integrated environment. You can use some front-end tools such as XXGDB, DDD, etc. They all have graphical interfaces, so they are easier to use, but they are just a shell for GDB. Therefore, you should still be familiar with GDB commands. In fact, when you use these graphical interfaces for a long time, you will discover the importance of becoming familiar with GDB commands.
-----Excerpted from oschina
[root@a3d3f47671d9 /]# php -v PHP 7.4.15 (cli) (built: Feb 21 2021 09:07:07) ( NTS ) Copyright (c) The PHP Group Zend Engine v3.4.0, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies [root@a3d3f47671d9 /]# gbv bash: gbv: command not found [root@a3d3f47671d9 /]# gdb bash: gdb: command not found [root@a3d3f47671d9 /]# yum install gdb
..........
Create a new PHP file
[root@a3d3f47671d9 cui]# vim php7-4-test-zval.php php7-4-test-zval.php Buffers <?php $a="abcdefg"; echo $a; $b=88; echo $b; $c = $a; echo $c; echo $a; $c ="abc"; echo $c; echo $a;
Use gdb to run PHP
[root@a3d3f47671d9 cui]# gdb php
GNU gdb (GDB) Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.2-12.el8
Copyright (C) 2018 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
Type "show copying" and "show warranty" for details.
This GDB was configured as "x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu".
Type "show configuration" for configuration details.
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
<http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/bugs/>.
Find the GDB manual and other documentation resources online at:
<http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/documentation/>.
For help, type "help".
Type "apropos word" to search for commands related to "word"...
Reading symbols from php...done.
(gdb) b ZEND_ECHO_SPEC_CV_HANDLER # b 命令意思是打断点
Breakpoint 1 at 0x6dfe80: file /cui/php-7.4.15/Zend/zend_vm_execute.h, line 36987.
(gdb) r php7-4-test-zval.php
Starting program: /usr/local/bin/php php7-4-test-zval.php
warning: Error disabling address space randomization: Operation not permitted
Missing separate debuginfos, use: yum debuginfo-install glibc-2.28-127.el8.x86_64
warning: Loadable section ".note.gnu.property" outside of ELF segments
warning: Loadable section ".note.gnu.property" outside of ELF segments
warning: Loadable section ".note.gnu.property" outside of ELF segments
[Thread debugging using libthread_db enabled]
Using host libthread_db library "/lib64/libthread_db.so.1".
warning: Loadable section ".note.gnu.property" outside of ELF segments
warning: Loadable section ".note.gnu.property" outside of ELF segments
Breakpoint 1, ZEND_ECHO_SPEC_CV_HANDLER () at /cui/php-7.4.15/Zend/zend_vm_execute.h:36987
36987SAVE_OPLINE();
Missing separate debuginfos, use: yum debuginfo-install libxcrypt-4.1.1-4.el8.x86_64 libxml2-2.9.7-8.el8.x86_64 sqlite-libs-3.26.0-11.el8.x86_64 xz-libs-5.2.4-3.el8.x86_64 zlib-1.2.11-16.el8_2.x86_64You can see that my error is reported because I am running the centos image in docker. I checked some information and the solution is as follows
Edit /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Debuginfo .repo file
Modify enable=1
Then yum install yum-utils
Then dnf install glibc-langpack-en
yum debuginfo-install libxcrypt -4.1.1-4.el8.x86_64 libxml2-2.9.7-8.el8.x86_64 sqlite-libs-3.26.0-11.el8.x86_64 xz-libs-5.2.4-3.el8.x86_64 zlib-1.2 .11-16.el8_2.x86_64
yum debuginfo-install glibc-2.28-127.el8.x86_64
Let’s run gdb again
[root@a3d3f47671d9 cui]# vim php7-4-test-zval.php
[root@a3d3f47671d9 cui]# gdb php
GNU gdb (GDB) Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8.2-12.el8
Copyright (C) 2018 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
Type "show copying" and "show warranty" for details.
This GDB was configured as "x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu".
Type "show configuration" for configuration details.
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
<http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/bugs/>.
Find the GDB manual and other documentation resources online at:
<http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/documentation/>.
For help, type "help".
Type "apropos word" to search for commands related to "word"...
Reading symbols from php...done.
(gdb)In gdb mode command b You can set breakpoints, which you can understand as PHP's xdebug
Do you still remember the content of our php7-4-test-zval.php file
<?php $a="abcdefg"; echo $a; $b=88; echo $b; $c = $a; echo $c; echo $a; $c ="abc"; echo $c; echo $a;
This echo language structure is for our debugging use Here is a little trick
(ps The language structure I am talking about here does not say that echo is a function. There is an interview question about the main difference between echo() and var_dump() in php?)
This echo In fact, it is for us to set the breakpoint ZEND_ECHO_SPEC_CV_HANDLER
ZEND_ECHO_SPEC_CV_HANDLER is actually a macro. It will be explained in detail during the lexical analysis and syntax analysis execute, as shown in the figure
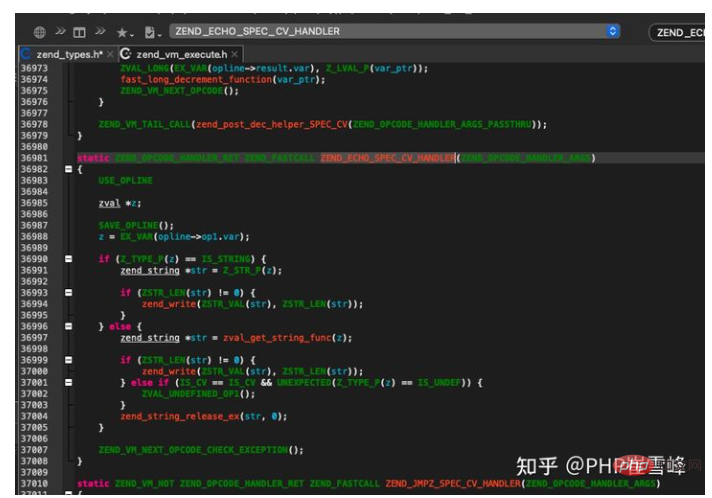
我们设置这个断点的意义是为了让程序在拼接echo 的时候暂停代码 以便我们分析
(gdb) b ZEND_ECHO_SPEC_CV_HANDLER Breakpoint 1 at 0x6dfe80: file /cui/php-7.4.15/Zend/zend_vm_execute.h, line 36987.
在gdb中 使用 r 运行文件
(gdb) r php7-4-test-zval.php Starting program: /usr/local/bin/php php7-4-test-zval.php warning: Error disabling address space randomization: Operation not permitted [Thread debugging using libthread_db enabled] Using host libthread_db library "/lib64/libthread_db.so.1". Breakpoint 1, ZEND_ECHO_SPEC_CV_HANDLER () at /cui/php-7.4.15/Zend/zend_vm_execute.h:36987 36987SAVE_OPLINE();
在gdb中 用 n 可以执行下一步操作
(gdb) n 36988z = EX_VAR(opline->op1.var);
这里我们暂且忽略继续往下走
ZEND_ECHO_SPEC_CV_HANDLER的完整代码如下(我贴出来只是想告诉你代码里有这行代码 让你知道为什么往下走,你现阶段不需要理解代码,慢慢来 )
static ZEND_OPCODE_HANDLER_RET ZEND_FASTCALL ZEND_ECHO_SPEC_CV_HANDLER(ZEND_OPCODE_HANDLER_ARGS)
{
USE_OPLINE
zval *z;
SAVE_OPLINE();
//****************走到了此处**************
z = EX_VAR(opline->op1.var);
if (Z_TYPE_P(z) == IS_STRING) {
zend_string *str = Z_STR_P(z);
if (ZSTR_LEN(str) != 0) {
zend_write(ZSTR_VAL(str), ZSTR_LEN(str));
}
} else {
zend_string *str = zval_get_string_func(z);
if (ZSTR_LEN(str) != 0) {
zend_write(ZSTR_VAL(str), ZSTR_LEN(str));
} else if (IS_CV == IS_CV && UNEXPECTED(Z_TYPE_P(z) == IS_UNDEF)) {
ZVAL_UNDEFINED_OP1();
}
zend_string_release_ex(str, 0);
}
ZEND_VM_NEXT_OPCODE_CHECK_EXCEPTION();
}
(gdb) n
441return pz->u1.v.type;
(gdb) n
36991zend_string *str = Z_STR_P(z);这里到了关键位置 变量z出现了
gdb中 用p 查看变量
(gdb) p z $1 = (zval *) 0x7f4235a13070
这是一个 zval 结构体的指针地址
(gdb) p *z
$2 = {
value = {lval = 139922344256128, dval = 6.9130823382525114e-310, counted = 0x7f4235a02280,
str = 0x7f4235a02280, arr = 0x7f4235a02280, obj = 0x7f4235a02280, res = 0x7f4235a02280, ref = 0x7f4235a02280,
ast = 0x7f4235a02280, zv = 0x7f4235a02280, ptr = 0x7f4235a02280, ce = 0x7f4235a02280, func = 0x7f4235a02280,
ww = {w1 = 899687040, w2 = 32578}},
u1 = {v = {type = 6 '\006', type_flags = 0 '\000', u = {extra = 0}},
type_info = 6},
u2 = {next = 0, cache_slot = 0, opline_num = 0, lineno = 0, num_args = 0, fe_pos = 0,
fe_iter_idx = 0, access_flags = 0, property_guard = 0, constant_flags = 0, extra = 0}}看到这里应该很熟悉了 这就是源码里的 结构体 格式
再次复习下 zval
struct _zval_struct {
zend_value value; //变量
union {
struct {
ZEND_ENDIAN_LOHI_3(
zend_uchar type, //变量类型
zend_uchar type_flags,//可以用于变量的分类
union {
uint16_t extra; /* not further specified */
} u)
} v;
uint32_t type_info;//变量类型
} u1;
u2;
};gdb中变量$2 中 u1.v.type=6 我们拿出第二节的 类型定义源码部分对比下
/* regular data types */ #define IS_UNDEF0 #define IS_NULL1 #define IS_FALSE2 #define IS_TRUE3 #define IS_LONG4 #define IS_DOUBLE5 #define IS_STRING6 #define IS_ARRAY7 #define IS_OBJECT8 #define IS_RESOURCE9 #define IS_REFERENCE10 ..... //其实有20种 剩下的不是常用类型 代码就不全部粘出来了 u1.v.type=6 类型是 IS_STRING
再看下 zval种 value 对应的 zend_value联合体中的代码
ypedef union _zend_value {
zend_long lval;/* long value */
double dval;/* double value */
zend_refcounted *counted;
zend_string *str;
zend_array *arr;
zend_object *obj;
zend_resource *res;
zend_reference *ref;
zend_ast_ref *ast;
zval *zv;
void *ptr;
zend_class_entry *ce;
zend_function *func;
struct {
uint32_t w1;
uint32_t w2;
} ww;
} zend_value;还记得联合体的特性吗 ? 所有值公用一个内存空间
上面的gdb中变量$2 的v.type=6 所以 在value中 值被str占用了 同时str 前面有个*
*星号 在C语言里代表指针 指向另外一个值的地址 所以指向 zend_string结构体
关于C语言指针您可以参考 菜鸟学院-指针
所以 接下来我们可以通过获取value中的str来获取 查看值
(gdb) p *z.value .str
$4 = {gc = {refcount = 1, u = {type_info = 70}},
h = 9223601495925209889, len = 7, val = "a"}对比下 zend_string 源码
struct _zend_string {
zend_refcounted_h gc;//引用计数
zend_ulong h; /* hash value */
size_t len;//字符串长度
char val[1];
};* 你可能有疑问 val为啥 是val=“a” 我们不是定义$a="abcdefg"; 吗 ? 还记得柔性数组吗?:)
接下来继续往下走
gdb中 用c 来执行到下一个断点处
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Breakpoint 1, ZEND_ECHO_SPEC_CV_HANDLER () at /cui/php-7.4.15/Zend/zend_vm_execute.h:36987
36987SAVE_OPLINE();
(gdb) n
36988z = EX_VAR(opline->op1.var);
(gdb) n
441return pz->u1.v.type;
(gdb) n
36997zend_string *str = zval_get_string_func(z);
(gdb) p *z
$6 = {
value = {lval = 88, dval = 4.3477776834029696e-322, counted = 0x58, str = 0x58, arr = 0x58, obj = 0x58,
res = 0x58, ref = 0x58, ast = 0x58, zv = 0x58, ptr = 0x58, ce = 0x58, func = 0x58, ww = {w1 = 88, w2 = 0}},
u1 = {v = {type = 4 '\004', type_flags = 0 '\000', u = {extra = 0}}, type_info = 4},
u2 = {next = 0,
cache_slot = 0, opline_num = 0, lineno = 0, num_args = 0, fe_pos = 0, fe_iter_idx = 0, access_flags = 0,
property_guard = 0, constant_flags = 0, extra = 0}}u1.v.type=4 对应的是IS_LONG 代表整型 所以 在value中 值被lval占用了
可以看到值就是88 (lval不是指针 无需再跟进去查看了)
至此 我们用gdb 结合之前所看的核心源码 亲自实战了 PHP的zval
下一节我们继续 进行写时复制 的gdb跟踪
看完此文 希望你务必也用gdb调试下 深度体会zval的巧妙之处
感谢陈雷前辈的《PHP7源码底层设计与实现》
▏本文经原作者PHP崔雪峰同意,发布在php中文网,原文地址:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/353173325
The above is the detailed content of Analyzing variables in PHP's underlying kernel source code (3). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 A guide to using Windows 11 and 10 environment variables for profiling
Nov 01, 2023 pm 08:13 PM
A guide to using Windows 11 and 10 environment variables for profiling
Nov 01, 2023 pm 08:13 PM
Environment variables are the path to the location (or environment) where applications and programs run. They can be created, edited, managed or deleted by the user and come in handy when managing the behavior of certain processes. Here's how to create a configuration file to manage multiple variables simultaneously without having to edit them individually on Windows. How to use profiles in environment variables Windows 11 and 10 On Windows, there are two sets of environment variables – user variables (apply to the current user) and system variables (apply globally). However, using a tool like PowerToys, you can create a separate configuration file to add new and existing variables and manage them all at once. Here’s how: Step 1: Install PowerToysPowerTo
 Strict mode for variables in PHP7: how to reduce potential bugs?
Oct 19, 2023 am 10:01 AM
Strict mode for variables in PHP7: how to reduce potential bugs?
Oct 19, 2023 am 10:01 AM
Strict mode was introduced in PHP7, which can help developers reduce potential errors. This article will explain what strict mode is and how to use strict mode in PHP7 to reduce errors. At the same time, the application of strict mode will be demonstrated through code examples. 1. What is strict mode? Strict mode is a feature in PHP7 that can help developers write more standardized code and reduce some common errors. In strict mode, there will be strict restrictions and detection on variable declaration, type checking, function calling, etc. Pass
 What are instance variables in Java
Feb 19, 2024 pm 07:55 PM
What are instance variables in Java
Feb 19, 2024 pm 07:55 PM
Instance variables in Java refer to variables defined in the class, not in the method or constructor. Instance variables are also called member variables. Each instance of a class has its own copy of the instance variable. Instance variables are initialized during object creation, and their state is saved and maintained throughout the object's lifetime. Instance variable definitions are usually placed at the top of the class and can be declared with any access modifier, which can be public, private, protected, or the default access modifier. It depends on what we want this to be
 PHP function introduction—is_string(): Check whether the variable is a string
Jul 24, 2023 pm 09:33 PM
PHP function introduction—is_string(): Check whether the variable is a string
Jul 24, 2023 pm 09:33 PM
PHP function introduction—strpos(): Check whether a variable is a string In PHP, is_string() is a very useful function, which is used to check whether a variable is a string. When we need to determine whether a variable is a string, the is_string() function can help us achieve this goal easily. Below we will learn about how to use the is_string() function and provide some related code examples. The syntax of the is_string() function is very simple. it only needs to
 How to get variables from PHP method using Ajax?
Mar 09, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
How to get variables from PHP method using Ajax?
Mar 09, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Using Ajax to obtain variables from PHP methods is a common scenario in web development. Through Ajax, the page can be dynamically obtained without refreshing the data. In this article, we will introduce how to use Ajax to get variables from PHP methods, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to write a PHP file to handle the Ajax request and return the required variables. Here is sample code for a simple PHP file getData.php:
 Mind map of Python syntax: in-depth understanding of code structure
Feb 21, 2024 am 09:00 AM
Mind map of Python syntax: in-depth understanding of code structure
Feb 21, 2024 am 09:00 AM
Python is widely used in a wide range of fields with its simple and easy-to-read syntax. It is crucial to master the basic structure of Python syntax, both to improve programming efficiency and to gain a deep understanding of how the code works. To this end, this article provides a comprehensive mind map detailing various aspects of Python syntax. Variables and Data Types Variables are containers used to store data in Python. The mind map shows common Python data types, including integers, floating point numbers, strings, Boolean values, and lists. Each data type has its own characteristics and operation methods. Operators Operators are used to perform various operations on data types. The mind map covers the different operator types in Python, such as arithmetic operators, ratio
 Deep understanding of const in C language
Feb 18, 2024 pm 12:56 PM
Deep understanding of const in C language
Feb 18, 2024 pm 12:56 PM
Detailed explanation and code examples of const in C In C language, the const keyword is used to define constants, which means that the value of the variable cannot be modified during program execution. The const keyword can be used to modify variables, function parameters, and function return values. This article will provide a detailed analysis of the use of the const keyword in C language and provide specific code examples. const modified variable When const is used to modify a variable, it means that the variable is a read-only variable and cannot be modified once it is assigned a value. For example: constint
 Explain the life cycle of variables in C language
Sep 02, 2023 pm 07:37 PM
Explain the life cycle of variables in C language
Sep 02, 2023 pm 07:37 PM
Storage classes specify the scope, lifetime, and binding of variables. To fully define a variable, it is necessary to mention not only its "type" but also its storage class. A variable name identifies a physical location in computer memory where a set of bits is allocated to store the variable's value. Storage class tells us the following factors - Where are the variables stored (in memory or CPU registers)? If not initialized, what is the initial value of the variable? What is the scope of a variable (the scope within which the variable can be accessed)? What is the life cycle of a variable? The lifetime of a lifetime variable defines the duration for which the computer allocates memory (the duration between memory allocation and deallocation). In C language, variables can have automatic, static or dynamic life cycle. Automatic - create a life cycle with automatic






