 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Quickly understand the NgRx/Store framework in Angular in one article
Quickly understand the NgRx/Store framework in Angular in one article
Quickly understand the NgRx/Store framework in Angular in one article
What is NgRx/Store framework in
Angular? What is the use? This article will take you to understand the NgRx/Store data state management framework, the basic principles in ngrx/store, and learn the simple usage of the framework through examples.

【Related tutorial recommendation: "angular tutorial"】
ngrx/store Yes A state management library based on RxJS, inspired by Redux. In NgRx, state is composed of a map containing functions of action and reducer. The Reducer function is called via the dispatch of action and the current or initial state, and finally an immutable state is returned by reducer.
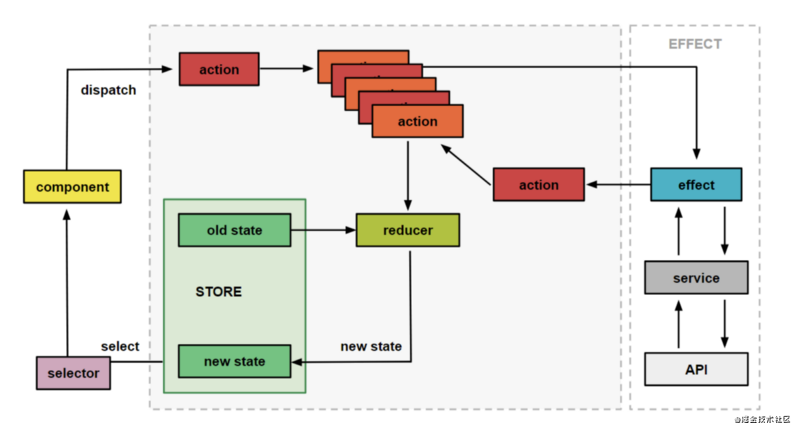
State Management
State management of large and complex front-end Angular/AngularJS projects has always been a frustrating task Headache problem. In AngularJS (version 1.x), state management is usually handled by a mix of services, events, $rootScope. In Angular (version 2), component communication makes state management clearer, but it is still a bit complicated, and many methods are used depending on the data flow direction.
Basic principles in ngrx/store
The view layer initiates an action through dispatch, and Reducer receives it action, based on the action.type type, determines execution, changes the state, returns a new state to store, and is updated by store ##state.

- ##State
- (state) is the state (
state) memory Action - (Behavior) Describes changes in state
- (Reducer/Reduction function) Calculate the new state based on the previous state and current behavior. The method inside is pure The function
state uses the observable object ofState - and the observer of
Action-Storeto access
Actions
is the carrier of information. It sends data to reducer, and then reducer updates store. Actions is the only way store can accept data. In
, the interface of Action is as follows: <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>// actions包括行为类型和对应的数据载体
export interface Action {
type: string;
payload?: any;
}</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>
Describes the expected status change type. For example, add to-do ADD_TODO, add DECREMENT, etc. payload is the data sent to store to be updated. storeThe code for dispatching action is similar to the following: <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>// 派发action,从而更新store
store.dispatch({
type: &#39;ADD_TODO&#39;,
payload: &#39;Buy milk&#39;
});</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>
Reducers
Specifies the specific state changes corresponding to the behavior. It is a pure function that changes the state by receiving the previous state and dispatching behavior to return a new object as the next state. The new object is usually implemented using Object.assign and extended syntax. <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>// reducer定义了action被派发时state的具体改变方式
export const todoReducer = (state = [], action) => {
switch(action.type) {
case &#39;ADD_TODO&#39;:
return [...state, action.payload];
default:
return state;
}
}</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>When developing, special attention should be paid to the purity of the function. Because pure functions:
- The output only depends on the input
- The same input will always get the same output
store
stores all the immutable state in the application. The store in ngrx/store is the observable object of the RxJS state and the observer of the behavior. You can use
to distribute actions. You can also use the Store's select() method to obtain observable objects, then subscribe to observe and react after the status changes. What we describe above is the basic process. In the actual development process, asynchronous operations such as API requests and browser storage will be involved, which requires
and services. effects consists of actionTrigger, perform a series of logic and then issue one or more action that need to be added to the queue, and then processed by reducers.

Simple example
A brief introduction to the login module of a management system.
Create Form1. Add components:
LoginComponent, mainly layout, the code is component logic2. Define user:
<div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>export class User {
id: number;
username: string;
password: string;
email: string;
avatar: string;
clear(): void {
this.id = undefined;
this.username = "";
this.password = "";
this.email = "";
this.avatar = "./assets/default.jpg";
}
}</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div><p>3、添加表单:在组件<code>LoginComponent增加Form表单
NGRX Store
按照上述的4个原则定义相应的Actions
reducers定义状态在文件
auth.reducers.ts中创建状态,并初始化export interface AuthState { isAuthenticated: boolean; user: User | null; errorMessage: string | null; } export const initialAuthState: AuthState = { isAuthenticated: false, user: null, errorMessage: null };Copy after loginactions定义行为export enum AuthActionTypes { Login = "[Auth] Login", LoginSuccess = "[Auth] Login Success", LoginFailure = "[Auth] Login Failure" } export class Login implements Action { readonly type = AuthActionTypes.Login; constructor(public payload: any) {} }Copy after loginservice实现数据交互(服务器)@Injectable() export class AuthService { private BASE_URL = "api/user"; constructor(private http: HttpClient) {} getToken(): string { return localStorage.getItem("token"); } login(email: string, pwd: string): Observable<any> { const url = `${this.BASE_URL}/login`; return this.http.post<User>(url, { email, pwd }); } }Copy after logineffects侦听从Store调度的动作,执行某些逻辑,然后分派新动作
一般情况下只在这里调用API
通过返回一个action给reducer进行操作来改变store的状态
effects总是返回一个或多个action(除非
@Effect with {dispatch: false}))
@Effect() Login: Observable<any> = this.actions.pipe( ofType(AuthActionTypes.Login), //执行Login响应 map((action: Login) => action.payload), switchMap(payload => { return this.authService.login(payload.email, payload.password).pipe( map(user => { return new LoginSuccess({ uid: user.id, email: payload.email }); }), catchError(error => { return of(new LoginFailure(error)); }) ); }) ); //失败的效果 @Effect({ dispatch: false }) LoginFailure: Observable<any> = this.actions.pipe(ofType(AuthActionTypes.LoginFailure)); //成功的效果 @Effect({ dispatch: false }) LoginSuccess: Observable<any> = this.actions.pipe( ofType(AuthActionTypes.LoginSuccess), tap(user => { localStorage.setItem("uid", user.payload.id); this.router.navigateByUrl("/sample"); }) );Copy after login完
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
The above is the detailed content of Quickly understand the NgRx/Store framework in Angular in one article. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of commercial support for Java frameworks
Jun 05, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
How to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of commercial support for Java frameworks
Jun 05, 2024 pm 05:25 PM
Evaluating the cost/performance of commercial support for a Java framework involves the following steps: Determine the required level of assurance and service level agreement (SLA) guarantees. The experience and expertise of the research support team. Consider additional services such as upgrades, troubleshooting, and performance optimization. Weigh business support costs against risk mitigation and increased efficiency.
 How do the lightweight options of PHP frameworks affect application performance?
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:53 AM
How do the lightweight options of PHP frameworks affect application performance?
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:53 AM
The lightweight PHP framework improves application performance through small size and low resource consumption. Its features include: small size, fast startup, low memory usage, improved response speed and throughput, and reduced resource consumption. Practical case: SlimFramework creates REST API, only 500KB, high responsiveness and high throughput
 How does the learning curve of PHP frameworks compare to other language frameworks?
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
How does the learning curve of PHP frameworks compare to other language frameworks?
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
The learning curve of a PHP framework depends on language proficiency, framework complexity, documentation quality, and community support. The learning curve of PHP frameworks is higher when compared to Python frameworks and lower when compared to Ruby frameworks. Compared to Java frameworks, PHP frameworks have a moderate learning curve but a shorter time to get started.
 Performance comparison of Java frameworks
Jun 04, 2024 pm 03:56 PM
Performance comparison of Java frameworks
Jun 04, 2024 pm 03:56 PM
According to benchmarks, for small, high-performance applications, Quarkus (fast startup, low memory) or Micronaut (TechEmpower excellent) are ideal choices. SpringBoot is suitable for large, full-stack applications, but has slightly slower startup times and memory usage.
 Golang framework documentation best practices
Jun 04, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
Golang framework documentation best practices
Jun 04, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
Writing clear and comprehensive documentation is crucial for the Golang framework. Best practices include following an established documentation style, such as Google's Go Coding Style Guide. Use a clear organizational structure, including headings, subheadings, and lists, and provide navigation. Provides comprehensive and accurate information, including getting started guides, API references, and concepts. Use code examples to illustrate concepts and usage. Keep documentation updated, track changes and document new features. Provide support and community resources such as GitHub issues and forums. Create practical examples, such as API documentation.
 How to choose the best golang framework for different application scenarios
Jun 05, 2024 pm 04:05 PM
How to choose the best golang framework for different application scenarios
Jun 05, 2024 pm 04:05 PM
Choose the best Go framework based on application scenarios: consider application type, language features, performance requirements, and ecosystem. Common Go frameworks: Gin (Web application), Echo (Web service), Fiber (high throughput), gorm (ORM), fasthttp (speed). Practical case: building REST API (Fiber) and interacting with the database (gorm). Choose a framework: choose fasthttp for key performance, Gin/Echo for flexible web applications, and gorm for database interaction.
 Detailed practical explanation of golang framework development: Questions and Answers
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:57 AM
Detailed practical explanation of golang framework development: Questions and Answers
Jun 06, 2024 am 10:57 AM
In Go framework development, common challenges and their solutions are: Error handling: Use the errors package for management, and use middleware to centrally handle errors. Authentication and authorization: Integrate third-party libraries and create custom middleware to check credentials. Concurrency processing: Use goroutines, mutexes, and channels to control resource access. Unit testing: Use gotest packages, mocks, and stubs for isolation, and code coverage tools to ensure sufficiency. Deployment and monitoring: Use Docker containers to package deployments, set up data backups, and track performance and errors with logging and monitoring tools.
 What are the common misunderstandings in the learning process of Golang framework?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:59 PM
What are the common misunderstandings in the learning process of Golang framework?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:59 PM
There are five misunderstandings in Go framework learning: over-reliance on the framework and limited flexibility. If you don’t follow the framework conventions, the code will be difficult to maintain. Using outdated libraries can cause security and compatibility issues. Excessive use of packages obfuscates code structure. Ignoring error handling leads to unexpected behavior and crashes.





