
In CSS, you can use the "!important" statement to set the weight, which provides developers with a way to increase the weight of the style; the syntax format is "property:property value !important;". The "!important" statement is a declaration of the entire style, including the attributes and attribute values of this style.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, CSS3&&HTML5 version, Dell G3 computer.
CSS weight
refers to the priority of the style. If there are two or more styles acting on an element, the one with the higher weight will Styles work on elements. If the weight is the same, the style written later will override the style written earlier.
Level of weight
(1) !important, added after the style attribute value, the weight value is 10000
(2) Inline style , such as: , the weight value is 1000
(3) ID selector, such as: #content, the weight value is 100
(4) Class, pseudo-class and attribute selection The weight value of label selectors and pseudo-element selectors, such as: content, :hover, is 10
(5). The weight value of label selectors and pseudo-element selectors, such as: div, p, :before, is 1
(6 ) Universal selector (*), child selector (>), adjacent selector (), sibling selector (~), weight value is 0
How to set the weight in css?
In CSS, you can use the "!important" statement to set the weight, which provides developers with a way to increase the weight of the style.
css weight value (overlap) example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
p{
color:red;
font-size: 10px;
}
#wrap{
color: deeppink;
font-size: 30px;
}
.box{
color:yellow;
font-size: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p id="wrap">
猜猜我是什么颜色
</p>
</body>
</html> can be executed and the result will be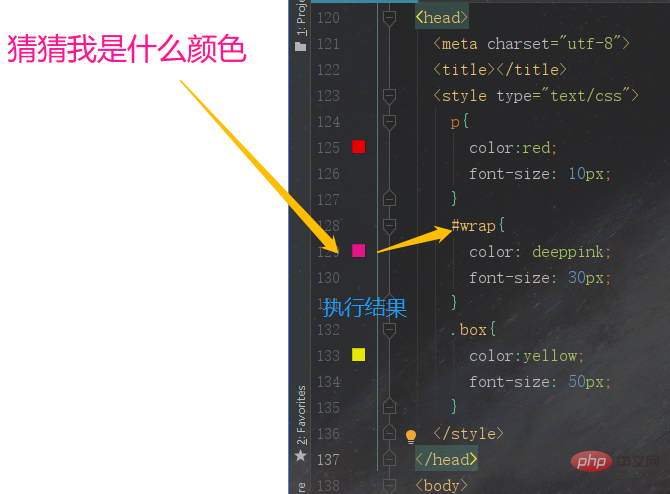
Summary: This effect occurs because the browser determines which css style to use based on the weight value. The higher the weight value, the higher its priority will be, and the css style and the weight value of the id selector will be displayed. For 100>Class Selector 10>Tag Selector 1, so the final result is the style set by the id selector
List 2 Code
!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
color: cyan;
}
div {
color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p id="wrap">
猜猜我是什么颜色
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>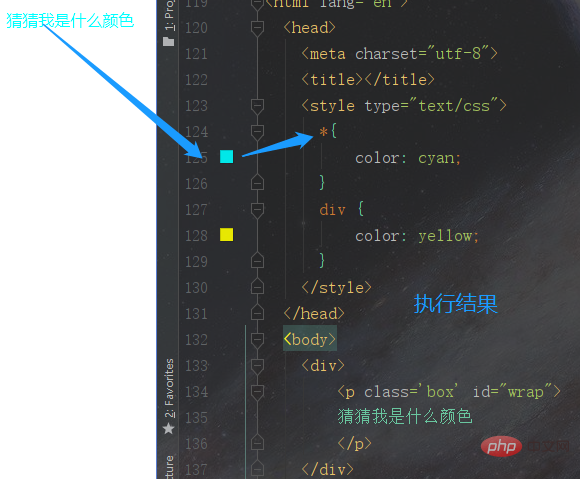
Summary: Inherited elements have no weight value, so the final result is set by the universal selector Style
Example 3 Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
p{
color: yellow;
}
*{
color: cyan;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p id="wrap">
猜猜我是什么颜色
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>Execution result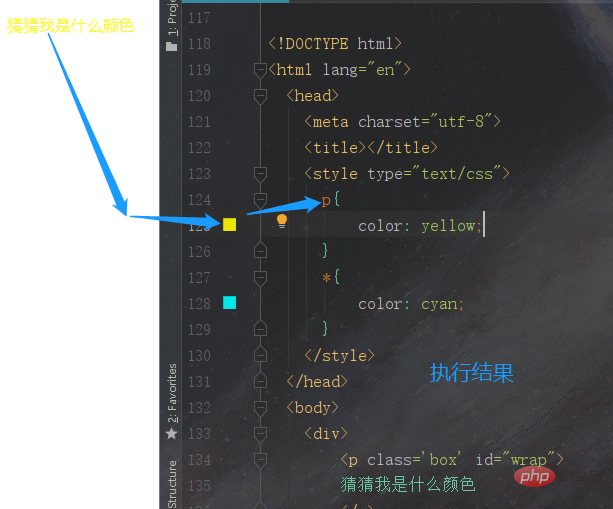
Summary: The weight value of the tag selector is 1, but it is still greater than the universal selector, so the final result is the style set by the tag selector
Example 4 Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
div p{
color: yellow;
}
div>p{
color: cyan;
}
p{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p id="wrap">
猜猜我是什么颜色
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>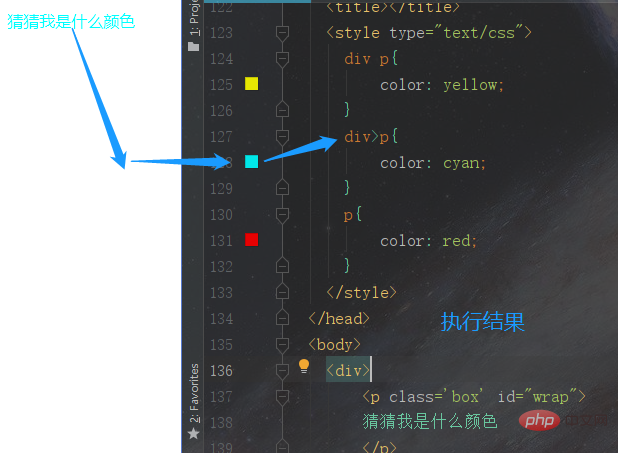
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
div>p{
color: cyan;
}
div p{
color: yellow;
}
p{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p id="wrap">
猜猜我是什么颜色
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>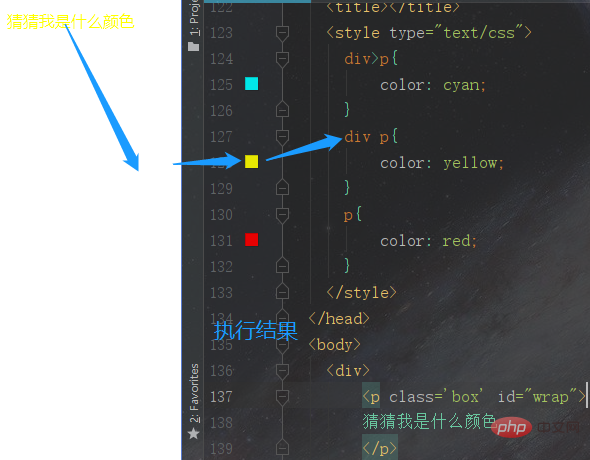
!important Example of increasing weight value
When we are doing web page code , there are some special situations where it is necessary to set the highest weight value for certain styles, what should I do? For example, we know that the weight value of the inline style is 1000, which is relatively large, then we can use !important to solve it.<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>!important的使用</title>
<style type="text/css">
div{
color:green !important;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box" style="color:red;">
<span>猜猜我是什么颜色</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>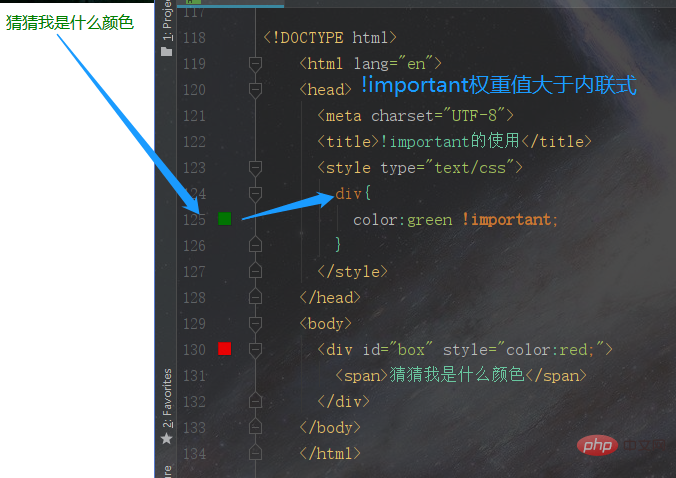
Under what circumstances can !important be used?
box p { color: blue; } p.awesome { color: red; }How can I make the text color red? In this case, if !important. does not apply, the first rule will always be greater than the second rule.
Summarize (Learning video sharing: css video tutorial)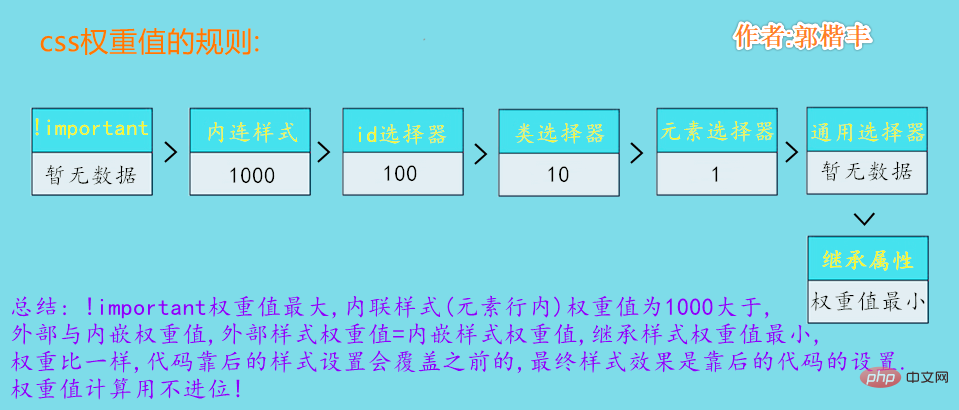
The above is the detailed content of How to set weight in css. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!