Preface
In the past few days, I finally completed a three-month demo version project of the company. During this period, I had countless arguments with the company's backend about the API.' There is no problem with my interface, but the way you requested is wrong! ', 'The parameters you requested must be wrong'... Problems like these have persisted throughout the past three months, just because we don't have good interface management habits, a bunch of trouble-free tools have not been used, and the interface definition is very random. Basically conveyed verbally. Therefore, I think the YApi interface management platform must be used first. Furthermore, Zhang Xinxu is also calling for interface management, and the front-end should also use the tools. Liberate productivity and improve efficiency!
Installing node
Because the installation of Yapi must rely on node, Google the various methods of installing node in the centos environment, and there are thousands of them. But I still stepped on a trap. I don’t know why my method of installing the source code based on wget failed. Of course, it was not a complete failure. It was when I waited too long during make, so I directly ctrl c. It’s better to use nvm to install it, although I don’t know if it is reasonable. Please speak with the code:
-
Wget download and install nvm
wget -qO- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/creationix/nvm/v0.33.8/install.sh | bash
Copy after loginor Curl
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/creationix/nvm/v0.33.11/install.sh | bash
Copy after login -
Join the system environment after the download is complete
source ~/.bashrc
Copy after login -
Verify installation
command -v nvm
Copy after login -
View remote node version
nvm ls-remote
Copy after login -
Install the required version required nodejs ( 7.6)
nvm install 10.2.1
Copy after login
Install mongdb
Yapi relies on mongodb (2.6, theoretically you can configure remote mlab, install centos mongdb here, the premise is to ensure that centos is 64 bit.
There are thousands of similar installation methods. Here, use yum to install
-
Modify the yum package management configuration
vi /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-3.4.repo // 会自动新建mongodb-org-3.4.repo文件
Copy after login -
Copy The following configuration information:
[mongodb-org-3.4] name=MongoDB Repository baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/$releasever/mongodb-org/3.4/x86_64/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1
Copy after login -
Install mongodb
yum install -y mongodb-org // 一路yes安装mongodb
Copy after login -
Modify mongdb configuration (public network accessible: 127.0.0.1 => 0.0.0.0 )
vi /etc/mongod.conf
Copy after login -
Start mongodb
systemctl start mongod.service // 启动mongodb
Copy after login
If it is an Alibaba Cloud server, add port 12071 to the security group to access it through the public address. Of course it is not safe at this time
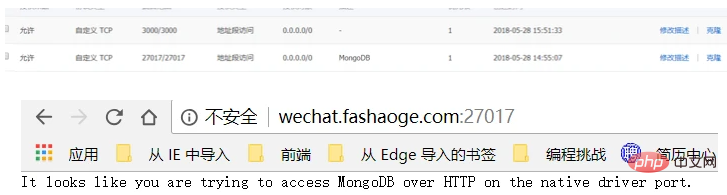
Anyone can tamper with your data by connecting to your mongdb data. Try adding verification at this time. There are thousands of methods here, please google by yourself, for example:
mongo --port 27017
use admin
db.createUser(
{
user: "adminUser",
pwd: "adminPass",
roles: [ { role: "userAdminAnyDatabase", db: "admin" } ]
}
)## Deploy yapi
According to the official documentation, there are two deployment methods. In view of the fact that I used the first one on my computer a few days ago The first method failed to install, so I used the second more complicated method
mkdir yapi
cd yapi
git clone https://github.com/YMFE/yapi.git vendors //或者下载 zip 包解压到 vendors 目录
cp vendors/config_example.json ./config.json //复制完成后请修改相关配置
cd vendors
npm install --production --registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org
npm run install-server //安装程序会初始化数据库索引和管理员账号,管理员账号名可在 config.json 配置
node server/app.js //启动服务器后,请访问 127.0.0.1:{config.json配置的端口},初次运行会有个编译的过程,请耐心等候At this time, it was only temporarily deployed successfully, and the yapi process must be permanently guarded. pm2 is used here
-
Install pm2
npm i pm2 -g
Copy after login -
Switch to the vendors directory of yapi and execute pm2 start
pm2 start server/app.js --watch
Copy after login
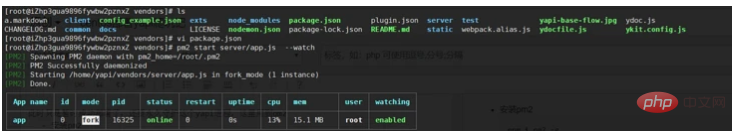
正常的话,应该能正常访问到,默认接口是3000
Summary
At this point, you have cloned the source code of yapi to your own intranet. Of course, you will still encounter a lot of pitfalls during the process. I The main pitfalls encountered are mongdb authentication pitfalls: such as unsuccessful authentication settings, incorrect config file configuration, and even pm2 failure to start Yapi. In short, try more and take more hands-on work. If you really can't solve it yourself, then ask the experts for advice.
① Failed to obtain mongdb authentication
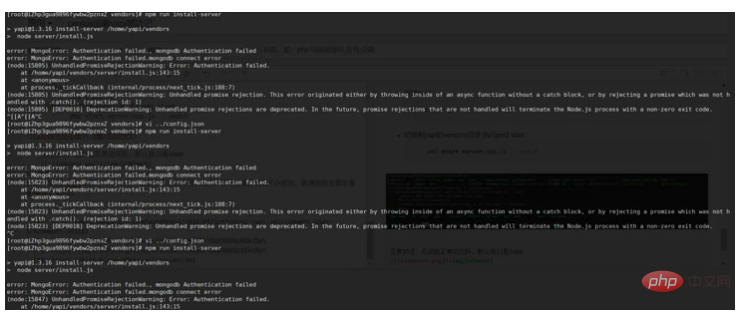
Solution: Check whether the mongdb configuration is correct, whether the authentication setting is successful, and whether the yapi config file is configured correctly
② PM2 failed to start yapi and kept restarting
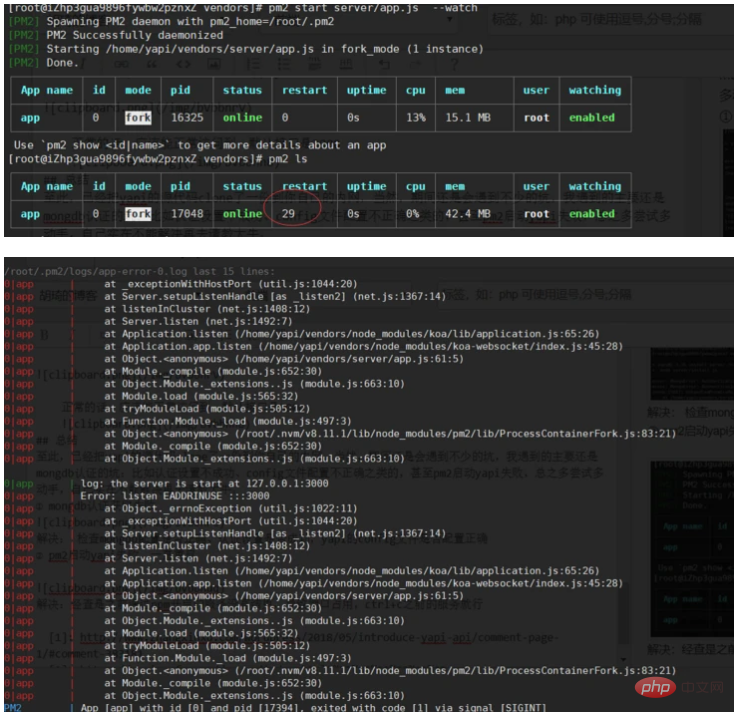
Solution: Use pm2 log to check that the service previously started through npm has not ended, resulting in port occupation. Just use the service before ctrl c
The first two problems don’t seem to be pitfalls, they are just roadblocks
③The configured mailbox fails
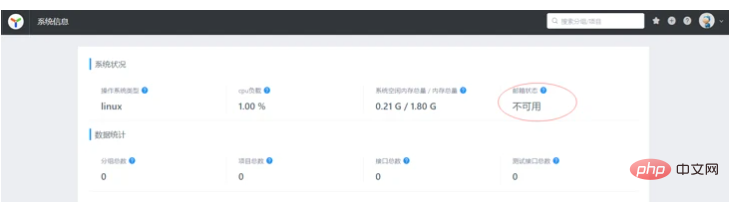
Solution: It must be that the mailbox configuration is incorrect. , come back! Then I continued to mine
I wasn’t sure if there was something wrong with the NetEase mailbox or something. Just change it to QQ. After modifying the config.json file, I thought everything would be fine if I re-npm run install-server. In fact-->
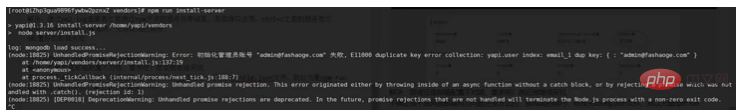
It should be that the administrator's information already exists in yapi in mongdb. If there is no data under admin, just delete it directly. If there is any, just modify the data. I was very lazy, so I just used mongdb compass to delete the entire Yapi. I deleted the database and ran away!
不足之处欢迎拍砖指正!
yapi开启https访问
虽然对小白来说https然并卵,我还是想捣鼓一下试着通过https来访问我的yapi,首先证书我是有了,获取证书的方法也有千千万万种,我这里用的阿里云的免费证书,总之有证书的话应该能拿到证书文件如.pem、.key、.pfx之类文件。技术菜的我天真的以为还能开启3000端口的https访问,结果啪啪啪打脸打的很清脆,于是乎把https的端口设定成了8443。大概步骤如下:
- 获取证书文件(默认有证书并且能拿到.key和.pem文件或者.pfx文件)

- 上传证书(我直接放在app.js同级,根据个人喜好)

-
修改app.js 是基于koa的 不过我没有再引用koa-ssl,直接用的node的https方法的第一种
// 引入相关的服务和文件 const fs = require('fs'); const https = require('https'); const options = { key: fs.readFileSync(__dirname + '/server.key'), cert: fs.readFileSync(__dirname + '/server.pem') }; const port = 8443; //... //开启https端口 https.createServer(options, app.callback()).listen(port)Copy after login - 成功开启https

-
同样还是踩了不少坑
- 文件径不对 not such file
解决:用__dirname - mac verify failure
解决: 用node https提供的第一种方法引入证书文件
- 文件径不对 not such file