What are the sorting methods in C language?
C language sorting methods include: 1. Simple selection sort, a sorting algorithm based on O(n2) time complexity; 2. Bubble sort; 3. Simple insertion sort; 4. Hill sort; 5. Merge sort, a sorting algorithm based on merge operations; 6. Quick sort, a type of divide and conquer method; 7. Heap sort, etc.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, C 17 version, Dell G3 computer.
1. Selection sort-simple selection sort
Selection sort is the simplest sorting algorithm based on O(n2) time complexity. The basic idea is to start from i=0 position to i=n-1 finds the minimum (largest) value from position i to position n-1 through the inner loop each time.
Algorithm implementation:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
|
As shown in the implementation, the complexity of simple selection sorting is fixed at O(n2), and each inner loop finds out whether The minimum value in the sorted sequence is then exchanged with the current data. Since selection sort sorts by finding the maximum value, the number of loops is almost fixed. An optimization method is to find the maximum and minimum values at the same time each loop. This can reduce the number of loops to (n/2), just add in the loop. In order to record the maximum value, the principle is the same, and this article will no longer implement this method.
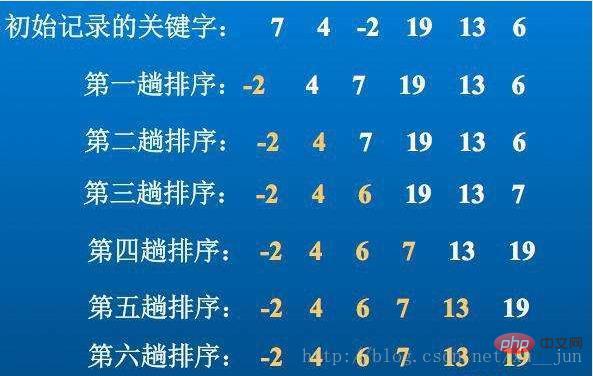
2. Bubble sorting
Bubble sorting In a group of arrays that need to be sorted, when the order of pairs of data is opposite to the required order, the data is exchanged so that the larger data is moved back , each sorting operation puts the largest number in the last position, as follows:
Algorithm implementation:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
|
The above is the simplest implementation method, what needs to be paid attention to may be the boundary problem of i, j. This method fixes the number of cycles and can definitely solve various situations. However, the purpose of the algorithm is to improve efficiency. According to the process diagram of bubble sorting, it can be seen that this algorithm at least Optimization can be made from two points:
1) For the outer loop, if the current sequence is already in order, that is, no exchange will be performed, the next loop should be jumped out directly.
2) When the maximum value after the inner loop is already in order, the loop should no longer be performed.
Optimized code implementation:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
|
As above, when nflag is 0, it means that no exchange has occurred in this cycle, the sequence is in order and there is no need to cycle again. If nflag>0, the last time is recorded At the position where the exchange occurs, the sequences after this position are all in order, and the cycle will not proceed further.
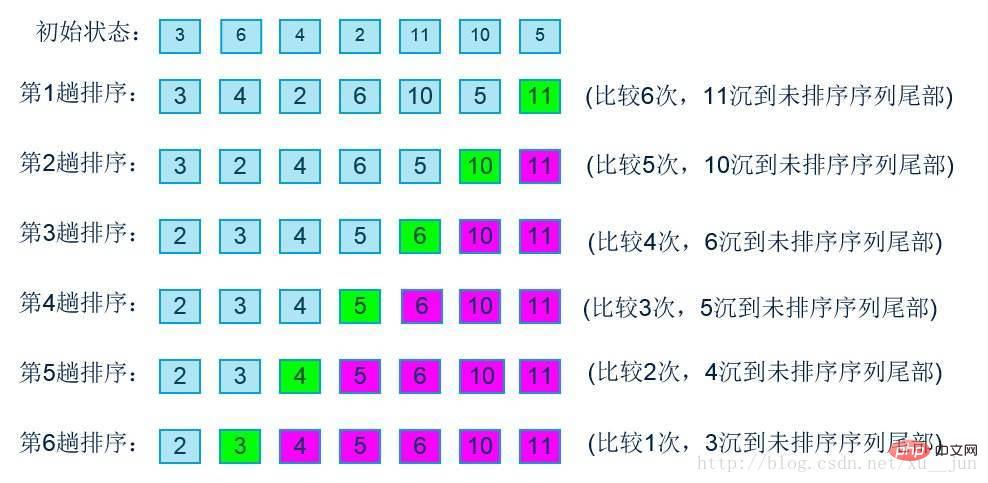
3. Insertion sort - simple insertion sort
Insertion sort is to insert a record into an already ordered sequence and obtain an ordered sequence of new elements plus one. The first element is regarded as an ordered sequence. Starting from the second element, a complete ordered sequence is obtained by inserting one by one. The insertion process is as follows:
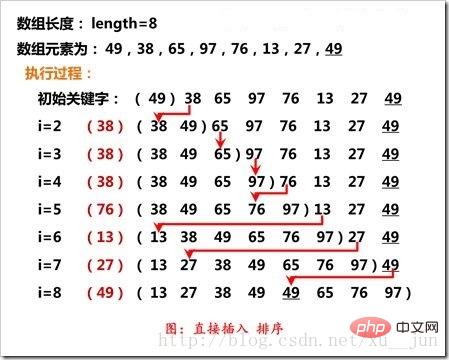
As shown in the figure, Insertion sorting compares the i-th element with the adjacent previous element. If the sort order is reversed, it swaps positions with the previous element and loops until the appropriate position is reached.
Algorithm implementation:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
|
As mentioned above, selection sorting is always a fixed O(n2) algorithm under any circumstances. Although the insertion algorithm is also an O(n2) algorithm, It can be seen that when it is already ordered, the insertion can jump out of the loop directly. In extreme cases (completely ordered) insertion sort can be an O(n) algorithm. However, in the actual completely out-of-order test cases, compared with the selection sort in this article, it is found that the running time of insertion sort is longer than that of selection sort in the case of the same sequence. This is because each outer loop of selection sort only matches the selected most Values are exchanged, while insertion sorting requires constant exchange with adjacent elements to find the appropriate position. The three assignment operations of the exchange also affect the running time, so this point is optimized below:
After optimization:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
|
The optimized code caches the value that needs to be inserted, moves the element after the insertion position backward by one, and changes the three assignments of the exchange to one assignment to reduce the execution time.
4. Insertion sort-Hill sort
The basic idea of Hill sort is to first take an integer d1 less than n as the first increment and group all elements. All records whose distance is a multiple of d1 are placed in the same group. First perform direct insertion sorting within each group; then, take the second increment d2 < d1 and repeat the above grouping and sorting until the increment taken = 1 ( < ...< d2 < d1), that is Until all records are placed in the same group for direct insertion sorting, Hill sorting mainly improves insertion sorting based on the following two properties of insertion sorting:
1) Insertion sorting is performed on almost already sorted records. When operating data, the efficiency is high, that is, the efficiency of linear sorting can be achieved.
2)但插入排序一般来说是低效的,因为插入排序每次只能将数据移动一位
排序过程如下:
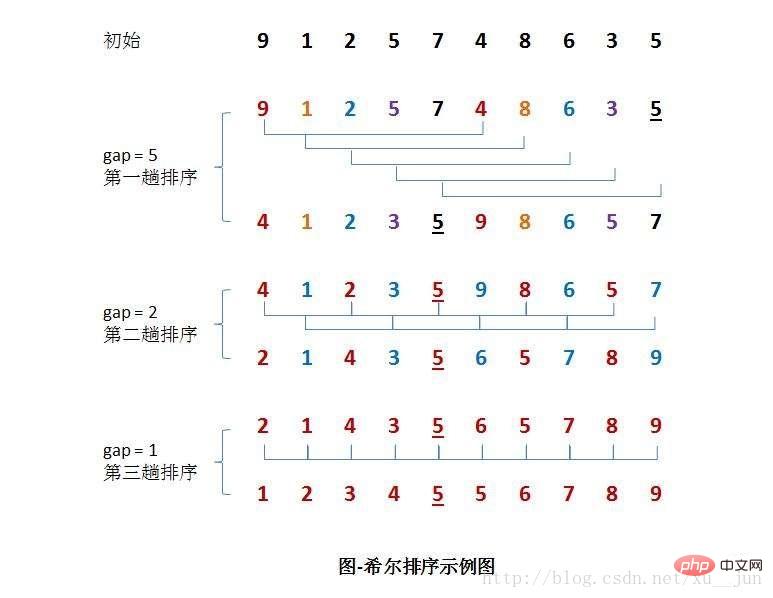
算法实现:基于一种简单的增量分组方式{n/2,n/4,n/8……,1}
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
|
5.归并排序
归并排序是基于归并操作的一种排序算法,归并操作的原理就是将一组有序的子序列合并成一个完整的有序序列,即首先需要把一个序列分成多个有序的子序列,通过分解到每个子序列只有一个元素时,每个子序列都是有序的,在通过归并各个子序列得到一个完整的序列。
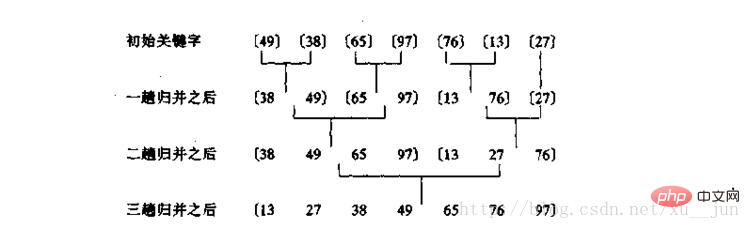
合并过程:
把序列中每个单独元素看作一个有序序列,每两个单独序列归并为一个具有两个元素的有序序列,每两个有两个元素的序列归并为一个四个元素的序列依次类推。两个序列归并为一个序列的方式:因为两个子序列都是有序的(假设由小到大),所有每个子序列最左边都是序列中最小的值,整个序列最小值只需要比较两个序列最左边的值,所以归并的过程不停取子序列最左边值中的最小值放到新的序列中,两个子序列值取完后就得到一个有序的完整序列。
归并的算法实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
|
归并的迭代算法:
迭代算法如上面所说,从单个元素开始合并,子序列长度不停增加直到得到一个长度为n的完整序列。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 |
|
另一种是通过递归的方式,递归方式可以理解为至顶向下的操作,即先将完整序列不停分解为子序列,然后在将子序列归并为完整序列。
递归算法实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
|
对于归并算法大家可以考虑到由于子序列都是有序的,所有如果左边序列的最大值都比右边序列的最小值小,那么整个序列就是有序的,不需要进行merge操作,因此可以在每次merge操作加一个if(arr[mid] > arr[mid+1])判断进行优化,这种优化对于近乎有序的序列非常有效果,不过对于一般的情况会有一次判断的额外开销,可以根据具体情况处理。
6.快速排序
快速排序跟归并排序类似属于分治法的一种,基本思想是通过一趟排序将要排序的数据分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分的所有数据都比另外一部分的所有数据都要小,然后再按此方法对这两部分数据分别进行快速排序,整个排序过程可以递归进行,以此达到整个数据变成有序序列。
排序过程如图:
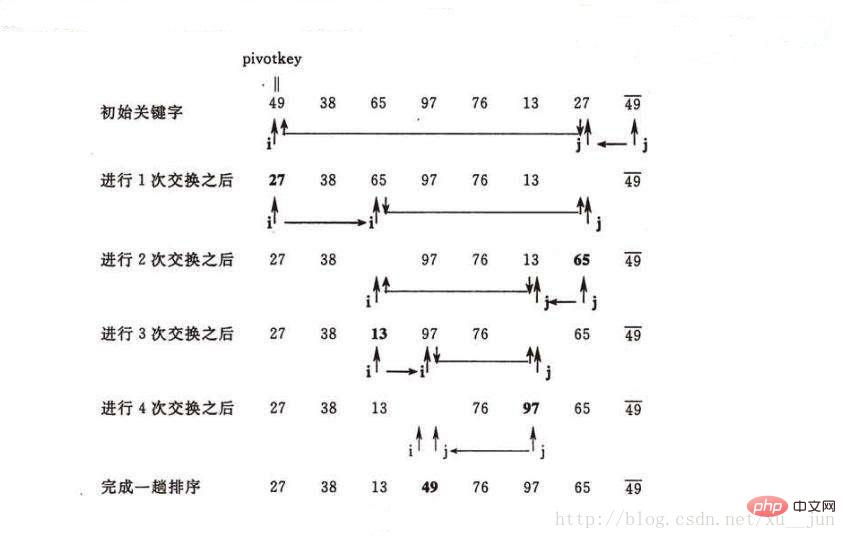
因此,快速排序每次排序将一个序列分为两部分,左边部分都小于等于右边部分,然后在递归对左右两部分进行快速排序直到每部分元素个数为1时则整个序列都是有序的,因此快速排序主要问题在怎样将一个序列分成两部分,其中一部分所有元素都小于另一部分,对于这一块操作我们叫做partition,原理是先选取序列中的一个元素做参考量,比它小的都放在序列左边,比它大的都放在序列右边。
算法实现:
快速排序-单路快排:
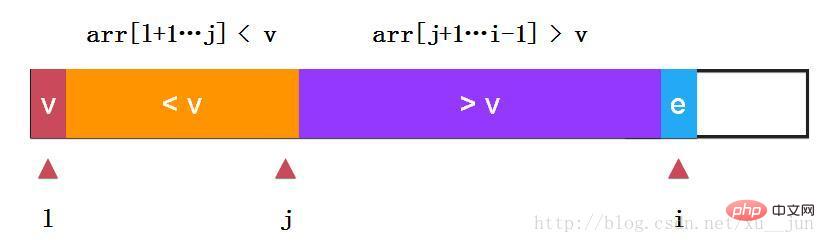
如上:我们选取第一个元素v作为参考量及arr[l],定义j变量为两部分分割哨兵,变量i从l+1开始遍历每个变量,如果当前变量e > v则i++检测下一个元素,如果当前变量e < v 则e与arr[j+1]交换,可以看到arr[j+1]由交换前大于v变成小于v arr[i]变成大于v,同时对i++,j++,始终保持:arr[l+1….j] < v, arr[j+1….i-1] > v
代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
|
因为有变量i从左到右依次遍历序列元素,所有这种方式叫单路快排,不过细心的同学可以发现我们忽略了考虑e等于v的情况,这种快排方式一大缺点就是对于高重复率的序列即大量e等于v的情况会退化为O(n2)算法,原因在大量e等于v的情况划分情况会如下图两种情况:
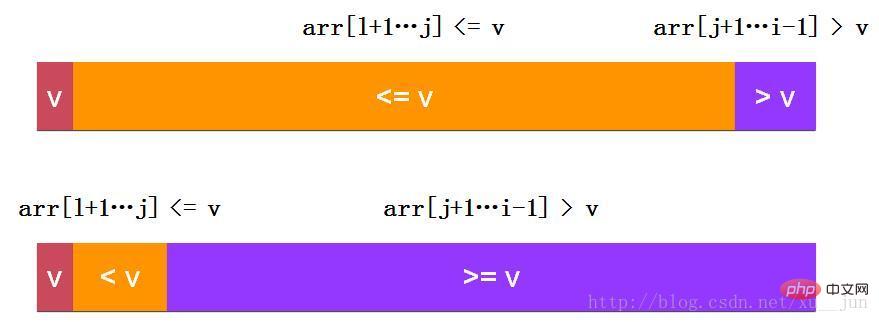 解决这种问题的一另种方法:
解决这种问题的一另种方法:
快速排序-两路快排:
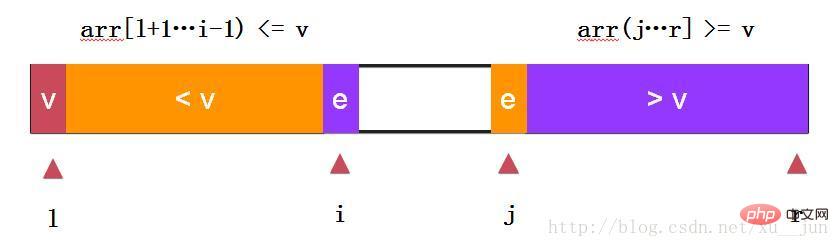
两路快排通过i和j同时向中间遍历元素,e==v的元素分布在左右两个部分,不至于在多重复元素时划分严重失衡。依旧去第一个元素arr[l]为参考量,始终保持arr[l+1….i) <= arr[l], arr(j…r] >=arr[l]原则.
代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
|
针对重复元素比较多的情况还有一种实现方式:
快速排序-三路快排:
三路快排是在两路快排的基础上对e==v的情况做单独的处理,对于重复元素非常多的情况优势很大:
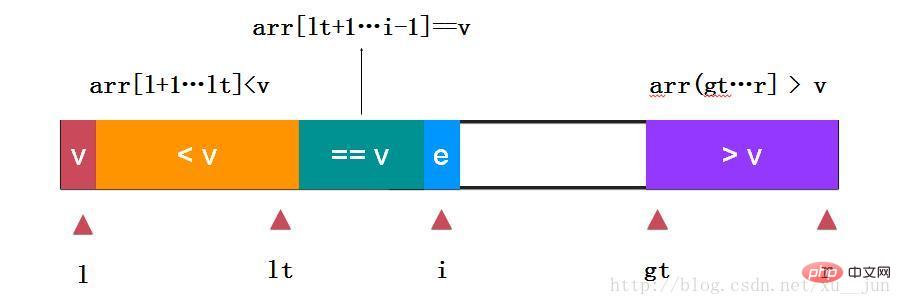
如上:取arr[l]为参考量,定义变量lt为小于v和等于v的分割点,变量i为遍历指针,gt为大于v和未遍历元素分割点,gt指向未遍历元素,边界条件跟个人定义有关本文始终保持arr[l+1…lt] < v,arr[lt+1….i-1],arr(gt…..r]>v的状态。
代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 |
|
三路快排在重复率比较高的情况下比前两种有较大优势,但就完全随机情况略差于两路快排,可以根据具体情况进行合理选择,另外本文在选取参考值时为了方便一直选择第一个元素为参考值,这种方式对于近乎有序的序列算法会退化到O(n2),因此一般选取参考值可以随机选择参考值或者其他选择参考值的方法然后再与arr[l]交换,依旧可以使用相同的算法。
7.堆排序
堆其实一种树形结构,以二叉堆为例,是一颗完全二叉树(即除最后一层外每个节点都有两个子节点,且非满的二叉树叶节点都在最后一层的左边位置),二叉树满足每个节点都大于等于他的子节点(大顶堆)或者每个节点都小于等于他的子节点(小顶堆),根据堆的定义可以得到堆满足顶点一定是整个序列的最大值(大顶堆)或者最小值(小顶堆)。如下图:
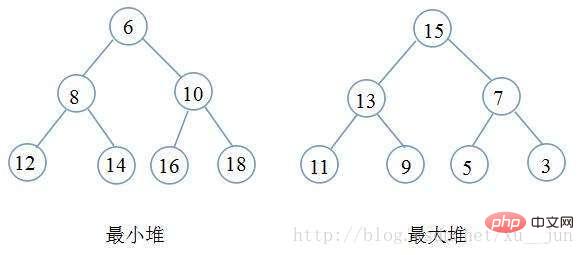
堆排序就是一种基于堆得选择排序,先将需要排序的序列构建成堆,在每次选取堆顶点的最大值和最小值知道完成整个堆的遍历。
用数组表示堆:
二叉堆作为树的一种,通常用结构体表示,为了排序的方便,我们通常使用数组来表示堆,如下图:
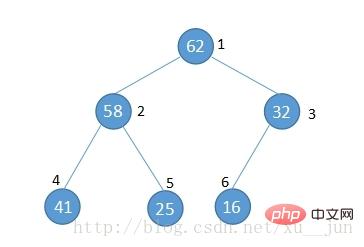
将一个堆按图中的方式按层编号可以得到如下结论:
1)节点的父节点编号满足parent(i) = i/2
2)节点的左孩子编号满足 left child (i) = 2*i
3)节点右孩子满足 right child (i) = 2*i + 1
由于数组编号是从0开始对上面结论修改得到:
parent(i) = (i-1)/2
left child (i) = 2*i + 1
right child (i) = 2*i + 2
堆的两种操作方式:
根据堆的主要性质(父节点大于两个子节点或者小于两个子节点),可以得到堆的两种主要操作方式,以大顶堆为例:
a)如果子节点大于父节点将子节点上移(shift up)
b)如果父节点小于两个子节点中的最大值则父节点下移(shift down)
shift up:
如果往已经建好的堆中添加一个元素,如下图,此时不再满足堆的性质,堆遭到破坏,就需要执行shift up 操作将添加的元素上移调整直到满足堆的性质。
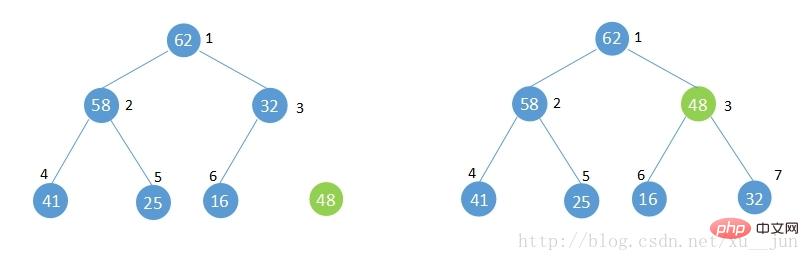
调整堆的方法:
1)7号位新增元素48与其父节点[i/2]=3比较大于父节点的32不满足堆性质,将其与父节点交换。
2)此时新增元素在3号位,再与3号位父节点[i/2]=1比较,小于1号位的62满足堆性质,不再交换,如果此步骤依旧不满足堆性质则重复1步骤直到满足堆的性质或者到根节点。
3)堆调整完成。
代码实现:
代码中基于数组实现,数组下表从0开始,父子节点关系如用数组表示堆
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
|
shift down:
与shift up相反,如果从一个建好的堆中删除一个元素,此时不再满足堆的性质,此时应该怎样来调整堆呢? 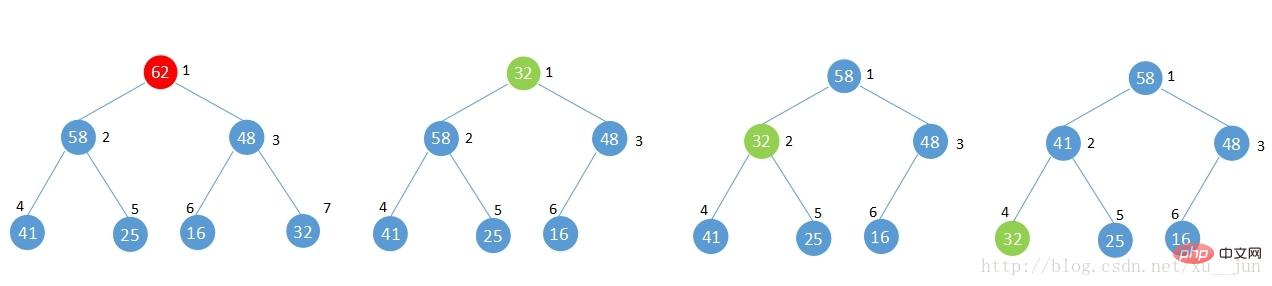
如上图,将堆中根节点元素62删除调整堆的步骤为:
1)将最后一个元素移到删除节点的位置
2)与删除节点两个子节点中较大的子节点比较,如果节点小于较大的子节点,与子节点交换,否则满足堆性质,完成调整。
3)重复步骤2,直到满足堆性质或者已经为叶节点。
4)完成堆调整
代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
|
知道了上面两种堆的操作后,堆排序的过程就非常简单了
1)首先将待排序序列建成堆,由于最后一层即叶节点没有子节点所以可以看成满足堆性质的节点,第一个可能出现不满足堆性质的节点在第一个父节点的位置,假设最后一个叶子节点为(n - 1) 则第一个父节点位置为(n-1-1)/2,只需要依次对第一个父节点之前的节点执行shift down操作到根节点后建堆完成。
2)建堆完成后(以大顶堆为例)第一个元素arr[0]必定为序列中最大值,将最大值提取出来(与数组最后一个元素交换),此时堆不再满足堆性质,再对根节点进行shift down操作,依次循环直到根节点,排序完成。
代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 |
|
推荐教程:《C#》
The above is the detailed content of What are the sorting methods in C language?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to use various symbols in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 04:48 PM
How to use various symbols in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 04:48 PM
The usage methods of symbols in C language cover arithmetic, assignment, conditions, logic, bit operators, etc. Arithmetic operators are used for basic mathematical operations, assignment operators are used for assignment and addition, subtraction, multiplication and division assignment, condition operators are used for different operations according to conditions, logical operators are used for logical operations, bit operators are used for bit-level operations, and special constants are used to represent null pointers, end-of-file markers, and non-numeric values.
 What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
In C, the char type is used in strings: 1. Store a single character; 2. Use an array to represent a string and end with a null terminator; 3. Operate through a string operation function; 4. Read or output a string from the keyboard.
 How to handle special characters in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to handle special characters in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
In C language, special characters are processed through escape sequences, such as: \n represents line breaks. \t means tab character. Use escape sequences or character constants to represent special characters, such as char c = '\n'. Note that the backslash needs to be escaped twice. Different platforms and compilers may have different escape sequences, please consult the documentation.
 The difference between char and wchar_t in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
The difference between char and wchar_t in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
In C language, the main difference between char and wchar_t is character encoding: char uses ASCII or extends ASCII, wchar_t uses Unicode; char takes up 1-2 bytes, wchar_t takes up 2-4 bytes; char is suitable for English text, wchar_t is suitable for multilingual text; char is widely supported, wchar_t depends on whether the compiler and operating system support Unicode; char is limited in character range, wchar_t has a larger character range, and special functions are used for arithmetic operations.
 The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous c#
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
The difference between multithreading and asynchronous is that multithreading executes multiple threads at the same time, while asynchronously performs operations without blocking the current thread. Multithreading is used for compute-intensive tasks, while asynchronously is used for user interaction. The advantage of multi-threading is to improve computing performance, while the advantage of asynchronous is to not block UI threads. Choosing multithreading or asynchronous depends on the nature of the task: Computation-intensive tasks use multithreading, tasks that interact with external resources and need to keep UI responsiveness use asynchronous.
 How to convert char in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
How to convert char in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:21 PM
In C language, char type conversion can be directly converted to another type by: casting: using casting characters. Automatic type conversion: When one type of data can accommodate another type of value, the compiler automatically converts it.
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 How to use char array in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:24 PM
How to use char array in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:24 PM
The char array stores character sequences in C language and is declared as char array_name[size]. The access element is passed through the subscript operator, and the element ends with the null terminator '\0', which represents the end point of the string. The C language provides a variety of string manipulation functions, such as strlen(), strcpy(), strcat() and strcmp().




