Five front-end tips that make people shine
In order to make programming easier for everyone, this book selects some useful but relatively rare and useful techniques. Without further ado, let’s drive.

1. Quick Hide
To hide a DOM element, no JavaScript is required. A native HTML attribute is enough to hide. The effect is similar to adding a style display: none;.
<p hidden>该段落在页面上是不可见的,它对HTML是隐藏的。</p>
However, this trick does not work on pseudo-elements.
2. Quick positioning
Are you familiar with the `inset` CSS property? It is the abbreviated version of `top`, `left`, `right` and `bottom`. Similar to the shorthand `margin` and `padding`, we can set all offsets of an element in a row.
// Before
div {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
}
// After
div {
position: absolute;
inset: 0;
}3. Front-end network speed test
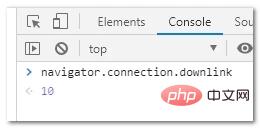
Chrome browser provides the original API navigator.connection.downlink to access the user’s current network environment network bandwidth.
navigator.connection.downlink;
connection.downlink does not return the network transmission speed displayed in the user's current environment, but the bandwidth of the current network. The official statement is: Returns the effective transmission speed in units of Mb/s bandwidth, and keep this value to the nearest integer multiple of 25kb/s.
For example, I ran the statement navigator.connection.downlink in my home Chrome browser console, and the result returned was 10, which means the download bandwidth is 10M.
4. Disable pull to refresh
CSS overscroll-behavior attribute allows developers to Overrides the browser's default overflow scrolling behavior when top/bottom. Use cases for this include disabling the "pull to refresh" feature on mobile devices, removing the over-scroll glow and rubber band effects, and preventing page content from scrolling under the modal/overlay
body {
overscroll-behavior-y: contain;
}This property is useful for organizing modals In-window scrolling is also very useful - it prevents the main page from intercepting scrolling when it reaches the boundary.
5. Insertion of text is prohibited
When the user initiates a "paste" operation in the browser user interface, the paste event will be triggered.
Sometime, I want to prohibit users from pasting text copied from somewhere into the input box. This can be easily done by listening to the paste event and calling its method preventDefault().
<input type="text"></input>
<script>
const input = document.querySelector('input');
input.addEventListener("paste", function(e){
e.preventDefault()
})
</script> It is impossible to know the possible bugs in real time after the code is deployed. In order to solve these bugs afterwards, a lot of time was spent on log debugging. By the way, I would like to recommend a useful BUG monitoring tool Fundebug.
Recommended learning: css video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Five front-end tips that make people shine. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools. In today's era of rapid development of the Internet, front-end development has become increasingly important. As users have higher and higher requirements for the experience of websites and applications, front-end developers need to use more efficient and flexible tools to create responsive and interactive interfaces. As two important technologies in the field of front-end development, PHP and Vue.js can be regarded as perfect tools when paired together. This article will explore the combination of PHP and Vue, as well as detailed code examples to help readers better understand and apply these two
 Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
In front-end development interviews, common questions cover a wide range of topics, including HTML/CSS basics, JavaScript basics, frameworks and libraries, project experience, algorithms and data structures, performance optimization, cross-domain requests, front-end engineering, design patterns, and new technologies and trends. . Interviewer questions are designed to assess the candidate's technical skills, project experience, and understanding of industry trends. Therefore, candidates should be fully prepared in these areas to demonstrate their abilities and expertise.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 Is Django front-end or back-end? check it out!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:37 AM
Is Django front-end or back-end? check it out!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:37 AM
Django is a web application framework written in Python that emphasizes rapid development and clean methods. Although Django is a web framework, to answer the question whether Django is a front-end or a back-end, you need to have a deep understanding of the concepts of front-end and back-end. The front end refers to the interface that users directly interact with, and the back end refers to server-side programs. They interact with data through the HTTP protocol. When the front-end and back-end are separated, the front-end and back-end programs can be developed independently to implement business logic and interactive effects respectively, and data exchange.
 What is a front-end modular ESM?
Feb 25, 2024 am 11:48 AM
What is a front-end modular ESM?
Feb 25, 2024 am 11:48 AM
What is front-end ESM? Specific code examples are required. In front-end development, ESM refers to ECMAScriptModules, a modular development method based on the ECMAScript specification. ESM brings many benefits, such as better code organization, isolation between modules, and reusability. This article will introduce the basic concepts and usage of ESM and provide some specific code examples. The basic concept of ESM In ESM, we can divide the code into multiple modules, and each module exposes some interfaces for other modules to
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service






