Get the container instance in the code (Laravel)
This article is written by the tutorial column of laravel to introduce how to obtain the container instance in the code. I hope it will be helpful to friends in need!
The laravel container instance is unique throughout the request life cycle and manages all service component instances. So what are the ways to get an instance of the laravel container? The following methods are commonly used:
1) Through the help function of app:
$app = app();
The auxiliary function of app is defined in

In the file, this file defines many help functions and will be automatically loaded into the project through composer. Therefore, the functions can be accessed from any code location involved in http request processing, such as app().
2) Through the App Facade
<?php
Route::get('/', function () {
dd(App::basePath());
return '';
});The way to get the container instance through the App Facade is different from the above. You cannot assign the App to a variable first and then call the container through the variable. Methods. This is because App is just a class name, and we cannot copy a class name into a variable. $app = App; is not a legal executable statement, but $app = app(); is a legal executable statement, because it is followed by app(), which represents a function call. App::basePath(); is also a legal statement, it is calling the static method of the class.
Add two more points:
The first point: Facade is a special feature in the laravel framework. Each Facade will be associated with an instance object in the container. We can directly pass the Facade A class static method call is used to invoke methods on its associated instance object. For example, the Facade of App, when calling App::basePath(), is actually equivalent to app()->basePath().
This underlying mechanism also depends on the characteristics of the PHP language. It needs to set a static member in each Facade and associate it with an instance object of the service. When calling the static method of the Facade class , parse out the called method name, then call the method of the same name of the associated service instance, and finally return the result.
I think it is enough to understand what role Facade can play. It is not necessary to delve into its bottom layer to understand the implementation details. After all, in actual development, Facade is not used and it does not affect the use of the laravel framework at all. . In addition, in actual coding, it is very easy to customize a Facade. Just inherit the Facade base class encapsulated by laravel:
<?php
namespace ThirdProviders\CasServer\Facades;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Facade;
use ThirdProviders\CasServer\CasServerManager;
class CasServer extends Facade
{
protected static function getFacadeAccessor()
{
return CasServerManager::class;
}
}Implement the getFacadeAccessor method of the Facade base class, and the laravel framework will know what this Facade class should be like Which service instance is associated. In fact, the name returned by this getFacadeAccess method is the service binding name to be introduced later. In the laravel container, a service instance will have a fixed binding name, and the instance can be found through this name. So why the Facade class only needs to return the service binding name.
We can look at the code of the App Facade class:
<?php
namespace Illuminate\Support\Facades;
/**
* @see \Illuminate\Foundation\Application
*/
class App extends Facade
{
/**
* Get the registered name of the component.
*
* @return string
*/
protected static function getFacadeAccessor()
{
return 'app';
}
}Its getFacadeAccessor returns a string "app", which is the name used by the laravel container to bind itself. .
Second point: From the source code of the App Facade in the previous point, we can see that the full class name of the App Facade is actually: Illuminate\Support\Facades\App, so why can we pass it directly in the code? App can be accessed by the short name:
<?php
Route::get('/', function () {
dd(App::basePath());
return '';
});You see that the above code does not use use or fully qualified way to use Illuminate\Support\Facades\App. In fact, App is completely equivalent to Illuminate\Support\Facades\App, except that App is much shorter than Illuminate\Support\Facades\App and does not require use, so it is convenient to use. So how is it implemented? This is related to the alias configured in the laravel container. In config/app.php,
has a section of aliases specifically used to configure some types of aliases:
'aliases' => [
'App' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\App::class,
'Artisan' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Artisan::class,
'Auth' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Auth::class,
'Blade' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Blade::class,
'Bus' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Bus::class,
'Cache' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache::class,
'Config' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Config::class,
'Cookie' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cookie::class,
'Crypt' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Crypt::class,
'DB' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB::class,
'Eloquent' => Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model::class,
'Event' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Event::class,
'File' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\File::class,
'Gate' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Gate::class,
'Hash' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Hash::class,
'Lang' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Lang::class,
'Log' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Log::class,
'Mail' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Mail::class,
'Notification' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Notification::class,
'Password' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Password::class,
'Queue' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Queue::class,
'Redirect' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Redirect::class,
'Redis' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Redis::class,
'Request' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Request::class,
'Response' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Response::class,
'Route' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route::class,
'Schema' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema::class,
'Session' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Session::class,
'Storage' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Storage::class,
'URL' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\URL::class,
'Validator' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\Validator::class,
'View' => Illuminate\Support\Facades\View::class
],Then the request is processed in the laravel framework During the process, these aliases will be registered into the global environment through the Illuminate\Foundation\Bootstrap\RegisterFacades class:
<?php
namespace Illuminate\Foundation\Bootstrap;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Facade;
use Illuminate\Foundation\AliasLoader;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Foundation\Application;
class RegisterFacades
{
/**
* Bootstrap the given application.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Contracts\Foundation\Application $app
* @return void
*/
public function bootstrap(Application $app)
{
Facade::clearResolvedInstances();
Facade::setFacadeApplication($app);
AliasLoader::getInstance($app->make('config')->get('app.aliases', []))->register();
}
}So we can directly use aliases instead of the complete type name to perform the same access function. If you have written some classes yourself with long names and are used a lot in the code, you can also consider configuring them in the config/app.php alias, and laravel will register them for us.
3) Another way to get the laravel container instance is to use $this->app
directly in the service provider. The service provider will be introduced later, but it is just introduced now. Because service provider classes are instantiated by the laravel container, these classes inherit from Illuminate\Support\ServiceProvider, which defines an instance attribute $app
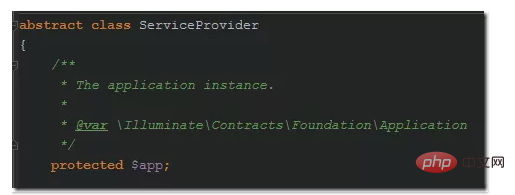
laravel in When instantiating the service provider, the laravel container instance will be injected into the $app. So in the service provider, we can always access the laravel container instance through $this->$app, without using the app() function or App Facade.
For more laravel technical articles, please visit the laravel tutorial column!
The above is the detailed content of Get the container instance in the code (Laravel). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Laravel - Artisan Commands
Aug 27, 2024 am 10:51 AM
Laravel - Artisan Commands
Aug 27, 2024 am 10:51 AM
Laravel - Artisan Commands - Laravel 5.7 comes with new way of treating and testing new commands. It includes a new feature of testing artisan commands and the demonstration is mentioned below ?
 Laravel - Pagination Customizations
Aug 27, 2024 am 10:51 AM
Laravel - Pagination Customizations
Aug 27, 2024 am 10:51 AM
Laravel - Pagination Customizations - Laravel includes a feature of pagination which helps a user or a developer to include a pagination feature. Laravel paginator is integrated with the query builder and Eloquent ORM. The paginate method automatical
 How to get the return code when email sending fails in Laravel?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:45 PM
How to get the return code when email sending fails in Laravel?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:45 PM
Method for obtaining the return code when Laravel email sending fails. When using Laravel to develop applications, you often encounter situations where you need to send verification codes. And in reality...
 Laravel schedule task is not executed: What should I do if the task is not running after schedule: run command?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
Laravel schedule task is not executed: What should I do if the task is not running after schedule: run command?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
Laravel schedule task run unresponsive troubleshooting When using Laravel's schedule task scheduling, many developers will encounter this problem: schedule:run...
 In Laravel, how to deal with the situation where verification codes are failed to be sent by email?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
In Laravel, how to deal with the situation where verification codes are failed to be sent by email?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
The method of handling Laravel's email failure to send verification code is to use Laravel...
 How to implement the custom table function of clicking to add data in dcat admin?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:09 AM
How to implement the custom table function of clicking to add data in dcat admin?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:09 AM
How to implement the table function of custom click to add data in dcatadmin (laravel-admin) When using dcat...
 Laravel Redis connection sharing: Why does the select method affect other connections?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:45 AM
Laravel Redis connection sharing: Why does the select method affect other connections?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:45 AM
The impact of sharing of Redis connections in Laravel framework and select methods When using Laravel framework and Redis, developers may encounter a problem: through configuration...
 Laravel - Dump Server
Aug 27, 2024 am 10:51 AM
Laravel - Dump Server
Aug 27, 2024 am 10:51 AM
Laravel - Dump Server - Laravel dump server comes with the version of Laravel 5.7. The previous versions do not include any dump server. Dump server will be a development dependency in laravel/laravel composer file.




