 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 What is the CommonJS module specification? A brief analysis of Nodejs module mechanism
What is the CommonJS module specification? A brief analysis of Nodejs module mechanism
What is the CommonJS module specification? A brief analysis of Nodejs module mechanism

NodeThe application is composed of modules. Its module system draws on the CommonJS module specification, but it is not implemented completely in accordance with the specification, but according to Some features have been added for its own needs, which can be regarded as a variant of the CommonJS module specification.
CommonJS Overview
CommonJS is a JavaScript modular specification proposed by the community, which can be said to be The most important milestone in the modularization process of JS, it constructs a beautiful vision-JS can run anywhere, but in fact, because its modules are loaded synchronously, it is only suitable for Other local environments such as the server are not suitable for browsers and other places that need to load resources asynchronously.
In order to enable JS to run anywhere, CommonJS has developed some interface specifications, which cover modules, binaries, Buffer , character set encoding, I/O streams, process environment, file system, socket, unit testing, web server, gateway, package management, etc., although most of them are in the draft stage , but it has deeply affected the development of Node.
The following figure shows the relationship between Node and the browser, W3C, CommonJS and ECMAScript, excerpted from "In-depth introduction to NodeJS"
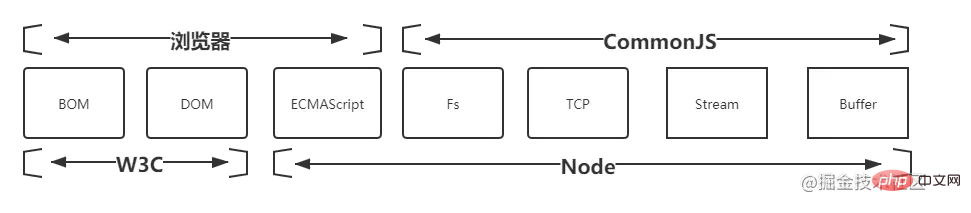
Module specifications of CommonJS
##The modules of CommonJS are mainly composed of modules It consists of three parts: reference , module definition and module identification .
Module identification
The module identification is unique for each module and is the basis for it to be referenced. It must comply with A camelCase named string that is either a relative or absolute path to a file.require('fs')// fs是内建模块,执行时会被直接载入内存,无须路径标识 require('./moduleA')//导入当前目录的moduleA require('../moduleB')// 导入上一个目录的moduleB require('C://moduleC')// 绝对路径导入moduleC
Module reference
Userequire() to reference a module. This method accepts a module identifier as a parameter , thereby introducing a module's API into the current context.
const fs = require('fs')// 引入内建的fs模块
Module definition
There are imports and exports. To export methods or variables in the current context as modules, you need to use built-in Themodule.exports object, which is the only export exported by the module.
CommonJSThe specification stipulates that inside each module, the module variable represents the current module. This variable is an object, and its exports attribute (that is, module.exports) is the external interface. Loading a module actually loads the module.exports attribute of the module.
// moduleA.js模块
let moduleA = {
name:"moduleA"
}
module.exports = {
moduleA
}
// moduleB.js模块
// 导入moduleA
const {moduleA} = require('./moduleA')CommonJSThe characteristics of the module are as follows:
- Each module has an independent context, and the code within the module is executed independently without polluting the global scope. The module can be loaded multiple times, but it will only run when it is loaded for the first time. The running results will be cached. Subsequent loading of the same module will directly read the cached results, and the cache will be stored in
- module. The loading of
modules in cache is executed in code order.
Node’s module implementation
NodeImporting the module requires 3 steps: Path Analysis -> File location -> Compile execution:
- Path analysis: Analyze the module type according to the module identification.
- File location: Find the location of the module based on the module type and module identifier.
- Compile and execute: Compile the file into machine code for execution, which requires a series of transformations.
nodejs Tutorial"]
Module types are divided into built-in modules and user modules:- Built-in module: The built-in module is provided by
Node
and has been compiled into a binary executable file. Whennodeis executed, the built-in module will be loaded directly Memory, so we can introduce it directly, and its loading speed is very fast, because it does not need to go through file location and compilation to perform these2steps. - File module: An extension module written using
js
orCneeds to be compiled into binary machine code first when executed. You need to go through the above three steps.
Module cache
Whether it is a built-in module or a file module,node is in the After a load, the result will be cached. The next time the same module is loaded, it will be searched from the cache first. If it can be found, it will be read directly from the cache. The cached result is the object after the module is compiled and executed, and is all The fastest loading module.
路径分析
路径分析依据的是模块标识符,模块标识符有以下几种类型:
- 内建模块标识,例如
fs,path等,不需要编译,node运行时被直接载入内存等待导入。 - 相对路径模块标识:使用相对路径描述的文件模块
- 绝对路径模块标识:使用绝对路径描述的文件模块
- 自定义模块标识:通常是
node_modules中的包,引入时也不需要写路径描述,node有一套算法来寻找,是所有模块标识中分析速度最慢的。
文件定位
文件定位主要包括文件扩展名分析、目录和包的处理。如果文件定位结束时都没找到任何文件,则会抛出文件查找失败的异常。
文件扩展名分析
由于模块标识可以不添加文件扩展名,因此Node会按.js、.json、.node的次序依次补足扩展名来尝试加载,尝试加载的过程需要调用fs模块同步阻塞式地判断文件是否存在,因此为了提高性能,可以在使用require()导入模块时,参数带上文件扩展名,这样会加快文件定位速度。
目录、包的处理
在分析文件扩展名时,可能得到的是一个目录,此时Node会将其作为一个包处理,用查找包的规则来查找:在当前目录下查找package.json,获得其中定义的main属性指定的文件名,以它来作为查找的入口,如果没有package.json,则默认将目录下的index当前默认文件名,然后依次查找index.js、index.json、index.node。
编译执行
编译和执行是模块导入的最后一个步骤,node会先创建一个Module实例,代表当前模块。它有以下属性:
module.id模块的识别符,通常是带有绝对路径的模块文件名。module.filename模块的文件名,带有绝对路径。module.loaded返回一个布尔值,表示模块是否已经完成加载。module.parent返回一个对象,表示调用该模块的模块。module.children返回一个数组,表示该模块要用到的其他模块。module.exports表示模块对外输出的值。
通过文件定位得到的信息,Node再载入文件并编译。对于不同的文件扩展名,其载入方法也有所不同:
.js文件:通过fs模块同步读取文件后编译执行。.node文件:这是C/C++编写的扩展文件,通过dlopen()方法加载。.json文件:通过fs模块读取后,用JSON.parse()解析返回结果。- 其余扩展名一律当
.js文件载入
每一个载入的模块都会被缓存,可以通过require.cache来查看。
使用ES-Module
目前,在node中使用ES-Module属于实验性功能,从8.5开始支持,执行时需要加上--experimental-modules参数。从12.17.0 LTS开始,去掉了--experimental-modules ,现在可以通过使用.mjs文件代替.js文件或在package.json中指定 type 为 module 两种方式使用。
// package.json
{
"name": "esm-project",
"version": "1.0.0",
"main": "index.js",
"type": "module",
...
}ES-Module相比于CommonJS的Module机制,最大不同是ES-Module对导出模块的变量、对象是动态引用,而且是在编译阶段暴露模块的导入接口,因此可以进行静态分析;而CommonJS-Module是运行时同步加载,且输出的是导出模块的浅拷贝。除此之外,ES-Module支持加载CommonJS-Module,而反过来则不行。
其次,Node 规定 ES6 模块之中不能使用 CommonJS 模块的特有的一些内部变量,这是因为ES-Module顶层this指向undefined,CommonJS模块的顶层this指向当前模块,而这些内部变量作为顶层变量能被直接使用。
CommonJS的内部变量有:
argumentsrequire- ##module
- exports
m - __filename
- __dirname
Summary
Node
The loading of the module is synchronous. Only when the loading is completed can subsequent operations be performed.- Each file is a module and has its own scope. Inside each module, the
module
object represents the current module, and itsexportsattribute serves as the export interface of the current module. - The imported module is a shallow copy of the exported module.
Programming Video! !
The above is the detailed content of What is the CommonJS module specification? A brief analysis of Nodejs module mechanism. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 The difference between nodejs and vuejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:17 AM
The difference between nodejs and vuejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:17 AM
Node.js is a server-side JavaScript runtime, while Vue.js is a client-side JavaScript framework for creating interactive user interfaces. Node.js is used for server-side development, such as back-end service API development and data processing, while Vue.js is used for client-side development, such as single-page applications and responsive user interfaces.
 Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Node.js can be used as a backend framework as it offers features such as high performance, scalability, cross-platform support, rich ecosystem, and ease of development.
 How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
To connect to a MySQL database, you need to follow these steps: Install the mysql2 driver. Use mysql2.createConnection() to create a connection object that contains the host address, port, username, password, and database name. Use connection.query() to perform queries. Finally use connection.end() to end the connection.
 What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
There are two npm-related files in the Node.js installation directory: npm and npm.cmd. The differences are as follows: different extensions: npm is an executable file, and npm.cmd is a command window shortcut. Windows users: npm.cmd can be used from the command prompt, npm can only be run from the command line. Compatibility: npm.cmd is specific to Windows systems, npm is available cross-platform. Usage recommendations: Windows users use npm.cmd, other operating systems use npm.
 What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
The following global variables exist in Node.js: Global object: global Core module: process, console, require Runtime environment variables: __dirname, __filename, __line, __column Constants: undefined, null, NaN, Infinity, -Infinity
 Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
The main differences between Node.js and Java are design and features: Event-driven vs. thread-driven: Node.js is event-driven and Java is thread-driven. Single-threaded vs. multi-threaded: Node.js uses a single-threaded event loop, and Java uses a multi-threaded architecture. Runtime environment: Node.js runs on the V8 JavaScript engine, while Java runs on the JVM. Syntax: Node.js uses JavaScript syntax, while Java uses Java syntax. Purpose: Node.js is suitable for I/O-intensive tasks, while Java is suitable for large enterprise applications.
 Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Yes, Node.js is a backend development language. It is used for back-end development, including handling server-side business logic, managing database connections, and providing APIs.
 How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Server deployment steps for a Node.js project: Prepare the deployment environment: obtain server access, install Node.js, set up a Git repository. Build the application: Use npm run build to generate deployable code and dependencies. Upload code to the server: via Git or File Transfer Protocol. Install dependencies: SSH into the server and use npm install to install application dependencies. Start the application: Use a command such as node index.js to start the application, or use a process manager such as pm2. Configure a reverse proxy (optional): Use a reverse proxy such as Nginx or Apache to route traffic to your application



