Is there any instruction for vuejs?
vuejs has instructions. Vuejs instructions start with "v-". They act on HTML elements. The instructions provide some special features. When the instructions are bound to elements, the instructions will add some special behaviors to the bound target elements. You can Think of directives as special HTML features.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, vue2.9.6 version, DELL G3 computer.
vuejs has instructions.
What are instructions in Vue
Vue.js instructions start with v-, they act on HTML elements, Directives provide some special features. When binding a directive to an element, the directive will add some special behavior to the bound target element. We can think of the directive as a special HTML attribute.
VueJS extends HTML with new attributes called directives.
ViueJS adds functionality to the application through built-in directives.
VueJS allows you to customize directives.
Characteristics of directives
All directives are included in the scope of Vue instance management .
vueJS directives are extended HTML attributes, prefixed with v-.
The v-model directive binds an element value (such as the value of an input field) to the application and stores the value.
vuejs common instructions
Vue.js provides some commonly used built-in instructions. Next we will introduce the following Several built-in commands:
- v-if command
- v-show command
- v-else command
- v-for command
- v-bind instruction
- v-on instruction
v-if instruction
v-if is a conditional rendering instruction , which deletes and inserts elements based on the true or false expression.
Basic syntax:
v-if="expression"
expression is an expression that returns a Boolean value. The expression can be a Boolean attribute. It can also be an expression that returns a Boolean.
<div id="app">
<div v-if="isMale">男士</div>
<div v-if="age>=20">age:{{age}}</div>
</div>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
age:25,
isMale:true,
}
})v-show command
The difference between v-show and v-if.
v-show will render html regardless of whether the condition is true, while v-if will render only if the condition is true.
Let’s look at two screenshots first. The first one is when isMale is true, and the second one is when isMale is true. The picture shows that when isMale is false and the condition is not met, you can see that the html of v-if is not rendered,
and p using v-show only changes its style display: none;

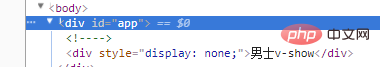
<div id="app">
<div v-if="isMale">男士v-if</div>
<div v-show="isMale">男士v-show</div>
</div>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
isMale:false
}
})v-else directive
The v-else directive is used simultaneously with v-if or v-show, v-if condition If it is not established, the v-else content will be displayed
<div id="app">
<div v-if="isMale">男士</div>
<div v-else>女士</div>
</div>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
isMale:true
}
})v-for instruction
The v-for instruction renders a list based on an array, which is similar to JavaScript's traversal syntax
v-for="item in list"
list is an array, item is the array element currently traversed
v-for="(item,index) in list"where index is the index of the current loop, The subscript starts from 0
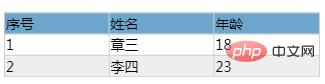
<div id="app">
<table>
<tr class="thead">
<td>序号</td>
<td>姓名</td>
<td>年龄</td>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(item,index) in list">
<td v-text="index+1"></td>
<td v-text="item.name"></td>
<td v-text="item.age"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
list:[{
name:'章三',
age:18
},{
name:'李四',
age:23
}]
}
})v-bind command
v-bind dynamically binds one or more features, You can take a parameter after its name and separate it with a colon. This parameter is usually an attribute of the HTML element. For example, v-bind: class
class can exist at the same time as v-bind:class. , that is to say, if there is a class, adding v-bind:class will not overwrite the original style class, but add a new class name on the original basis
<div id="app">
<img v-bind:src="img" class="logo"
v-bind:class="isLogo?'':'product'"
v-bind:style="{'border':hasBorder?'2px solid red':''}"></img>
</div>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
img:'https://www.baidu.com/img/bd_logo1.png',
isLogo:false,
hasBorder:true
}
})The above v-bind:src can also be used Abbreviated as: src, modify the above code
<div id="app">
<img :src="img" class="logo"
:class="isLogo?'':'product'"
:style="{'border':hasBorder?'2px solid red':''}"></img>
</div>v-on instruction
v-on is used to monitor DOM events. Its usage is similar to v-bind, for example, to button Add click event<button v-on:click="show">
Similarly, like v-bind, v-on can also use the abbreviation, replaced by the @ symbol, Modify the code: <button @click="show">
Let's take a look at an example:

The following is a code that clicks to hide and display p text paragraphs
<div id="app"> <p v-show="isShow">微风轻轻的吹来,带来了一丝丝凉意</p>
<div>
<button type="button" v-on:click="show(1)">显示</button>
<button type="button" v-on:click="show(0)">隐藏</button>
</div>
</div>
var vm = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { isShow:true
}, methods:{ show:function(type){ if(type){ this.isShow = true;
}else{ this.isShow = false;
}
}
}
})Comprehensive example
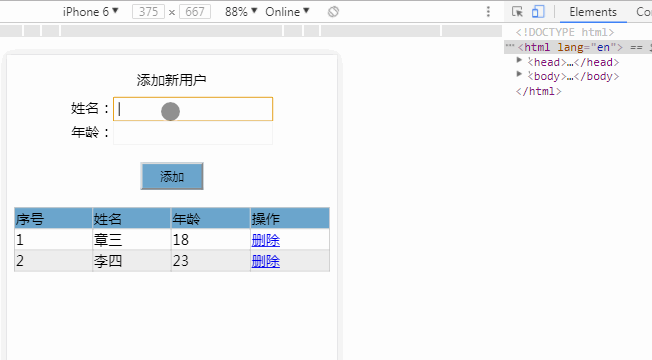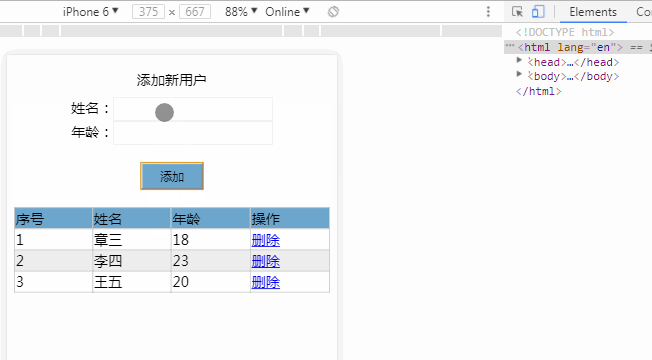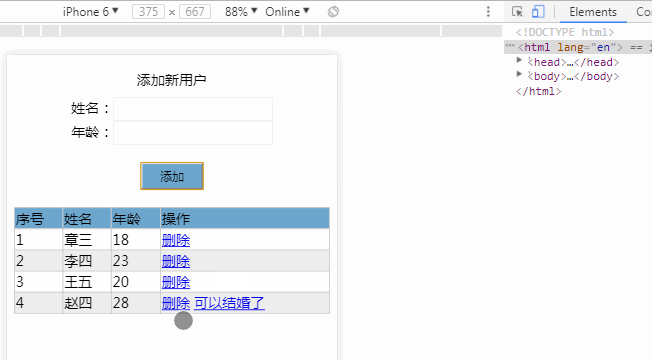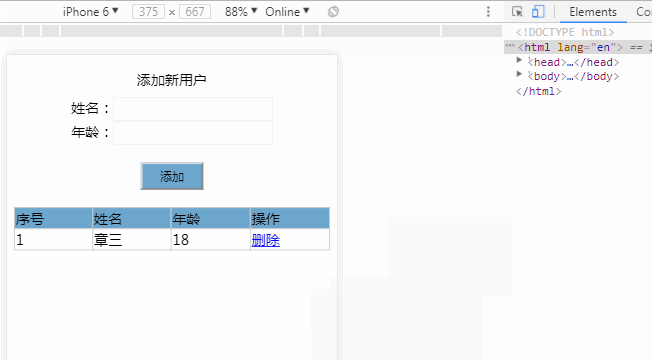
<div id="app">
<div class="title">添加新用户</div>
<div class="form">
姓名:<input type="text" v-model="person.name"><br/>
年龄:<input type="text" v-model="person.age"><br/>
<button class="btn" type="button" @click="add">添加</button>
</div>
<table>
<tr class="thead">
<td>序号</td>
<td>姓名</td>
<td>年龄</td>
<td>操作</td>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(item,index) in list">
<td v-text="index+1"></td>
<td v-text="item.name"></td>
<td v-text="item.age"></td>
<td>
<a href="javascript:;" @click="deleteItem(index)">删除</a>
<a v-if="item.age>=25" href="javascript:;" @click="marry(index)">可以结婚了</a>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
person:{
name:'',
age:'',
},
list:[{
name:'章三',
age:18
},{
name:'李四',
age:23
}]
},
methods:{
add:function(){
this.list.push(this.person);
this.person = {name:'',age:''};
},
deleteItem:function(index){
// 删除一个数组元素
this.list.splice(index,1);
},
marry:function(){
alert("不好意思,你没有女朋友结不了婚");
}
},
created:function(){
}
})Related recommendations:《 vue.js tutorial》
The above is the detailed content of Is there any instruction for vuejs?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to get items using commands in Terraria? -How to collect items in Terraria?
Mar 19, 2024 am 08:13 AM
How to get items using commands in Terraria? -How to collect items in Terraria?
Mar 19, 2024 am 08:13 AM
How to get items using commands in Terraria? 1. What is the command to give items in Terraria? In the Terraria game, giving command to items is a very practical function. Through this command, players can directly obtain the items they need without having to fight monsters or teleport to a certain location. This can greatly save time, improve the efficiency of the game, and allow players to focus more on exploring and building the world. Overall, this feature makes the gaming experience smoother and more enjoyable. 2. How to use Terraria to give item commands 1. Open the game and enter the game interface. 2. Press the "Enter" key on the keyboard to open the chat window. 3. Enter the command format in the chat window: "/give[player name][item ID][item quantity]".
 Some tips for developing Android applications using Vue.js and Kotlin language
Jul 31, 2023 pm 02:17 PM
Some tips for developing Android applications using Vue.js and Kotlin language
Jul 31, 2023 pm 02:17 PM
Some tips for developing Android applications using Vue.js and Kotlin language. With the popularity of mobile applications and the continuous growth of user needs, the development of Android applications has attracted more and more attention from developers. When developing Android apps, choosing the right technology stack is crucial. In recent years, Vue.js and Kotlin languages have gradually become popular choices for Android application development. This article will introduce some techniques for developing Android applications using Vue.js and Kotlin language, and give corresponding code examples. 1. Set up the development environment at the beginning
 Some tips for developing data visualization applications using Vue.js and Python
Jul 31, 2023 pm 07:53 PM
Some tips for developing data visualization applications using Vue.js and Python
Jul 31, 2023 pm 07:53 PM
Some tips for developing data visualization applications using Vue.js and Python Introduction: With the advent of the big data era, data visualization has become an important solution. In the development of data visualization applications, the combination of Vue.js and Python can provide flexibility and powerful functions. This article will share some tips for developing data visualization applications using Vue.js and Python, and attach corresponding code examples. 1. Introduction to Vue.js Vue.js is a lightweight JavaScript
 Integration of Vue.js and Lua language, best practices and experience sharing in building front-end engines for game development
Aug 01, 2023 pm 08:14 PM
Integration of Vue.js and Lua language, best practices and experience sharing in building front-end engines for game development
Aug 01, 2023 pm 08:14 PM
The integration of Vue.js and Lua language, best practices and experience sharing for building a front-end engine for game development Introduction: With the continuous development of game development, the choice of game front-end engine has become an important decision. Among these choices, the Vue.js framework and Lua language have become the focus of many developers. As a popular front-end framework, Vue.js has a rich ecosystem and convenient development methods, while the Lua language is widely used in game development because of its lightweight and efficient performance. This article will explore how to
 How to use PHP and Vue.js to implement data filtering and sorting functions on charts
Aug 27, 2023 am 11:51 AM
How to use PHP and Vue.js to implement data filtering and sorting functions on charts
Aug 27, 2023 am 11:51 AM
How to use PHP and Vue.js to implement data filtering and sorting functions on charts. In web development, charts are a very common way of displaying data. Using PHP and Vue.js, you can easily implement data filtering and sorting functions on charts, allowing users to customize the viewing of data on charts, improving data visualization and user experience. First, we need to prepare a set of data for the chart to use. Suppose we have a data table that contains three columns: name, age, and grades. The data is as follows: Name, Age, Grades Zhang San 1890 Li
 Develop efficient web crawlers and data scraping tools using Vue.js and Perl languages
Jul 31, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
Develop efficient web crawlers and data scraping tools using Vue.js and Perl languages
Jul 31, 2023 pm 06:43 PM
Use Vue.js and Perl languages to develop efficient web crawlers and data scraping tools. In recent years, with the rapid development of the Internet and the increasing importance of data, the demand for web crawlers and data scraping tools has also increased. In this context, it is a good choice to combine Vue.js and Perl language to develop efficient web crawlers and data scraping tools. This article will introduce how to develop such a tool using Vue.js and Perl language, and attach corresponding code examples. 1. Introduction to Vue.js and Perl language
 Integration of Vue.js and Dart language, practical and development skills for building cool mobile application UI interfaces
Aug 02, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
Integration of Vue.js and Dart language, practical and development skills for building cool mobile application UI interfaces
Aug 02, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
Integration of Vue.js and Dart language, practice and development skills for building cool mobile application UI interfaces Introduction: In mobile application development, the design and implementation of the user interface (UI) is a very important part. In order to achieve a cool mobile application interface, we can integrate Vue.js with the Dart language, and use the powerful data binding and componentization features of Vue.js and the rich mobile application development library of the Dart language to build Stunning mobile application UI interface. This article will show you how to
 How to use Vue to implement QQ-like chat bubble effects
Sep 20, 2023 pm 02:27 PM
How to use Vue to implement QQ-like chat bubble effects
Sep 20, 2023 pm 02:27 PM
How to use Vue to implement QQ-like chat bubble effects In today’s social era, the chat function has become one of the core functions of mobile applications and web applications. One of the most common elements in the chat interface is the chat bubble, which can clearly distinguish the sender's and receiver's messages, effectively improving the readability of the message. This article will introduce how to use Vue to implement QQ-like chat bubble effects and provide specific code examples. First, we need to create a Vue component to represent the chat bubble. The component consists of two main parts




