How to initialize a c++ array
c Method to initialize an array: 1. Define the array first and then assign a value to the array. The syntax is "data type array name [length]; array name [subscript] = value;"; 2. Initialize the array when defining the array. , syntax "data type array name [length] = [value list]".

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, C 17 version, Dell G3 computer.
Sometimes it is more appropriate to set the variable value in the program than to enter the variable value. However, writing separate assignment statements for each element of the array can mean a lot of typing, especially for large arrays.
For example, consider a program:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
const int NUM_MONTHS = 12;
int days[NUM_MONTHS];
days[0] = 31; // January
days[1] = 28; // February
days[2] = 31; // March
days[3] = 30; // April
days[4] = 31; // May
days[5] = 30; // June
days[6] = 31; // July
days[7] = 31; // August
days[8] = 30; // September
days[9] = 31; // October
days[10] = 30; // November
days[11] = 31; // December
for (int month = 0; month < NUM_MONTHS; month++)
{
cout << "Month "<< setw (2) << (month+1) << " has ";
cout << days[month] << " days.\n";
}
return 0;
}Program output:
Month 1 has 31 days. Month 2 has 28 days. Month 3 has 31 days. Month 4 has 30 days. Month 5 has 31 days. Month 6 has 30 days. Month 7 has 31 days. Month 8 has 31 days. Month 9 has 30 days. Month 10 has 31 days. Month 11 has 30 days. Month 12 has 31 days.
Fortunately, there is an option. C allows initializing arrays when they are defined. By using an initializer list, you can easily initialize all elements of an array when you create it. The following statement defines the days array and initializes it with the same values established by the set of assignment statements in the previous program:
int days [NUM_MONTHS] = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30, 31};The values are stored in the array elements in the order in which they appear in the list (the first The value 31 is stored in days[0], the second value 28 is stored in days[1], etc.). The following figure shows the contents of the array after initialization.
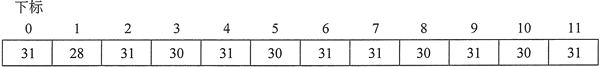
The following program is a modified version of the above program. It initializes the days array when it is created, rather than using a separate assignment statement. Note that the initialization list is spread across multiple lines. The program also adds an array of string objects to hold the month names:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
const int NUM_MONTHS = 12;
string name[NUM_MONTHS]={ "January", "February", "March", "April", "May" , "June", "July", "August", "September", "october", "November", "December"};
int days[NUM_MONTHS] = {31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
for (int month = 0; month < NUM_MONTHS; month++)
{
cout << setw(9) << left << name[month] << " has ";
cout << days [month] << " days. \n";
}
return 0;
}Program output:
January has 31 days. February has 28 days. March has 31 days. April has 30 days. May has 31 days. June has 30 days. July has 31 days. August has 31 days. September has 30 days. october has 31 days. November has 30 days. December has 31 days.
So far, it has been demonstrated how to fill the array with numerical values and then display all the values . However, sometimes more functionality may be needed, such as retrieving a specific value from an array. The following program is a variation of the above program that displays the number of days in a month selected by the user.
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
const int NUM_MONTHS = 12;
int choice;
string name[NUM_MONTHS]={ "January", "February", "March", "April", "May" , "June", "July", "August", "September", "october", "November", "December"};
int days[NUM_MONTHS] = {31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
cout << "This program will tell you how many days are "<< "in any month.\n\n";
// Display the months
for (int month = 1; month <= NUM_MONTHS; month++)
cout << setw (2) << month << " " << name [month-1] << endl;
cout << "\nEnter the number of the month you want: ";
cin >> choice;
// Use the choice the user entered to get the name of
// the month and its number of days from the arrays.
cout << "The month of " << name [choice-1] << " has " << days[choice-1] << " days.\n";
return 0;
}The program output is:
This program will tell you how many days are in any month. 1 January 2 February 3 March 4 April 5 May 6 June 7 July 8 August 9 September 10 october 11 November 12 December Enter the number of the month you want: 4 The month of April has 30 days.
Start from array element 1
There is a lot of logic in the real world When building a model for things starting with 1, many teachers will prefer that students not use element 0, but instead start storing actual data from element 1. The number of months in the year is a good example. In this case, you can declare the name and days arrays to have 13 elements each and initialize them as follows:
string name[NUM_MONTHS+1]={" ", "January", "February", "March", "April", "May" , "June", "July", "August", "September", "october", "November", "December"};
int days[NUM_MONTHS+1] = {0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};Note that array element 0 is not used. It's just a virtual value. This will store the name of January in name[1], the name of February in name[2], and so on. Likewise, the number of days in January will be stored in the days[1] element, the number of days in February in the days[2] element, and so on.
If you use the above method to define and initialize the array, the loop should be rewritten in the following form. It will display the contents of array elements 1~12 instead of elements 0~11 like before.
for (int month = 1; month <= NUM_MONTHS; month++)
{
cout << setw(9) << left << name[month] << " has ";
cout << days[month] << " days.\n";
}If the actual data is stored starting with element 1, then there is no need to add 1 to the array subscript to locate specific data. The following is a modification of the statement that lists the number and name of each month:
for (int month = 1; month <= NUM_MONTHS; month++)
cout << setw (2) << month << " " << name [month] << endl;The code that displays the number of days in the month selected by the user should be modified as follows.
cout << "The month of " << name[choice] << " has "<< days [choice] << " days . \n";
Partial initialization of array
When an array is initialized, C does not have to get the value of each element, it can also just initialize it Part of the array, as shown below:
int numbers[7] = {1, 2, 4, 8};This definition only initializes the first 4 elements of a 7-element array, as shown below.
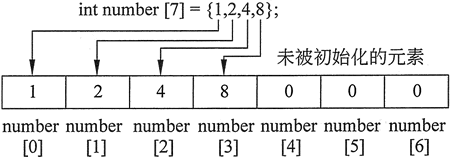
Figure 2
It is worth mentioning that the uninitialized elements in Figure 2 will all be set to zero. This is what happens when the numeric array is partially initialized. When an array of string objects is partially initialized, the uninitialized elements will all contain empty strings, that is, strings of length 0. This is true even if the partially initialized array is defined locally. However, if a local array is completely uninitialized, its elements will contain "garbage", just like other local variables.
The following program shows the contents of the numbers array after partial initialization:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
const int SIZE = 7;
int numbers[SIZE] = {1, 2, 4, 8}; // Initialize the first 4 elements
cout << "Here are the contents of the array: \n";
for (int index = 0; index < SIZE; index++)
cout << numbers [index] << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}Program output:
Here are the contents of the array: 1 2 4 8 0 0 0
Although the value of the array initialization list can be larger than the elements of the array Fewer, but no more values than array elements are allowed. The following statement is illegal because the numbers array can only contain 7 values, but the initialization list contains 8 values.
int numbers [7] = {1, 2, 4, 8, 3, 5, 7, 9}; //不合法Also, if an element is left uninitialized, all elements after that element should be left uninitialized. C does not provide a way to skip elements in an initialization list. Here is another illegal example:
int numbers [7] = {1, , 4, , 3, 5, 7}; // 不合法Implicit array size
可以通过提供一个包含每个元素值的初始化列表来定义一个数组而不指定它的大小。C++ 会计算初始化列表中的项目数,并为数组提供相应数量的元素。例如,以下定义创建 了一个包含5个元素的数组:
double ratings [] = {1.0,1.5,2.0,2.5,3.0};注意,如果省略大小声明符,则必须指定一个初始化列表。否则,C++ 不知道该数组有多大。
初始化变量的新方法
到目前为止,已经介绍过的定义和初始化常规变量的方法是使用赋值语句,示例如下:
int value = 5;
但是,我们已经学习过使用函数、数组以及类,所以现在是时候来介绍另外两种在定义变量的同时即进行初始化的方法。
第一种新方法是使用函数符号初始化变量。它看起来就像是给一个函数传递参数。如果您已经掌握了类的内容,那么就会注意到,它也很像是在创建类对象时给一个构造函数传递值。以下是使用函数符号定义变量 value 并初始化其值为 5 的示例语句:
int value (5);
第二种初始化变量的新方法是 C++ 11 中新引入的,使用大括号表示法。它看起来就像是刚刚上面所看到的初始化数组的方法,但是其中有两点区别:
因为常规变量只能一次保存一个值,所以通过这种方法初始化变量时,大括号中只有一个值;
和数组初始化列表不一样,通过这种方法初始化变量时,在大括号前面没有赋值运算符(=)。
以下是使用大括号表示法定义变量 value 并初始化其值为5的示例语句。
int value{5}; //该语句仅在C++ 11或更高版本中合法绝大多数程序员会继续使用赋值运算符来初始化常规变量,本书也将如此,但是,大括号表示法提供了一项优点,它会检查用来初始化变量的值,并确保匹配变量的数据类型。例如,假设 doubleVal 是一个 double 类型变量,存储在其中的值为 6.2。则使用赋值运算符时,可以编写以下两种形式的语句之一:
int valuel = 4.9; //该语句将给valuel赋值为。4 int vaule2 = doubleVal; // 该语句将给 value2 赋值为 6
在这两种情况下,值的小数点部分都会被先截断,然后才赋值给被定义的变量。这虽然可能会导致一些问题,但 C++ 编译器是允许的,它也会提出警告,但却仍然能生成可执行文件,并且可以运行。不过,如果在这里使用的是大括号表示法,则编译器会指出这些语句产生了一个错误,并且不会生成可执行文件。必须先修复该错误,然后重新编译项目才能运行该程序。
相关推荐:《C++视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of How to initialize a c++ array. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
What is the role of char in C strings
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:15 PM
In C, the char type is used in strings: 1. Store a single character; 2. Use an array to represent a string and end with a null terminator; 3. Operate through a string operation function; 4. Read or output a string from the keyboard.
 Four ways to implement multithreading in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
Four ways to implement multithreading in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
Multithreading in the language can greatly improve program efficiency. There are four main ways to implement multithreading in C language: Create independent processes: Create multiple independently running processes, each process has its own memory space. Pseudo-multithreading: Create multiple execution streams in a process that share the same memory space and execute alternately. Multi-threaded library: Use multi-threaded libraries such as pthreads to create and manage threads, providing rich thread operation functions. Coroutine: A lightweight multi-threaded implementation that divides tasks into small subtasks and executes them in turn.
 How to calculate c-subscript 3 subscript 5 c-subscript 3 subscript 5 algorithm tutorial
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:33 PM
How to calculate c-subscript 3 subscript 5 c-subscript 3 subscript 5 algorithm tutorial
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:33 PM
The calculation of C35 is essentially combinatorial mathematics, representing the number of combinations selected from 3 of 5 elements. The calculation formula is C53 = 5! / (3! * 2!), which can be directly calculated by loops to improve efficiency and avoid overflow. In addition, understanding the nature of combinations and mastering efficient calculation methods is crucial to solving many problems in the fields of probability statistics, cryptography, algorithm design, etc.
 distinct function usage distance function c usage tutorial
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:27 PM
distinct function usage distance function c usage tutorial
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:27 PM
std::unique removes adjacent duplicate elements in the container and moves them to the end, returning an iterator pointing to the first duplicate element. std::distance calculates the distance between two iterators, that is, the number of elements they point to. These two functions are useful for optimizing code and improving efficiency, but there are also some pitfalls to be paid attention to, such as: std::unique only deals with adjacent duplicate elements. std::distance is less efficient when dealing with non-random access iterators. By mastering these features and best practices, you can fully utilize the power of these two functions.
 How to apply snake nomenclature in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to apply snake nomenclature in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
In C language, snake nomenclature is a coding style convention, which uses underscores to connect multiple words to form variable names or function names to enhance readability. Although it won't affect compilation and operation, lengthy naming, IDE support issues, and historical baggage need to be considered.
 Usage of releasesemaphore in C
Apr 04, 2025 am 07:54 AM
Usage of releasesemaphore in C
Apr 04, 2025 am 07:54 AM
The release_semaphore function in C is used to release the obtained semaphore so that other threads or processes can access shared resources. It increases the semaphore count by 1, allowing the blocking thread to continue execution.
 Issues with Dev-C version
Apr 03, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Issues with Dev-C version
Apr 03, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Dev-C 4.9.9.2 Compilation Errors and Solutions When compiling programs in Windows 11 system using Dev-C 4.9.9.2, the compiler record pane may display the following error message: gcc.exe:internalerror:aborted(programcollect2)pleasesubmitafullbugreport.seeforinstructions. Although the final "compilation is successful", the actual program cannot run and an error message "original code archive cannot be compiled" pops up. This is usually because the linker collects
 C and System Programming: Low-Level Control and Hardware Interaction
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:06 AM
C and System Programming: Low-Level Control and Hardware Interaction
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:06 AM
C is suitable for system programming and hardware interaction because it provides control capabilities close to hardware and powerful features of object-oriented programming. 1)C Through low-level features such as pointer, memory management and bit operation, efficient system-level operation can be achieved. 2) Hardware interaction is implemented through device drivers, and C can write these drivers to handle communication with hardware devices.




