What are the five ways to pass values in vue components?
Five ways to pass values in vue components: 1. Parent component passes value to child component; 2. Child component passes value to parent component; 3. Passes parameters between adjacent sibling components; 4. Parameters are passed between distant sibling components; 5. EventBus parameters are passed.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, vue2.9.6 version, DELL G3 computer.
Vue’s communication method can also be said to be the parameter passing method:
Parent component passes value to child component:
Subcomponents pass values to parent components:
Pass parameters between adjacent sibling components (brothers)
Passing parameters from distant brothers (cousins)
EventBus passing parameters
1. Passing parameters from father to son
Principle : The parent controls the child. Through the props attribute of the child component, it throws the child component's custom label attribute to receive the operating status of the parent component.
Example: A button in the parent controls the display and hiding of a p in the child component.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<style>
.div{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background:pink;
}
</style>
<body>
<!-- 这里的app范围就是 子组件son 的父级 -->
<div id="app">
<button @click='change'>父按钮</button>
<hr>
<!-- ********** 自定义标签属性test,接收父级的state ************-->
<son :test='state'></son>
</div>
<template id="tp1">
<div>
<!-- ************ 调用自定义属性test **************-->
<div v-show='test'>我是子组件的div</div>
</div>
</template>
<script src="../vue/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 局部定义 子组件son
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
state:true
},
methods:{
change(){
this.state = !this.state;
}
},
components:{
son:{
template:"#tp1",
//*********** 抛出自定义标签属性 ***************
props:['test']
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>Effect:

2. Passing parameters from parent to child
Principle: The child controls the parent, and the child component binds custom events. To handle the method function of the parent component, trigger your own custom event through .$emit('custom event',[parameter])
Example: a button in the child component controls a p in the parent component Show hide
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<style>
.div{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background:pink;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<c1></c1>
</div>
<!-- 父组件c1 子组件c2 子组件自定义事件test-->
<template id="c1">
<div>
<div v-show='state'>father显示/隐藏</div>
<hr>
<!--************ 子组件c2自定义事件,执行父组件c1的方法函数change_f ***************** -->
<c2 @test='change_f'></c2>
</div>
</template>
<template id="c2">
<div>
<button @click='change_son'>子按钮</button>
</div>
</template>
<!-- 引入Vue.js框架文档,可在官方文档下载-->
<script src='../vue/vue.js'></script>
<script>
//全局定义
// 实例化 父组件c1
Vue.component("c1",{
template:"#c1",
data(){
return {
state:true
}
},
methods:{
change_f(){
this.state = !this.state;
}
}
})
// 实例化 子组件c2
Vue.component("c2",{
template:"#c2",
methods:{
change_son(){
// ************ 在子组件方法里,触发子组件自定义事件 ******************
this.$emit("test")
}
}
})
//实例化一个Vue对象
new Vue({
el:"#app"
})
</script>
</body>
</html>Effect:

3. Passing parameters from adjacent brothers (brothers)
Principle: through a public parent The element serves as a bridge (instance component), combined with parent-child props parameter passing and child-parent custom events
Example: c1 and c2 are brothers. c1 can control the display and hiding of elements in c2
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<style>
.div{
width:200px;
height:200px;
background:pink;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
父级状态
<p>{{state}}</p>
<hr>
<c1 @test_c1='change_f'></c1>
<hr>
<c2 :test_c2='state'></c2>
</div>
<template id="c1">
<div>这里是c1组件
<button @click='change_c1'>c1按钮</button>
</div>
</template>
<template id="c2">
<div>这里是c2组件,状态:{{test_c2}}
<div v-show='test_c2'>我是c2中的div</div>
</div>
</template>
<script src='../vue/vue.js'></script>
<script>
Vue.component("c2",{
template:"#c2",
props:['test_c2']
})
Vue.component("c1",{
template:"#c1",
methods:{
change_c1(){
this.$emit("test_c1")
}
}
})
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
state:true
},
methods:{
change_f(){
this.state = !this.state;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>Effect :

4. Passing parameters from distant brothers (cousins)
Principle: By creating an intermediate instance and registering an event, in the controlled component, The function to be executed is carried through the event. In the main control component, the corresponding operation is changed through the event

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<father></father>
</div>
<template id="father">
<div>
这是父组件
<hr>
<son1></son1>
<hr>
<son2></son2>
</div>
</template>
<template id="son1">
<div>
{{name}}
<button @click='click_son1'>触发angle中间事件</button>
</div>
</template>
<template id="son2">
<div>
{{name}}
</div>
</template>
<script src='../vue/vue.js'></script>
<script>
//********** 创建一个angle实例,作为中间变量(全局) **************
let angel = new Vue();
new Vue({
el:"#app",
components:{
father:{
template:"#father",
components:{
son1:{
template:"#son1",
data(){
return {
name:"我是son1"
}
},
methods:{
click_son1(){
// *************** 通过angel注册的test事件,修改son2中name的值 ************
angel.$emit('test','哈哈!修改成功!')
}
}
},
son2:{
template:"#son2",
data(){
return {
name:"我是son2"
}
},
methods:{
change(val){
this.name = val;
}
},
//生命周期,自动执行,组件准备ok就可用
mounted(){
// *************** 通过angel注册的test事件,将son1的修改方法传过去 ************
angel.$on('test',this.change)
}
}
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>Effect:
Before clicking :
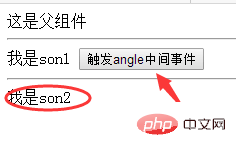
After clicking:
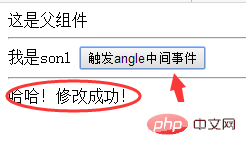
##5. EventBus passing parameters
1. Mount the global EventBus in main.jsVue.prototype.$EventBus = new Vue()
<template>
<div class="wrap">
<div>我是组件A</div>
<button @click="sendMsg">发送</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "A",
methods:{
sendMsg(){
this.$EventBus.$emit('sendMsg',"这是组件A发送的消息!")
}
}
}
</script><template>
<div>
<div>我是组件B</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "B",
mounted(){
this.$EventBus.$on('sendMsg',(msg)=>{
console.log(msg);//这是组件A发送的消息!
})
},
}
</script>vue.js Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What are the five ways to pass values in vue components?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 The role of export default in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:48 PM
The role of export default in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:48 PM
Question: What is the role of export default in Vue? Detailed description: export default defines the default export of the component. When importing, components are automatically imported. Simplify the import process, improve clarity and prevent conflicts. Commonly used for exporting individual components, using both named and default exports, and registering global components.
 How to use map function in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:54 PM
How to use map function in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:54 PM
The Vue.js map function is a built-in higher-order function that creates a new array where each element is the transformed result of each element in the original array. The syntax is map(callbackFn), where callbackFn receives each element in the array as the first argument, optionally the index as the second argument, and returns a value. The map function does not change the original array.
 How to disable the change event in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 07:21 PM
How to disable the change event in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 07:21 PM
In Vue, the change event can be disabled in the following five ways: use the .disabled modifier to set the disabled element attribute using the v-on directive and preventDefault using the methods attribute and disableChange using the v-bind directive and :disabled
 Where should the script tag in vue be placed?
May 09, 2024 pm 06:42 PM
Where should the script tag in vue be placed?
May 09, 2024 pm 06:42 PM
The script tag in Vue should be immediately inside the template element <template> to achieve tight coupling between logic and template and ensure the normal operation of the component.
 Adaptation of Java framework and front-end Vue framework
Jun 01, 2024 pm 09:55 PM
Adaptation of Java framework and front-end Vue framework
Jun 01, 2024 pm 09:55 PM
The Java framework and Vue front-end adaptation implement communication through the middle layer (such as SpringBoot), and convert the back-end API into a JSON format that Vue can recognize. Adaptation methods include: using the Axios library to send requests to the backend and using the VueResource plug-in to send simplified API requests.
 What does async mean in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 07:03 PM
What does async mean in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 07:03 PM
Vue's async modifier is used to create asynchronous components or methods to achieve dynamic loading of components and execution of asynchronous operations to avoid blocking the main thread.
 The function of render function in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 07:06 PM
The function of render function in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 07:06 PM
The render function in Vue.js is responsible for converting component data into virtual DOM, which can improve performance, enable templating, and support cross-platform. Specific functions include: 1. Generating virtual DOM; 2. Improving performance; 3. Implementing templates; 4. Supporting cross-platform.
 What is the function of setup in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
What is the function of setup in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:45 PM
The function of the setup function in Vue is to initialize component state and logic, including defining responsive data, methods and life cycle hooks. Replaces data(), methods(), computed(), and watch() options in the options API. Provide better performance through responsive handling. Supports Composition API for sharing and reusing logic. Improves testability because logic is separated from template code.






