
Why is it not recommended to use index as key in Vue? The following article will analyze the reasons for you. I hope it will be helpful to you. Come and collect it!

In front-end development, as long as list rendering is involved, whether it is the React or Vue framework, each list item will be prompted or required to use a unique key. Many developers It will directly use the index of the array as the value of the key without knowing the principle of the key. Then this article will explain the role of key and why it is best not to use index as the attribute value of key.
Vue uses virtual dom and compares the old and new DOM according to the diff algorithm to update the real dom. Key is the unique identifier of the virtual DOM object. Key plays a role in the diff algorithm. extremely important role. [Related recommendation: "vue.js Tutorial"]
In fact, the diff algorithm in React, Vue, is roughly the same, but There are still big differences in the diff comparison methods, and even each version of diff is very different. Next, we will use the Vue3.0 diff algorithm as the starting point to analyze the role of key in the diff algorithm
The specific diff process is as follows
In Vue3.0 There is such a piece of source code in the patchChildren method
if (patchFlag > 0) {
if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.KEYED_FRAGMENT) {
/* 对于存在 key 的情况用于 diff 算法 */
patchKeyedChildren(
...
)
return
} else if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.UNKEYED_FRAGMENT) {
/* 对于不存在 key 的情况,直接 patch */
patchUnkeyedChildren(
...
)
return
}
}patchChildren performs a real diff or a direct patch based on whether the key exists. We will not delve into the case where the key does not exist.
Let’s take a look at some declared variables first.
/* c1 老的 vnode c2 新的vnode */ let i = 0 /* 记录索引 */ const l2 = c2.length /* 新 vnode的数量 */ let e1 = c1.length - 1 /* 老 vnode 最后一个节点的索引 */ let e2 = l2 - 1 /* 新节点最后一个节点的索引 */
The first step is to find the same vnode from the beginning, and then patch it. If it is found that it is not the same node, jump out immediately cycle.
//(a b) c
//(a b) d e
/* 从头对比找到有相同的节点 patch ,发现不同,立即跳出*/
while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {
const n1 = c1[i]
const n2 = (c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[i]))
/* 判断 key ,type 是否相等 */
if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
patch(
...
)
} else {
break
}
i++
}The process is as follows:
isSameVNodeType is used to determine whether the current vnode type and the key of the vnode are equal
export function isSameVNodeType(n1: VNode, n2: VNode): boolean {
return n1.type === n2.type && n1.key === n2.key
}In fact, seeing this, Do you already know the role of key in the diff algorithm, which is used to determine whether it is the same node.
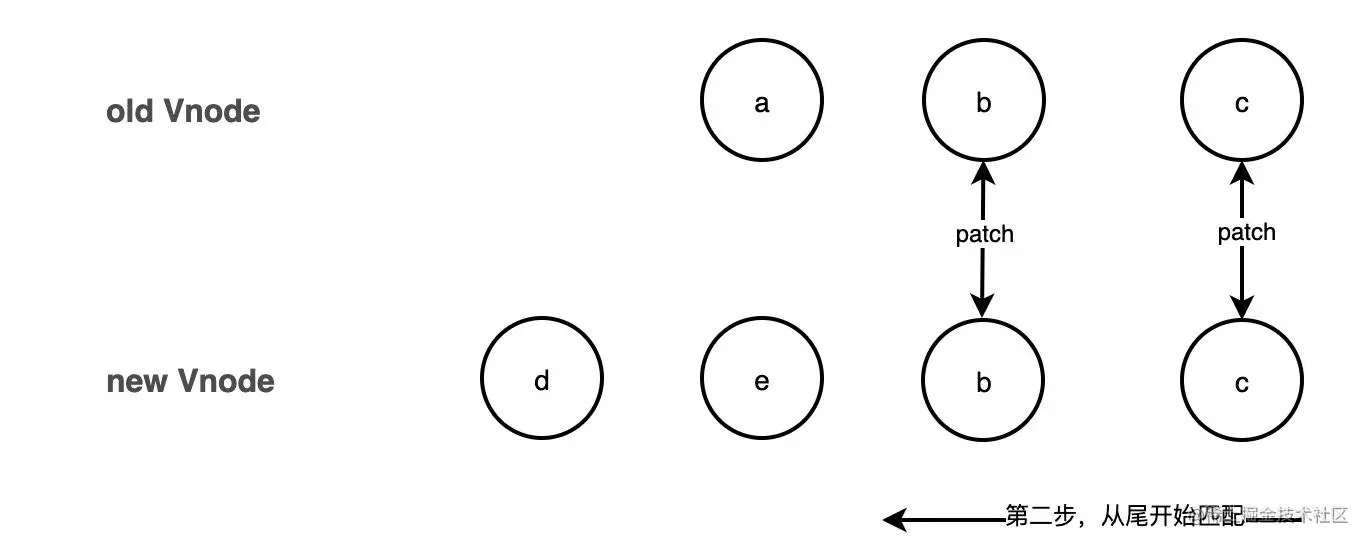
The second step starts from the end and is the same as the previous diff
//a (b c)
//d e (b c)
/* 如果第一步没有 patch 完,立即,从后往前开始 patch 如果发现不同立即跳出循环 */
while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {
const n1 = c1[e1]
const n2 = (c2[e2] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[e2] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[e2]))
if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
patch(
...
)
} else {
break
}
e1--
e2--
}After the first step of operation, if it is found that the patch is not completed, Then proceed to the second step immediately, starting from the tail and traversing forward diff in sequence. If it is found that they are not the same node, jump out of the loop immediately. The process is as follows:
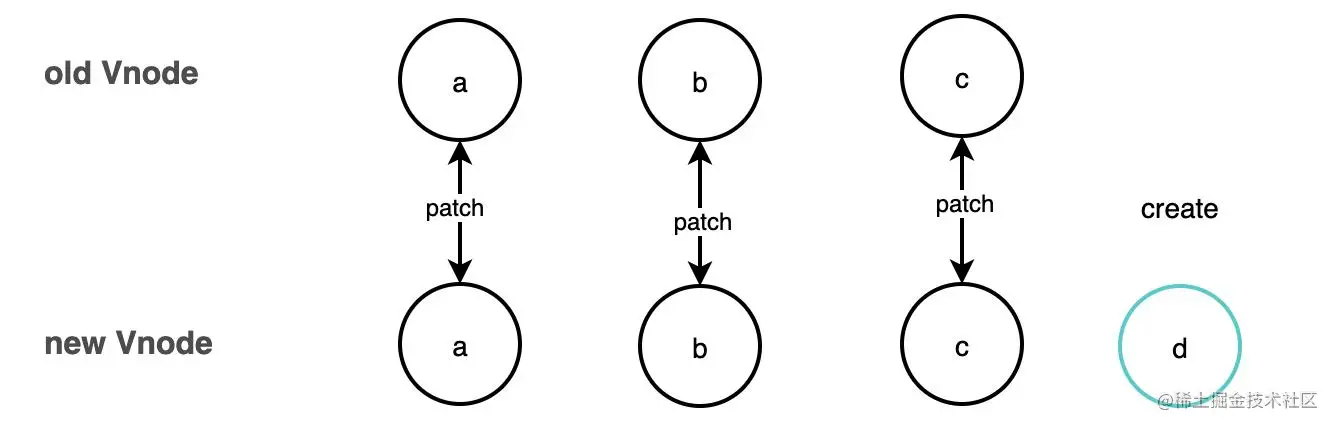
The third step is if all the old nodes are patched and the new node is not patched. ,Create a new vnode
//(a b)
//(a b) c
//i = 2, e1 = 1, e2 = 2
//(a b)
//c (a b)
//i = 0, e1 = -1, e2 = 0
/* 如果新的节点大于老的节点数 ,对于剩下的节点全部以新的 vnode 处理(这种情况说明已经 patch 完相同的 vnode ) */
if (i > e1) {
if (i <= e2) {
const nextPos = e2 + 1
const anchor = nextPos < l2 ? (c2[nextPos] as VNode).el : parentAnchor
while (i <= e2) {
patch( /* 创建新的节点*/
...
)
i++
}
}
}The process is as follows:
Step 4 If new All nodes are patched, and there are remaining old nodes, then uninstall all old nodes
//i > e2
//(a b) c
//(a b)
//i = 2, e1 = 2, e2 = 1
//a (b c)
//(b c)
//i = 0, e1 = 0, e2 = -1
else if (i > e2) {
while (i <= e1) {
unmount(c1[i], parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
i++
}
}The process is as follows:
At this point, the core scene has not yet appeared. If we are lucky, it may end here, but we cannot rely solely on luck. The remaining scenario is when both the old and new nodes have multiple child nodes. Then let’s see how Vue3 does it. In order to combine the operations of move, add and uninstall
Every time we move an element, we can find a rule. If we want to move the least number of times, It means that some elements need to be stable, so what are the rules for elements that can remain stable?
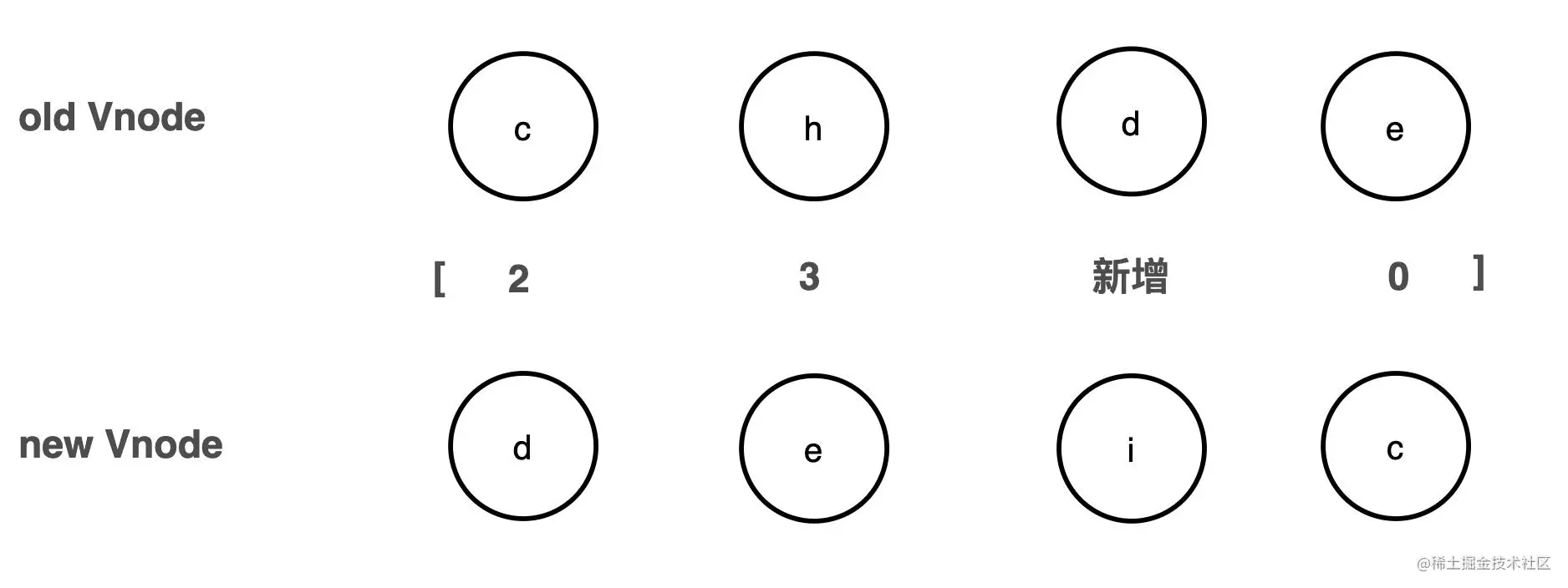
You can take a look at the above example: c h d e VS d e i c. When comparing, you can see with the naked eye that you only need to move c to the end, then uninstall h, and add i would be fine. d e can remain unchanged. It can be found that the order of d e in the old and new nodes remains unchanged. d is behind e and the subscript is in an increasing state.
这里引入一个概念,叫最长递增子序列。 官方解释:在一个给定的数组中,找到一组递增的数值,并且长度尽可能的大。 有点比较难理解,那来看具体例子: const arr = [10, 9, 2, 5, 3, 7, 101, 18] => [2, 3, 7, 18] 这一列数组就是arr的最长递增子序列,其实[2, 3, 7, 101]也是。 所以最长递增子序列符合三个要求: 1、子序列内的数值是递增的 2、子序列内数值的下标在原数组中是递增的 3、这个子序列是能够找到的最长的 但是我们一般会找到数值较小的那一组数列,因为他们可以增长的空间会更多。
那接下来的思路是:如果能找到老节点在新节点序列中顺序不变的节点们,就知道,哪一些节点不需要移动,然后只需要把不在这里的节点插入进来就可以了。**因为最后要呈现出来的顺序是新节点的顺序,移动是只要老节点移动,所以只要老节点保持最长顺序不变,通过移动个别节点,就能够跟它保持一致。**所以在此之前,先把所有节点都找到,再找对应的序列。最后其实要得到的则是这一个数组:[2, 3, 新增 , 0]。其实这就是 diff 移动的思路了
使用 index 做 key,破坏顺序操作的时候, 因为每一个节点都找不到对应的 key,导致部分节点不能复用,所有的新 vnode 都需要重新创建。
例子:
<template>
<div class="hello">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in studentList" :key="index">{{item.name}}</li>
<br>
<button @click="addStudent">添加一条数据</button>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data() {
return {
studentList: [
{ id: 1, name: '张三', age: 18 },
{ id: 2, name: '李四', age: 19 },
],
};
},
methods:{
addStudent(){
const studentObj = { id: 3, name: '王五', age: 20 };
this.studentList=[studentObj,...this.studentList]
}
}
}
</script>我们先把 Chorme 调试器打开,我们双击把里面文本修改一下
我们运行以上上面的代码,看下运行结果

从上面运行结果可以看出来,我们只是添加了一条数据,但是三条数据都需要重新渲染是不是很惊奇,我明明只是插入了一条数据,怎么三条数据都要重新渲染?而我想要的只是新增的那一条数据新渲染出来就行了。
上面我们也讲过 diif 比较方式,下面根据 diff 比较绘制一张图,看看具体是怎么比较的吧
当我们在前面加了一条数据时 index 顺序就会被打断,导致新节点 key 全部都改变了,所以导致我们页面上的数据都被重新渲染了。
下面我们下面生成1000个 DOM 来比较一下采用 index ,和不采用 index 性能比较,为了保证 key 的唯一性我们采用 uuid 作为 key
我们用 index 做为 key 现执行一遍
<template>
<div class="hello">
<ul>
<button @click="addStudent">添加一条数据</button>
<br>
<li v-for="(item,index) in studentList" :key="index">{{item.id}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import uuidv1 from 'uuid/v1'
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data() {
return {
studentList: [{id:uuidv1()}],
};
},
created(){
for (let i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
this.studentList.push({
id: uuidv1(),
});
}
},
beforeUpdate(){
console.time('for');
},
updated(){
console.timeEnd('for')//for: 75.259033203125 ms
},
methods:{
addStudent(){
const studentObj = { id: uuidv1() };
this.studentList=[studentObj,...this.studentList]
}
}
}
</script>换成 id 作为 key
<template>
<div class="hello">
<ul>
<button @click="addStudent">添加一条数据</button>
<br>
<li v-for="(item,index) in studentList" :key="item.id">{{item.id}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
beforeUpdate(){
console.time('for');
},
updated(){
console.timeEnd('for')//for: 42.200927734375 ms
},从上面比较可以看出,用唯一值作为 key 可以节约开销
上述例子可能觉得用 index 做 key 只是影响页面加载的效率,认为少量的数据影响不大,那面下面这种情况,可能用 index 就可能出现一些意想不到的问题了,还是上面的场景,这时我先再每个文本内容后面加一个 input 输入框,并且手动在输入框内填写一些内容,然后通过 button 向前追加一位同学看看
<template>
<div class="hello">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in studentList" :key="index">{{item.name}}<input /></li>
<br>
<button @click="addStudent">添加一条数据</button>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data() {
return {
studentList: [
{ id: 1, name: '张三', age: 18 },
{ id: 2, name: '李四', age: 19 },
],
};
},
methods:{
addStudent(){
const studentObj = { id: 3, name: '王五', age: 20 };
this.studentList=[studentObj,...this.studentList]
}
}
}
</script>我们往 input 里面输入一些值,添加一位同学看下效果:

这时候我们就会发现,在添加之前输入的数据错位了。添加之后王五的输入框残留着张三的信息,这很显然不是我们想要的结果。
从上面比对可以看出来这时因为采用 index 作为 key 时,当在比较时,发现虽然文本值变了,但是当继续向下比较时发现DOM 节点还是和原来一摸一样,就复用了,但是没想到 input 输入框残留输入的值,这时候就会出现输入的值出现错位的情况
既然知道用 index 在某些情况下带来很不好的影响,那平时我们在开发当中怎么去解决这种情况呢?其实只要保证 key 唯一不变就行,一般在开发中用的比较多就是下面三种情况。
在开发中最好每条数据使用唯一标识固定的数据作为 key,比如后台返回的 ID,手机号,身份证号等唯一值
可以采用 Symbol 作为 key,Symbol 是 ES6 引入了一种新的原始数据类型 Symbol ,表示独一无二的值,最大的用法是用来定义对象的唯一属性名。
let a=Symbol('测试') let b=Symbol('测试') console.log(a===b)//false
可以采用 uuid 作为 key ,uuid 是 Universally Unique Identifier 的缩写,它是在一定的范围内(从特定的名字空间到全球)唯一的机器生成的标识符
我们采用上面第一种方案作为 key 在看一下上面情况,如图所示。key 相同的节点都做到了复用。起到了diff 算法的真正作用。

Original address: https://juejin.cn/post/7026119446162997261
Author: Zhengcaiyun Front-end Team
For more programming-related knowledge, please visit: Introduction to Programming! !
The above is the detailed content of In-depth analysis of the reasons why index is not recommended as key in Vue. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!