 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 A brief analysis of how nodejs loads json files in the ECMAScript module
A brief analysis of how nodejs loads json files in the ECMAScript module
A brief analysis of how nodejs loads json files in the ECMAScript module
ECMAScript modulenodeHow to load json files》The following article will introduce to you how nodejs loads json files in the ECMAScript module. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

After reading this article, you will learn:
1, nodejs How to load and parse json files
2. How to read json files in fs module
3. Learn about import.meta.url
3. Learn about new URL()
4. Learn the load-json-file library
As we all know, if you load a json file in the CommonJS module, just pass require ()The function can be loaded directly, and the json object can be obtained.
But when loading the json file directly in the ECMAScript module, an error will be reported. The error is as follows:
First, enable
ESMmode, in fact, the official document (http://nodejs.cn/api/esm.html#introduction) also explains:Node.js will be used by default JavaScript code is treated as a CommonJS module. Authors can tell Node via the
.mjsfile extension,package.json"type"field, or--input-typeflag .js treats JavaScript code as an ECMAScript module
So how can I load a json file in the ECMAScript module? In fact, there are two solutions:
Assume there is a json file now: test.json
The content of the file is as follows:
{
"name": "project"
}Next, Introduce test.json: into
1. Read the json file through the fs file system
import { readFile } from "fs/promises"; // 以promise的方式引入 readFile API
const json = JSON.parse(
await readFile(new URL('./test.json', import.meta.url))
)
console.log('[json1]:', json); // 输出: { "name": "project" }Explanation:
await: According to ECMAScript top-level await proposal, await keyword Can be used at the top level within the module (outside the asynchronous function);
import.meta.url:nodejsReturns the module’s local file:/ /The absolute path of the protocol, for example: file://home/user/main.js, if there is another file test.js in the module, then ## The path of #test.js is new URL('test.js', import.meta.url);
new URL: Generate file: An object of the protocol (for most fs module functions, the path or filename parameter can be used as file: The object of the protocol is passed in).
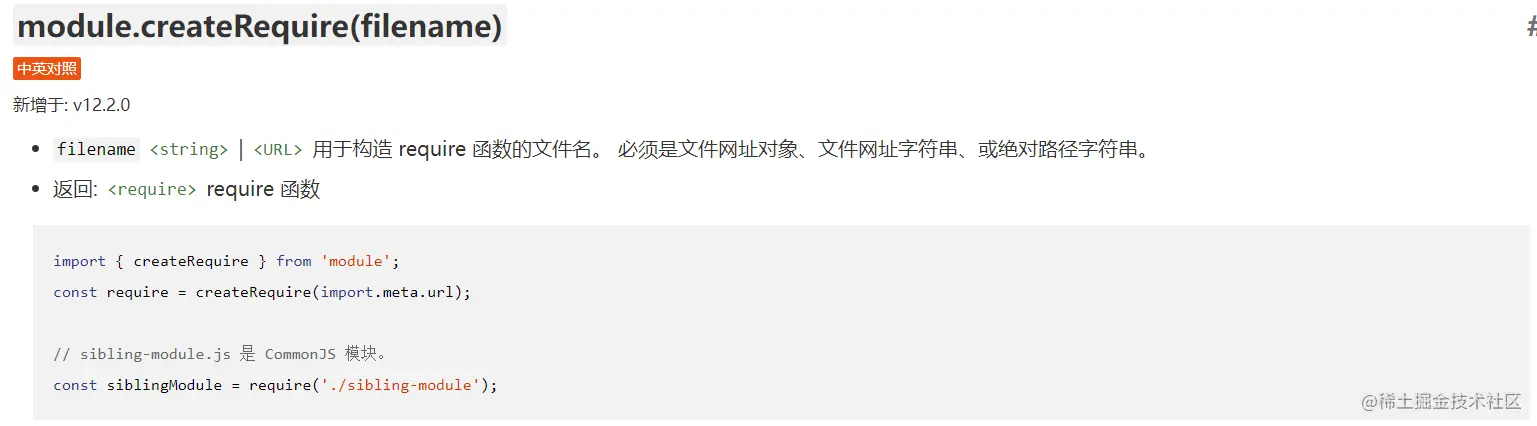
createRequire method of the nodejs built-in module module import { createRequire } from "module";
const require = createRequire(import.meta.url);
const json = require('./test.json');
console.log('[json2]:', json); // 输出: { "name": "project" }Copy after login
This method is based on import { createRequire } from "module";
const require = createRequire(import.meta.url);
const json = require('./test.json');
console.log('[json2]:', json); // 输出: { "name": "project" } The createRequire method provided by nodejs is implemented.

load-json-file
load-json-file I accidentally discovered it on the npm website. The source code only has 24 lines, as follows:
import {readFileSync, promises as fs} from 'node:fs';
const {readFile} = fs;
const parse = (buffer, {beforeParse, reviver} = {}) => {
// Unlike `buffer.toString()` and `fs.readFile(path, 'utf8')`, `TextDecoder`` will remove BOM.
// 这里对buffer进行转义,没有用`buffer.toString()`和`fs.readFile(path, 'utf8')`,是因为`new TextDecoder().decode(buffer)`这种方式可以删除字节顺序标记(BOM)
// 解码 buffer 并返回字符串
let data = new TextDecoder().decode(buffer);
// 在parse解析之前对字符串进行处理
if (typeof beforeParse === 'function') {
data = beforeParse(data);
}
return JSON.parse(data, reviver);
};
// 导出异步方法
export async function loadJsonFile(filePath, options) {
// 如果未指定编码,则返回原始缓冲区。
const buffer = await readFile(filePath);
return parse(buffer, options);
}
// 导出同步方法
export function loadJsonFileSync(filePath, options) {
// 如果未指定编码,则返回原始缓冲区。
const buffer = readFileSync(filePath);
return parse(buffer, options);
}load-json-file source code Overall, it is relatively simple, but there are many things that can be done Learn to dig deep into the knowledge points.
For more node-related knowledge, please visit:nodejs tutorial! !
The above is the detailed content of A brief analysis of how nodejs loads json files in the ECMAScript module. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 The difference between nodejs and vuejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:17 AM
The difference between nodejs and vuejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:17 AM
Node.js is a server-side JavaScript runtime, while Vue.js is a client-side JavaScript framework for creating interactive user interfaces. Node.js is used for server-side development, such as back-end service API development and data processing, while Vue.js is used for client-side development, such as single-page applications and responsive user interfaces.
 Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Node.js can be used as a backend framework as it offers features such as high performance, scalability, cross-platform support, rich ecosystem, and ease of development.
 How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
To connect to a MySQL database, you need to follow these steps: Install the mysql2 driver. Use mysql2.createConnection() to create a connection object that contains the host address, port, username, password, and database name. Use connection.query() to perform queries. Finally use connection.end() to end the connection.
 What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
There are two npm-related files in the Node.js installation directory: npm and npm.cmd. The differences are as follows: different extensions: npm is an executable file, and npm.cmd is a command window shortcut. Windows users: npm.cmd can be used from the command prompt, npm can only be run from the command line. Compatibility: npm.cmd is specific to Windows systems, npm is available cross-platform. Usage recommendations: Windows users use npm.cmd, other operating systems use npm.
 What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
The following global variables exist in Node.js: Global object: global Core module: process, console, require Runtime environment variables: __dirname, __filename, __line, __column Constants: undefined, null, NaN, Infinity, -Infinity
 Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
The main differences between Node.js and Java are design and features: Event-driven vs. thread-driven: Node.js is event-driven and Java is thread-driven. Single-threaded vs. multi-threaded: Node.js uses a single-threaded event loop, and Java uses a multi-threaded architecture. Runtime environment: Node.js runs on the V8 JavaScript engine, while Java runs on the JVM. Syntax: Node.js uses JavaScript syntax, while Java uses Java syntax. Purpose: Node.js is suitable for I/O-intensive tasks, while Java is suitable for large enterprise applications.
 Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Yes, Node.js is a backend development language. It is used for back-end development, including handling server-side business logic, managing database connections, and providing APIs.
 How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Server deployment steps for a Node.js project: Prepare the deployment environment: obtain server access, install Node.js, set up a Git repository. Build the application: Use npm run build to generate deployable code and dependencies. Upload code to the server: via Git or File Transfer Protocol. Install dependencies: SSH into the server and use npm install to install application dependencies. Start the application: Use a command such as node index.js to start the application, or use a process manager such as pm2. Configure a reverse proxy (optional): Use a reverse proxy such as Nginx or Apache to route traffic to your application



