What are JavaScript event types
In JavaScript, event type refers to the way the event is triggered. A simple understanding is what event is triggered; event types include: UI events, focus events, mouse and wheel events, keyboard and text events, and compound events. , change events, HTML5 events, device events, touch and gesture events, etc.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, javascript version 1.8.5, Dell G3 computer.
Events refer to behaviors that can be detected by JavaScript and are a "trigger-response" mechanism. These behaviors refer to specific actions such as page loading, mouse click/double-click, mouse pointer sliding over a certain area, etc. It plays a very important role in achieving the interactive effect of the page.
Events consist of three parts: event source, event type and event handler, also known as the "three elements of events".
Event source: the element that triggers (is) the event
Event type: the way the event is triggered (such as mouse click or keyboard click)
Event handler: code to be executed after the event is triggered (function form)
The above three elements can be simply understood as "who triggers event", "what event was triggered", "what to do after the event is triggered".
There are many types of events that may occur in web browsers. Here I will mainly focus on the following commonly used event types:
- UI events
- Focus events
- Mouse and wheel events
- Keyboard and Text event
- Composite event
- Change event
- HTML5 event
- Device event
- Touch and gesture event
Part One: UI Events
The UI in the UI event is (User Interface, User Interface), which is triggered when the user interacts with the elements of the page sauna.
UI events mainly include load, unload, abort, error, select, resize, scroll events.
1.load event
This event occurs when the page is completely loaded (including all images, js files, css external resources such as files), the load event on the window will be triggered.
This event is the most commonly used event in JavaScript. For example, we often use window.onload=function(){}; this form, that is, when the page Execute the functions after it is completely loaded.
In addition, I have never known that this event can also be used on other elements, such as image elements, as shown below:
<img src="smile.png" onload="alert('loaded')">
That is, when the image is fully loaded There will be a pop-up window after coming out. Of course, it can also be implemented using JS, as shown below:
var img=document.getElementById("img");
EventUtil.addHandler(img,"load",function(){
event=EventUtil.getEvent(event);
alert(EventUtil.getTarget(event).src);
});2.unload event
Obviously, this event is relative to the load event of. Triggered after the document is completely unloaded. The unload time is triggered when the user switches from one page to another. The most common use of this event is to clear references to avoid memory leaks.
This event also has two ways to specify. One is the JavaScript method, using EventUtil.addHandler(); the other is to add a feature to the body element.
It is worth noting that you must be careful when writing the code in the onload event, because it is triggered after the page is unloaded, so Those objects that exist after the page is loaded may not necessarily exist after onload is triggered!
<body onload="alert('changed')">
3.resize event
When the browser window is resized to a new width or height, the resize event is triggered. This event is triggered on the window. #So the handler can also be specified through the onresize attribute in JS or the body element.
<body onresize="alert('changed')">
If you write this code, a window will pop up when the size of the browser changes.
4.scroll event
This event will be triggered repeatedly while the document is scrolled, so the code of the event handler should be kept as simple as possible.
第二部分:焦点事件
焦点事件会在页面元素获得或失去焦点时触发。主要有下面几种:
- blur 在元素失去焦点时触发。这个事件不冒泡,所有浏览器都支持。
- focus 在元素获得焦点时触发。这个事件不冒泡,所有浏览器都支持。
- focusin 在元素获得焦点时触发。这个事件冒泡,某些浏览器不支持。
- focusout 在元素失去焦点时触发。这个事件冒泡,某些浏览器不支持。
注意:即使blur和focus不冒泡,也可以在捕获阶段侦听到他们。
第三部分:鼠标与滚轮事件
鼠标事件是Web开发中最常用的一类事件,因为鼠标是最主要的定位设备。
- click---用户单击鼠标左键或按下回车键触发
- dbclick---用户双击鼠标左键触发。
- mousedown---在用户按下了任意鼠标按钮时触发。
- mouseenter---在鼠标光标从元素外部首次移动到元素范围内时触发。此事件不冒泡。
- mouseleave---元素上方的光标移动到元素范围之外时触发。不冒泡。
- mousemove---光标在元素的内部不断的移动时触发。
- mouseover---鼠标指针位于一个元素外部,然后用户将首次移动到另一个元素边界之内时触发。
- mouseout---用户将光标从一个元素上方移动到另一个元素时触发。
- mouseup---在用户释放鼠标按钮时触发。
注意到:上述所有事件除了mouseenter和mouseleave外都冒泡。
重要:只有在同一个元素上相继触发mousedown和mouseup事件,才会触发click事件。同样,只有在同一个元素上触发两次click事件,才会触发dbclick事件。
dbclick事件的产生过程如下:
mousedown
mouseup
click
mousedown
mouseup
click
dbclick
上面介绍了有关鼠标的事件,下面介绍一些对于鼠标光标的位置:客户区坐标位置、页面坐标位置、屏幕坐标位置
一、客户区坐标位置
通过客户区坐标可以知道鼠标是在视口中什么位置发生的。
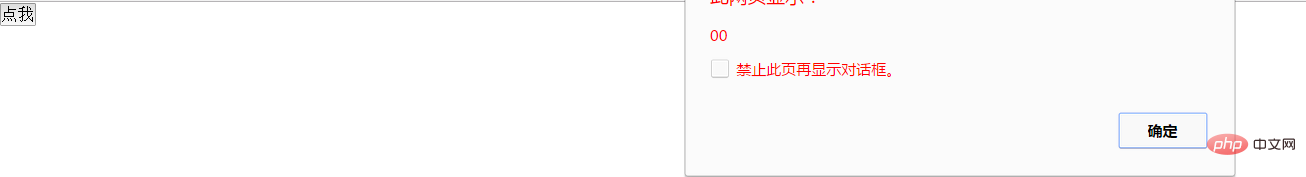
clientX和clientY分别表示鼠标点击的位置。以body的左上角为原点,向右为X的正方向,向下为Y的正方向。这两个都是event的属性。举例如下:
<button id="clickMe">点我</button>
<script>
var button=document.getElementById("clickMe");
button.onclick=function(event){
alert(event.clientY+""+event.clientX);
};
</script>当我点击按钮的左上角时,显示为00。效果如下:
二.页面坐标位置
和客户区坐标位置不同,页面坐标位置表示鼠标光标在页面而非视口中的位置。因此坐标是从页面本身而非视口的左边和顶边计算的。如果前面的话不能很好的理解,接着看这里:在页面没有滚动的情况下,页面坐标位置和客户区坐标位置是相同的。
页面坐标
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>页面坐标位置</title>
<style>
*{
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
p{
width: 800px;
height: 1200px; /*我的电脑的视口高度为960px;*/
background: #ccc;
} </style>
</head>
<body>
<p></p>
<button id="button"> 点击我</button>
<script>
var button=document.getElementById("button");
button.onclick=function(){
alert("pageX为"+event.pageX+"pageY为"+event.pageY);
}; </script>
</body>
</html>在上面的例子中,我把p的高设置为了1200px;而我的浏览器视口高度为960px;所以一定需要滚动我们才能点击按钮,最终得到的结果是:pageX为13pageY为1210。
然而IE8及更早的浏览器是不支持事件对象上的页面坐标的,即不能通过pageX和pageY来获得页面坐标,这时需要使用客户区坐标和滚动信息来计算了。而滚动信息需要使用document.body(混杂模式)、document.documentElement(标准模式)中的scrollLeft和scrollTop属性。举例如下:
<button id="button"> 点击我</button>
<script> var button=document.getElementById("button");
button.onclick=function(){
var pageX=event.clientX+(document.body.scrollLeft||document.documentElement.scrollLeft);
var pageY=event.clientY+(document.body.scrollRight||document.documentElement.scrollRight);
alert("pageX为"+pageX+"pageY为"+pageY);
};
</script>此例子在IE浏览器下可得到同样结果。
三.屏幕坐标位置
与前两者又有所不同,鼠标事件发生时,还有一个光标相对于整个电脑屏幕的位置。通过screenX和screenY属性就可以确定鼠标事件发生时鼠标指针相对于整个屏幕的位置。举例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>页面坐标位置</title>
<style>
*{
margin:0;
padding:0;
} </style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="button"> 点击我</button>
<script>
var button=document.getElementById("button");
button.onclick=function(){
alert("X为:"+event.screenX+"Y为:"+event.screenY);
};
</script>
</body>
</html>最终的结果如下:
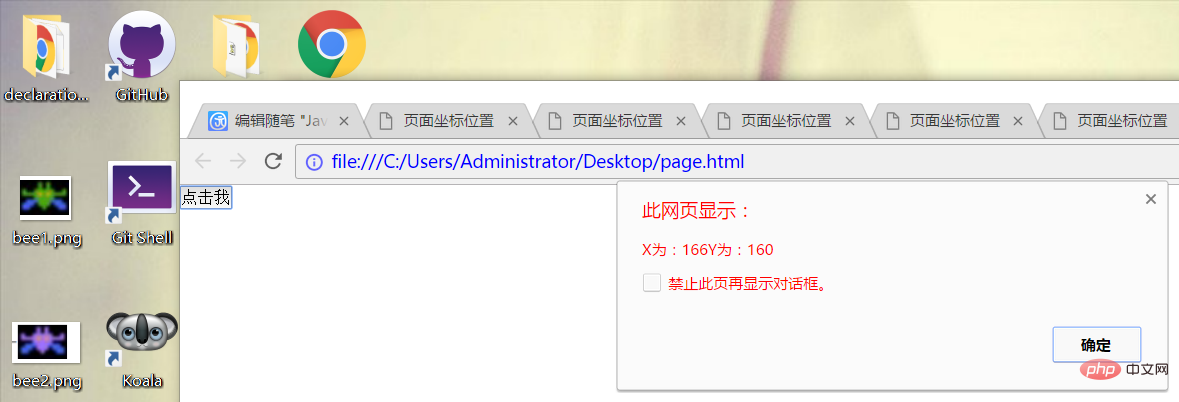
显然screenX和screenY是相对于屏幕的左方和上方的。
四.修改键
当点击某个元素时,如果我们同时按下了ctrl键,那么事件对象的ctrlKey属性值将为true,否则为false,对于alt、shift、meta(windows键盘的windows键、苹果机的Cmd键)的事件属性altKey、shiftKey、metaKey同样如此。下面举例如下:
<button id="button"> 点击我</button>
<script>
var button=document.getElementById("button");
button.onclick=function(){
var array=new Array();
if(event.shiftKey){
array.push("shift");
} if(event.ctrlKey){
array.push("ctrl");
} if(event.altKey){
array.push("alt");
} if(event.metaKey){
array.push("meta");
}
alert(array.join(","));
};
</script>这个例子中,我首先创建了一个array数组,接着如果我按下了那几个键,就会存入相应的名称。这里我同时按下了四个键,结果如下:

即最终将数组中的四个值拼接成了字符串显示出来。
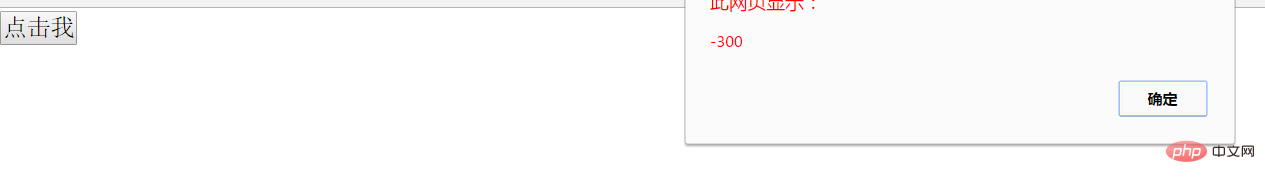
七、鼠标滚轮事件
<script>
document.onmousewheel=function(){
alert(event.wheelDelta);
};
</script>当我向下滚动滚轮时,效果如下:
第四部分:键盘和文本事件
该部分主要有下面几种事件:
keydown:当用户按下键盘上的任意键时触发。按住不放,会重复触发。
keypress:当用户按下键盘上的字符键时触发。按住不放,会重复触发。
keyup:当用户释放键盘上的键时触发。
textInput:这是唯一的文本事件,用意是将文本显示给用户之前更容易拦截文本。
这几个事件在用户通过文本框输入文本时才最常用到。
键盘事件:
document.addEventListener("keydown",handleKeyDownClick,false);
function handleKeyDownClick(event) {
var e = event||window.event||arguments.callee.caller.arguments[0];
if (e&&e.keyCode == 13) {
alert("keydown");
}
}【相关推荐:javascript学习教程】
The above is the detailed content of What are JavaScript event types. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time image processing system
Dec 17, 2023 am 08:41 AM
JavaScript is a programming language widely used in web development, while WebSocket is a network protocol used for real-time communication. Combining the powerful functions of the two, we can create an efficient real-time image processing system. This article will introduce how to implement this system using JavaScript and WebSocket, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to clarify the requirements and goals of the real-time image processing system. Suppose we have a camera device that can collect real-time image data




