An article to talk about module path analysis in Node.js
This article will take you through the module path analysis in Node.js and introduce the Node module path analysis method. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

##requireCase
- There is currently a project
- Current project Path
- /Users/rainbow/Documents/front-end/scaffolding development/rainbow-test
- /bin/index.js
console.log(require.resolve(".")); // /Users/rainbow/Documents/前端/脚手架开发/rainbow-test/bin/index.js 输出bin/index.js的绝对路径 console.log(require.resolve.paths(".")); // [ '/Users/rainbow/Documents/前端/脚手架开发/rainbow-test/bin' ] 输出的文件可能在的路径的数组Copy after loginconsole.log(require.resolve("yargs")); // /Users/rainbow/Documents/前端/脚手架开发/rainbow-test/node_modules/yargs/index.cjs console.log(require.resolve.paths("yargs")); /* [ '/Users/rainbow/Documents/前端/脚手架开发/rainbow-test/bin/node_modules', '/Users/rainbow/Documents/前端/脚手架开发/rainbow-test/node_modules', '/Users/rainbow/Documents/前端/脚手架开发/node_modules', '/Users/rainbow/Documents/前端/node_modules', '/Users/rainbow/Documents/node_modules', '/Users/rainbow/node_modules', '/Users/node_modules', '/node_modules', '/Users/rainbow/.node_modules', '/Users/rainbow/.node_libraries', '/usr/local/Cellar/node/14.3.0_1/lib/node' ] */Copy after login
requireThe process of parsing and finding the module execution file
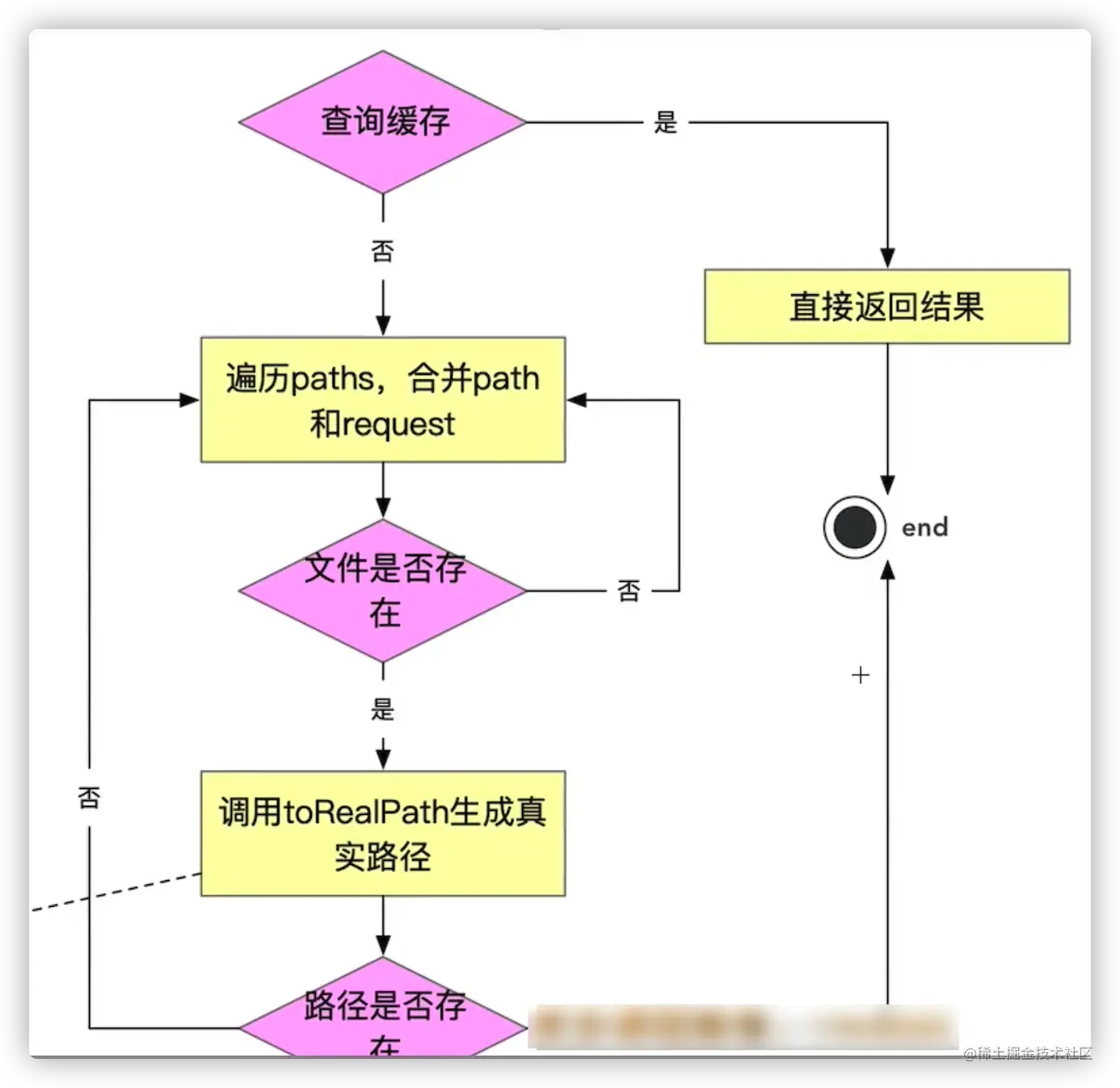
1、NodejsProject module path resolution is implemented through require.resolve.
- require.resolve is implemented through the
- Module._resolveFileName
method - Module._resolveFileName
The core process is:- Determine whether the path is a built-in moduleIf not, use the
- Module._resolveLookupPahts
method to generate possible paths for node_modules, if the incoming path is '/test/lerna/cli. js', add the path array ofnode_moduelsunder each level path Query the real path of the module through - Module._findPath
,
- Module._resolveLookupPahts
Module._findPath The core process is:
- Query cache (generated by merging request and paths through
- \x00
)Traverse the paths array generated by the - Module._resolveLookupPahts
method, and combinepathandrequestto form the file path basePathIf - basePath
exists, callfs.realPahtSyncto obtain the real path of the fileCache the real path of the file to - Module._pathCache
(key is cacheKey) (Module._pathCache is a map)
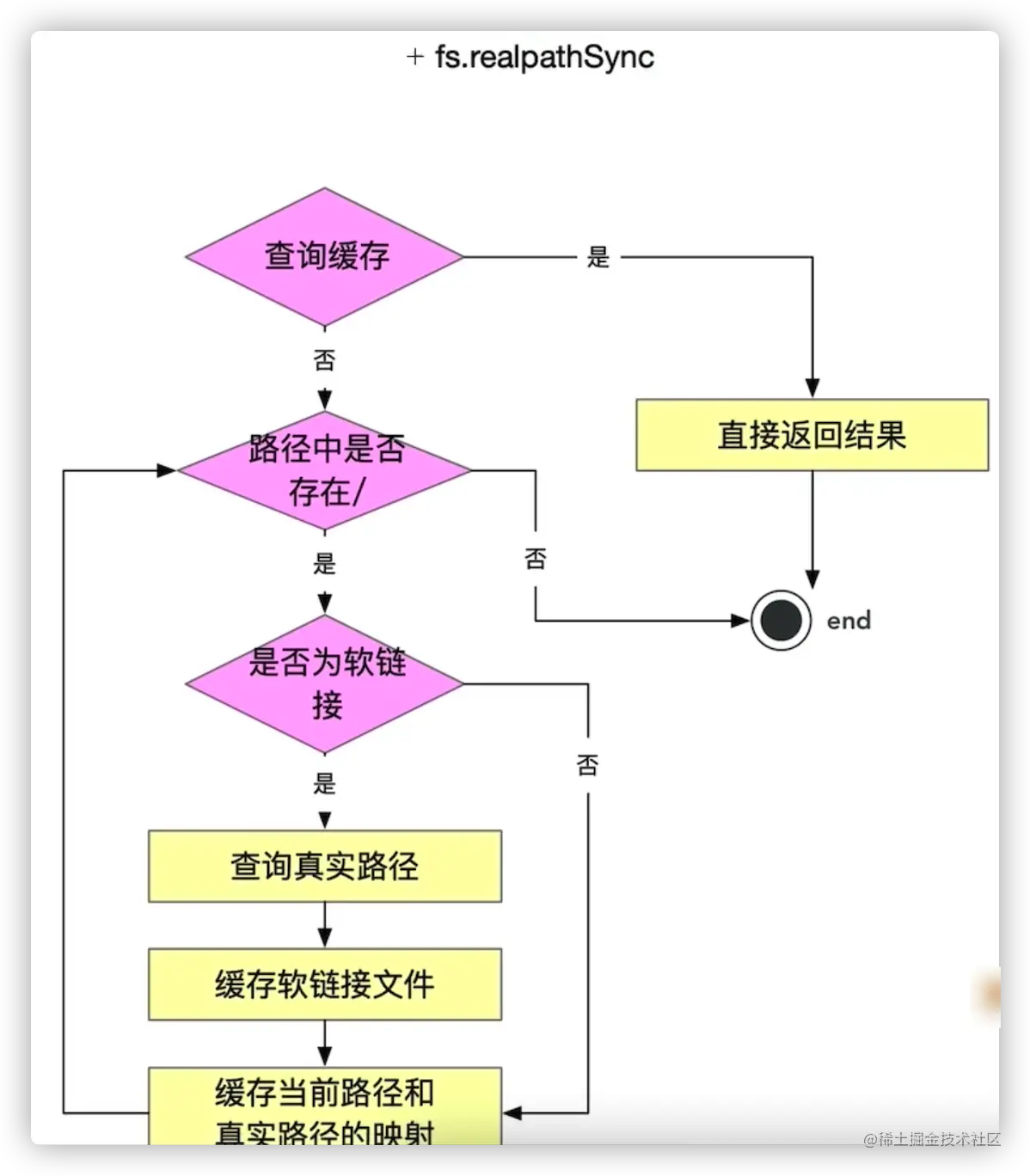
fs.realPahtSyncCore process:
- Query cache ( The cached key is p. That is, the path generated in Module._findPath)Traverse the path string from left to right, query /, split the path, and determine whether the path is a soft link. If it is a soft link, The link queries the real link, generates a new path p, and then continues to traverse. Here is a detail: The sub-path base generated during the traversal process will be cached in knownHard and cache to avoid repeated queriesAfter the traversal is completed, the real path corresponding to the module is obtained. At this time, the original path will be used as the key and the real path will be used as the value, which will be saved in the cache.
require.resolve. paths is equivalent to Module._resolveLookupPaths. This method obtains all possible paths of node_modules to form an array.
require.resolve.pathsThe implementation principle is:
- If it is
- /
(root path), returndirectly ['/node_modules'] Otherwise, traverse the path string from back to front. When / is queried, split the path, add node_modules at the end, and pass in a paths array until The paths array cannot be found/returned after querying
require uses the method of the built-in module
When we userequire('yargs')When
require method
- actually uses
- Module._load
method
Module.prototype.require = function(id) { //id = 'yargs'
validateString(id, 'id');
if (id === '') {
throw new ERR_INVALID_ARG_VALUE('id', id, 'must be a non-empty string');
}
requireDepth++;
try {
return Module._load(id, this, /* isMain */ false);
} finally {
requireDepth--;
}
};// 参数
id = 'yargs'
this={
paths: Module._nodeModulePaths(process.cwd())
}Module._nodeModulePathsMethod
##
// 进入mac电脑所在的逻辑:
// from => /Users/rainbow/Documents/前端/脚手架开发/lerna源码/lernas //'from' is the __dirname of the module.
Module._nodeModulePaths = function(from) {
from = path.resolve(from);
// Return early not only to avoid unnecessary work, but to *avoid* returning
// an array of two items for a root: [ '//node_modules', '/node_modules' ]
if (from === '/')
return ['/node_modules'];
const paths = [];
// 关键算法代码
for (let i = from.length - 1, p = 0, last = from.length; i >= 0; --i) {
const code = from.charCodeAt(i);
if (code === CHAR_FORWARD_SLASH) {
if (p !== nmLen)
paths.push(from.slice(0, last) + '/node_modules');
last = i;
p = 0;
} else if (p !== -1) {
if (nmChars[p] === code) {
++p;
} else {
p = -1;
}
}
}
// Append /node_modules to handle root paths.
paths.push('/node_modules');
return paths;
}; Core algorithm analysis of for loop:
Core algorithm analysis of for loop:

Module._loadMethod
The core implementation code is:
require.resolve
Project module path resolution is implemented through the require.resolve method.
- Module._resolveFileName
- method,
// node.js内置模块require的源代码 function resolve(request, options) { validateString(request, 'request'); return Module._resolveFilename(request, mod, false, options); //核心实现 } require.resolve = resolve; function paths(request) { validateString(request, 'request'); return Module._resolveLookupPaths(request, mod); //核心代码 } resolve.paths = paths;Copy after login
Module._resolveFileNameCore process
- If not, use the Module._resolveLookupPahts
- method to combine paths and Combine the paths in the environment
Query the real path of the module throughModule._findPath
Module._resolveFilename = function(request, parent, isMain, options) {
if (NativeModule.canBeRequiredByUsers(request)) { //是否为内置模块
return request;
}
let paths;
// 让paths和环境变量中的paths结合
paths = Module._resolveLookupPaths(request, parent); //核心代码
if (parent && parent.filename) {
// 读取filename对应的package.json文件,看是否有exports字段,当前filename = false
const filename = trySelf(parent.filename, request);
if (filename) { //false
const cacheKey = request + '\x00' +
(paths.length === 1 ? paths[0] : paths.join('\x00'));
Module._pathCache[cacheKey] = filename;
return filename;
}
}
//关键代码,找到本地执行文件 // Look up the filename first, since that's the cache key.
const filename = Module._findPath(request, paths, isMain, false);
if (filename) return filename;
// ...
};Module._resolveLookupPahts方法
- 生成要查找模块的所有路径上可能存在node_modules的路径数组
require.resolve.paths("yargs")核心实现方法
生成
[ '/Users/rainbow/Documents/前端/脚手架开发/rainbow-test/bin/node_modules', '/Users/rainbow/Documents/前端/脚手架开发/rainbow-test/node_modules', '/Users/rainbow/Documents/前端/脚手架开发/node_modules', '/Users/rainbow/Documents/前端/node_modules', '/Users/rainbow/Documents/node_modules', '/Users/rainbow/node_modules', '/Users/node_modules', '/node_modules', '/Users/rainbow/.node_modules', '/Users/rainbow/.node_libraries', '/usr/local/Cellar/node/14.3.0_1/lib/node' ]

Module._resolveLookupPaths = function(request, parent) {
if (NativeModule.canBeRequiredByUsers(request)) {
debug('looking for %j in []', request);
return null;
}
// Check for node modules paths.
if (request.charAt(0) !== '.' ||
(request.length > 1 &&
request.charAt(1) !== '.' &&
request.charAt(1) !== '/' &&
(!isWindows || request.charAt(1) !== '\'))){
let paths = modulePaths;
if (parent != null && parent.paths && parent.paths.length) {
paths = parent.paths.concat(paths);
}
debug('looking for %j in %j', request, paths);
return paths.length > 0 ? paths : null;
}
// In REPL, parent.filename is null.
if (!parent || !parent.id || !parent.filename) {
// Make require('./path/to/foo') work - normally the path is taken
// from realpath(__filename) but in REPL there is no filename
const mainPaths = ['.'];
debug('looking for %j in %j', request, mainPaths);
return mainPaths;
}
debug('RELATIVE: requested: %s from parent.id %s', request, parent.id);
const parentDir = [path.dirname(parent.filename)];
debug('looking for %j', parentDir);
return parentDir;
};Module._findPath核心流程
- 查询缓存(将request和paths通过
\x00合并生成cacheKey)(\x00是空格的16进制) - 遍历
Module._resolveLookupPahts方法生成的paths数组,将path与request组成文件路径basePath - 如果basePath存在则调用
fs.realPahtSync获取文件的真实路径

fs.realPahtSync
更多node相关知识,请访问:nodejs 教程!!
The above is the detailed content of An article to talk about module path analysis in Node.js. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Detailed graphic explanation of the memory and GC of the Node V8 engine
Mar 29, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
Detailed graphic explanation of the memory and GC of the Node V8 engine
Mar 29, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
This article will give you an in-depth understanding of the memory and garbage collector (GC) of the NodeJS V8 engine. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 An article about memory control in Node
Apr 26, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
An article about memory control in Node
Apr 26, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
The Node service built based on non-blocking and event-driven has the advantage of low memory consumption and is very suitable for handling massive network requests. Under the premise of massive requests, issues related to "memory control" need to be considered. 1. V8’s garbage collection mechanism and memory limitations Js is controlled by the garbage collection machine
 Let's talk about how to choose the best Node.js Docker image?
Dec 13, 2022 pm 08:00 PM
Let's talk about how to choose the best Node.js Docker image?
Dec 13, 2022 pm 08:00 PM
Choosing a Docker image for Node may seem like a trivial matter, but the size and potential vulnerabilities of the image can have a significant impact on your CI/CD process and security. So how do we choose the best Node.js Docker image?
 Let's talk in depth about the File module in Node
Apr 24, 2023 pm 05:49 PM
Let's talk in depth about the File module in Node
Apr 24, 2023 pm 05:49 PM
The file module is an encapsulation of underlying file operations, such as file reading/writing/opening/closing/delete adding, etc. The biggest feature of the file module is that all methods provide two versions of **synchronous** and **asynchronous**, with Methods with the sync suffix are all synchronization methods, and those without are all heterogeneous methods.
 Node.js 19 is officially released, let's talk about its 6 major features!
Nov 16, 2022 pm 08:34 PM
Node.js 19 is officially released, let's talk about its 6 major features!
Nov 16, 2022 pm 08:34 PM
Node 19 has been officially released. This article will give you a detailed explanation of the 6 major features of Node.js 19. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Let's talk about the GC (garbage collection) mechanism in Node.js
Nov 29, 2022 pm 08:44 PM
Let's talk about the GC (garbage collection) mechanism in Node.js
Nov 29, 2022 pm 08:44 PM
How does Node.js do GC (garbage collection)? The following article will take you through it.
 Let's talk about the event loop in Node
Apr 11, 2023 pm 07:08 PM
Let's talk about the event loop in Node
Apr 11, 2023 pm 07:08 PM
The event loop is a fundamental part of Node.js and enables asynchronous programming by ensuring that the main thread is not blocked. Understanding the event loop is crucial to building efficient applications. The following article will give you an in-depth understanding of the event loop in Node. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 What should I do if node cannot use npm command?
Feb 08, 2023 am 10:09 AM
What should I do if node cannot use npm command?
Feb 08, 2023 am 10:09 AM
The reason why node cannot use the npm command is because the environment variables are not configured correctly. The solution is: 1. Open "System Properties"; 2. Find "Environment Variables" -> "System Variables", and then edit the environment variables; 3. Find the location of nodejs folder; 4. Click "OK".




