 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 This article will give you a brief analysis of deep copying and shallow copying in JavaScript arrays
This article will give you a brief analysis of deep copying and shallow copying in JavaScript arrays
This article will give you a brief analysis of deep copying and shallow copying in JavaScript arrays
When using JavaScript to operate on arrays, we often need to back up the array. The following article will take you through deep copying and shallow copying in JavaScript arrays. I hope it will be helpful to you!

Introducing the deep copy and shallow copy of arrays, first of all, I will review the data types
Data types
1. Basic data types: number string boolean null undefined
- Storage method: Basic data types are stored in stack memory
Variables store the value
2. Reference data type: function array Object (introduced in the next article)
- Storage method: The reference data type is stored in heap memory
The variable stores the address. [Related recommendations: javascript learning tutorial]
As for the storage method, let’s analyze it:
First Let me introduce stack memory and heap memory to everyone, for understanding:
Stack memory: The memory space where the engine works when executing code. In addition to the engine, it is also used to save basic values and reference type values. the address of.
Heap memory: used to save a set of unordered and unique reference type values, which can be obtained using the key name in the stack.
Let’s look at it again:
var a = 2;
var b = a;
b++;//3
console.log(a); //2Analysis and analysis, assign the value of a to b, and then change the value of b, the value of a is not affected. But for reference data types, this is not the case. What is assigned is the address.
var arr = [1,2,3] ;
var arr2 = arr ;
arr2.push(4) ;
console.log(arr); // arr发生了改变Analysis and analysis, what arr copies is an address. What is an address? It can be compared to a room. Both arr and arr2 point to this room. If the structure of this room is changed, arr and arr2 will be affected. As shown below
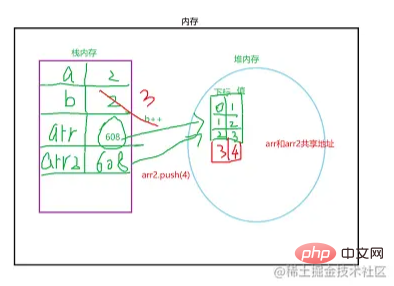
After understanding the above, then focus on
Deep copy and shallow copy
- Shallow copy of the array: only the address (shared address) is copied
- Deep copy of the array: copy the value
Traverse (store the value in the original array New array) var arr2 = [] ;
slice() intercepts all the values in the array and gets a new array. It is to open up a new space in the heap memory.
Shallow copy of array:
Only the address (shared address) is copied
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5] ;
// 数组的浅复制 --- 只是复制了地址
var arr2 = arr ;
//改变其中一个数组,两个数组都会改变,It is still very simple to understand shallow copy.
Deep copy of array:
Copy the values in the array
1. Define a new empty array, traverse the original array and assign the value to the new array Array
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
var arr3 = [];
arr.forEach(function(v) {
arr3.push(v)
})
console.log(arr3);
arr3.push('a');
console.log(arr, arr3);//arr[1,2,3,4,5],arr3[1,2,3,4,5,'a']Change the value in the new array, the original array will not change
2, slice() intercept all the values in the array, and get a new array
var arr3 = arr.slice() ;
console.log(arr3);
arr3.push('a') ;
console.log(arr3);//[1,2,3,4,5,'a']
console.log(arr);//[1,2,3,4,5]Change the value in the new array, the original array will not change
Let me mention it here:
The basic data type is passed by value. The reference data type transfers the address (the shared address of formal parameters and actual parameters)
Difficulties and difficulties, deep copying of multi-dimensional arrays, the above mentioned are all deep copying and Shallow copy
Two-dimensional array:A two-dimensional array is essentially an array with an array as an array element, that is, an "array of arrays", for example: arr=[ [1,2,3],[1,2],[1,2,3,4]]
Analyze the following code, which is a two-dimensional array traversal. The variables i and j represent, and the subscript is i The j-th element in the element (that is, the array).
var arr = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[2, 3, 4]
]
for (var i in arr) {
for (var j in arr[i]) {
console.log(arr[i][j]);
}
}Multi-dimensional array: Arrays of three dimensions and above
##Deep copy of multi-dimensional array
Deep copying of multi-dimensional arrays is not as easy to judge as one-dimensional arrays, because you cannot judge whether the elements in the array are arrays. There are arrays in arrays, endless, haha, so you need to use the previously mentioned recursion. Methods used:
Array.isArray(arr[i])Judge the array and return a Boolean value.
<script>
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, [5, 6, [7, 8]]];
var arr2 = arr.slice();
function deepArr(arr) {
var newArr = [];
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// newArr.push(arr[i]) 这个arr[i]有可能还是一个数组
if (Array.isArray(arr[i])) {
// 继续遍历数组 ,还是得到一个数组
var list = deepArr(arr[i]);
// 再把得到的数组放入newArr
newArr.push(list)
} else {
newArr.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return newArr
}
var res = deepArr(arr);
res[4].push('a');
console.log(res);//改变
console.log(arr);//不改变
</script>Programming Video! !
The above is the detailed content of This article will give you a brief analysis of deep copying and shallow copying in JavaScript arrays. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 PHP array copy strategy: deep copy and shallow copy, parsing and performance comparison
May 02, 2024 pm 02:57 PM
PHP array copy strategy: deep copy and shallow copy, parsing and performance comparison
May 02, 2024 pm 02:57 PM
In PHP, there are two strategies for array copying: deep copying and shallow copying. A deep copy creates an independent copy of the source array, and changes to one array do not affect the other array. Shallow copy only copies the references of the arrays, changes to one array are reflected in the other array. Deep copy requires traversing the array and creating new entities, so it is more resource intensive than shallow copy, but shallow copy can only copy references, so it is faster. Deep copy is used to create an independent collection of database records, while shallow copy is used to pass an array to a function.
 How to remove duplicate elements from PHP array using foreach loop?
Apr 27, 2024 am 11:33 AM
How to remove duplicate elements from PHP array using foreach loop?
Apr 27, 2024 am 11:33 AM
The method of using a foreach loop to remove duplicate elements from a PHP array is as follows: traverse the array, and if the element already exists and the current position is not the first occurrence, delete it. For example, if there are duplicate records in the database query results, you can use this method to remove them and obtain results without duplicate records.
 The Art of PHP Array Deep Copy: Using Different Methods to Achieve a Perfect Copy
May 01, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
The Art of PHP Array Deep Copy: Using Different Methods to Achieve a Perfect Copy
May 01, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
Methods for deep copying arrays in PHP include: JSON encoding and decoding using json_decode and json_encode. Use array_map and clone to make deep copies of keys and values. Use serialize and unserialize for serialization and deserialization.
 PHP array key value flipping: Comparative performance analysis of different methods
May 03, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
PHP array key value flipping: Comparative performance analysis of different methods
May 03, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
The performance comparison of PHP array key value flipping methods shows that the array_flip() function performs better than the for loop in large arrays (more than 1 million elements) and takes less time. The for loop method of manually flipping key values takes a relatively long time.
 Application of PHP array grouping function in data sorting
May 04, 2024 pm 01:03 PM
Application of PHP array grouping function in data sorting
May 04, 2024 pm 01:03 PM
PHP's array_group_by function can group elements in an array based on keys or closure functions, returning an associative array where the key is the group name and the value is an array of elements belonging to the group.
 Best Practices for Deep Copying PHP Arrays: Discover Efficient Methods
Apr 30, 2024 pm 03:42 PM
Best Practices for Deep Copying PHP Arrays: Discover Efficient Methods
Apr 30, 2024 pm 03:42 PM
The best practice for performing an array deep copy in PHP is to use json_decode(json_encode($arr)) to convert the array to a JSON string and then convert it back to an array. Use unserialize(serialize($arr)) to serialize the array to a string and then deserialize it to a new array. Use the RecursiveIteratorIterator to recursively traverse multidimensional arrays.
 PHP array multi-dimensional sorting practice: from simple to complex scenarios
Apr 29, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
PHP array multi-dimensional sorting practice: from simple to complex scenarios
Apr 29, 2024 pm 09:12 PM
Multidimensional array sorting can be divided into single column sorting and nested sorting. Single column sorting can use the array_multisort() function to sort by columns; nested sorting requires a recursive function to traverse the array and sort it. Practical cases include sorting by product name and compound sorting by sales volume and price.
 PHP array merging and deduplication algorithm: parallel solution
Apr 18, 2024 pm 02:30 PM
PHP array merging and deduplication algorithm: parallel solution
Apr 18, 2024 pm 02:30 PM
The PHP array merging and deduplication algorithm provides a parallel solution, dividing the original array into small blocks for parallel processing, and the main process merges the results of the blocks to deduplicate. Algorithmic steps: Split the original array into equally allocated small blocks. Process each block for deduplication in parallel. Merge block results and deduplicate again.



