How to implement the token bucket algorithm using Redis? (with code)
This article will share with you the principle of the token bucket algorithm and introduce the method of using Redis to implement the token bucket algorithm. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

Among the current limiting algorithms, there is a token bucket algorithm, which can deal with short bursts of traffic, which is particularly useful in real-life environments where the traffic is not very uniform. , the current limit will not be triggered frequently, and it is more friendly to the caller.
For example, the current limit is 10qps. Most of the time it will not exceed this amount, but occasionally it will reach 30qps and then return to normal soon. It is assumed that this burst of traffic will not have an impact on system stability. , we can allow this instantaneous burst traffic to a certain extent, thereby bringing a better availability experience to users. This is where the token bucket algorithm comes in.
Token Bucket Algorithm Principle
As shown in the figure below, the basic principle of the algorithm is: there is a token bucket with a capacity of into this bucket. If the number of tokens in the bucket exceeds X, then it will be discarded. When processing a request, you need to first remove the token from the token bucket. If you get the token, continue processing; if you cannot get the token, reject the request.
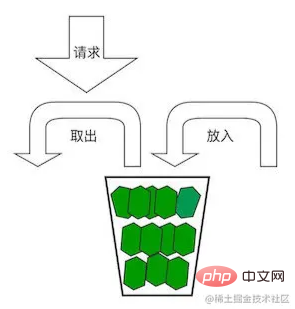
It can be seen that it is particularly important to set the number of X, Y and Z in the token bucket algorithm. Z should be slightly larger than the number of requests per Y unit time, and the system will be in this state for a long time; This indicates that the traffic has exceeded expectations, and the cause needs to be investigated promptly and corresponding measures taken.
Redis implements the token bucket algorithm
I have seen token buckets implemented by some programs before. The method of putting tokens into the bucket is to start a thread. Increase the number of tokens every Y unit time, or execute this process regularly in Timer. I am not very satisfied with this method. There are two reasons. One is a waste of thread resources, and the other is the inaccurate execution time due to scheduling issues. [Related recommendations: Redis Video Tutorial]
The method to determine the number of tokens in the token bucket is through calculation. First, calculate how much time has passed from the last request to this request. For a long time, whether the time threshold for issuing tokens is reached, then how many tokens are added, and how many of these tokens can be put into the bucket.
Talk is cheap!
Let’s take a look at how it is implemented in Redis. Because it involves multiple interactions with Redis, here in order to improve the throughput of current limiting processing and reduce program and The number of Redis interactions uses Lua script supported by Redis. The execution of Lua script is atomic, so there is no need to worry about dirty data.
The code is excerpted from FireflySoft.RateLimit. It not only supports ordinary master-slave deployment of Redis, but also supports clustered Redis, so throughput can be improved through horizontal expansion. For the convenience of reading, some comments are added here, but there are actually none.
-- 定义返回值,是个数组,包含:是否触发限流(1限流 0通过)、当前桶中的令牌数
local ret={}
ret[1]=0
-- Redis集群分片Key,KEYS[1]是限流目标
local cl_key = '{' .. KEYS[1] .. '}'
-- 获取限流惩罚的当前设置,触发限流惩罚时会写一个有过期时间的KV
-- 如果存在限流惩罚,则返回结果[1,-1]
local lock_key=cl_key .. '-lock'
local lock_val=redis.call('get',lock_key)
if lock_val == '1' then
ret[1]=1
ret[2]=-1
return ret;
end
-- 这里省略部分代码
-- 获取[上次向桶中投放令牌的时间],如果没有设置过这个投放时间,则令牌桶也不存在,此时:
-- 一种情况是:首次执行,此时定义令牌桶就是满的。
-- 另一种情况是:较长时间没有执行过限流处理,导致承载这个时间的KV被释放了,
-- 这个过期时间会超过自然投放令牌到桶中直到桶满的时间,所以令牌桶也应该是满的。
local last_time=redis.call('get',st_key)
if(last_time==false)
then
-- 本次执行后剩余令牌数量:桶的容量- 本次执行消耗的令牌数量
bucket_amount = capacity - amount;
-- 将这个令牌数量更新到令牌桶中,同时这里有个过期时间,如果长时间不执行这个程序,令牌桶KV会被回收
redis.call('set',KEYS[1],bucket_amount,'PX',key_expire_time)
-- 设置[上次向桶中放入令牌的时间],后边计算应放入桶中的令牌数量时会用到
redis.call('set',st_key,start_time,'PX',key_expire_time)
-- 返回值[当前桶中的令牌数]
ret[2]=bucket_amount
-- 无需其它处理
return ret
end
-- 令牌桶存在,获取令牌桶中的当前令牌数
local current_value = redis.call('get',KEYS[1])
current_value = tonumber(current_value)
-- 判断是不是该放入新令牌到桶中了:当前时间-上次投放的时间 >= 投放的时间间隔
last_time=tonumber(last_time)
local last_time_changed=0
local past_time=current_time-last_time
if(past_time<inflow_unit)
then
-- 不到投放的时候,直接从令牌桶中取走令牌
bucket_amount=current_value-amount
else
-- 需要放入一些令牌, 预计投放数量 = (距上次投放过去的时间/投放的时间间隔)*每单位时间投放的数量
local past_inflow_unit_quantity = past_time/inflow_unit
past_inflow_unit_quantity=math.floor(past_inflow_unit_quantity)
last_time=last_time+past_inflow_unit_quantity*inflow_unit
last_time_changed=1
local past_inflow_quantity=past_inflow_unit_quantity*inflow_quantity_per_unit
bucket_amount=current_value+past_inflow_quantity-amount
end
-- 这里省略部分代码
ret[2]=bucket_amount
-- 如果桶中剩余数量小于0,则看看是否需要限流惩罚,如果需要则写入一个惩罚KV,过期时间为惩罚的秒数
if(bucket_amount<0)
then
if lock_seconds>0 then
redis.call('set',lock_key,'1','EX',lock_seconds,'NX')
end
ret[1]=1
return ret
end
-- 来到这里,代表可以成功扣减令牌,则需要更新令牌桶KV
if last_time_changed==1 then
redis.call('set',KEYS[1],bucket_amount,'PX',key_expire_time)
-- 有新投放,更新[上次投放时间]为本次投放时间
redis.call('set',st_key,last_time,'PX',key_expire_time)
else
redis.call('set',KEYS[1],bucket_amount,'PX',key_expire_time)
end
return retThrough the above code, it can be seen that the main processing process is:
1. Determine whether there is a current limit penalty. If so, return directly. If not, go to the next step.
2. Determine whether the token bucket exists. If it does not exist, create the token bucket first, then deduct the token and return it. If it exists, go to the next step.
3. Determine whether tokens need to be issued. If not, the tokens will be deducted directly. If necessary, tokens will be issued first and then the tokens will be deducted.
4. Determine the number of tokens after deduction. If it is less than 0, return the current limit, and set the current limit penalty. If it is greater than or equal to 0, go to the next step.
5. Update the number of tokens in the bucket to Redis.
You can submit and run this Lua script in the Redis library of any development language. If you are using the .NET platform, you can refer to this article: ASP.NET Core Use token bucket rate limit (https://blog.bossma.cn/dotnet/asp-net-core-token-bucket-algorithm-of-rate-limit/).
About FireflySoft.RateLimit
FireflySoft.RateLimit is a current limiting class library based on .NET Standard. Its core is simple and lightweight, and can flexibly cope with various Demand current limiting scenarios.
Its main features include:
- Multiple current limiting algorithms: built-in four algorithms: fixed window, sliding window, leaky bucket, and token bucket, which can also be customized and expanded.
- Multiple counting storage: currently supports two storage methods: memory and Redis.
- Distributed friendly: Supports unified counting of distributed programs through Redis storage.
- Flexible current limiting target: Various data can be extracted from the request to set the current limiting target.
- Support current limiting penalty: you can lock the client for a period of time after triggering current limiting and not allow access.
- Dynamic change rules: Supports dynamically changing current limiting rules while the program is running.
- Customized error: You can customize the error code and error message after triggering the current limit.
- Universal applicability: In principle, it can meet any scenario that requires current limiting.
Github open source address: https://github.com/bosima/FireflySoft.RateLimit/blob/master/README.zh-CN.md
This article is reproduced from: https://juejin.cn/post/7039105263168651301
Author: Yinghuo Architecture
For more programming-related knowledge, please visit: Programming video! !
The above is the detailed content of How to implement the token bucket algorithm using Redis? (with code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to solve data loss with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
Redis data loss causes include memory failures, power outages, human errors, and hardware failures. The solutions are: 1. Store data to disk with RDB or AOF persistence; 2. Copy to multiple servers for high availability; 3. HA with Redis Sentinel or Redis Cluster; 4. Create snapshots to back up data; 5. Implement best practices such as persistence, replication, snapshots, monitoring, and security measures.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.




