When can I use custom instructions in Vue?
The logic of using custom instructions is the same as the logic of using event modifiers. When there is logic related to operating DOM/BOM in methods, it needs to be abstracted into a custom instruction so that it can be easily Business logic is decoupled from related DOM operations and makes it easier to unit test.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, vue2.9.6 version, DELL G3 computer.
1. How to create a custom directive
#Create a directive globally through Vue.directive, the first parameter of Vue.directive The name of the directive is defined. The following code creates a directive named resize.
Vue.directive("resize", {
});After registering this directive globally, it means that this directive can be used in any component. You can use the directive directly in the template of a single-file component, or you can use the directive in JSX. . By convention, the instruction name is prefixed with "v-", which is used to indicate that it is a prefix.

2. When to use custom instructions
Regarding when to use custom instructions, the logic is the same as that of using event modifiers.
The use of event modifiers is largely to make our code appear data-driven and easy to test. The logic of the DOM is delegated separately and agreed to some specific modifiers. . (Notes related to event modifiers: https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxuStudy/p/13233379.html#oneone)
In fact, the same logic applies to custom instructions. When there is logic related to operating DOM/BOM in our methods, we should consider whether it can be abstracted into a custom instruction to decouple the business logic from related DOM operations and make it easier to be unit tested.
3. Hook function
Vue strictly follows the design pattern here The opening and closing principle allows developers to operate components at different times through agreed hook functions. (Vue official website hook function related: https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/custom-directive.html#Hook function)
1. Hook function
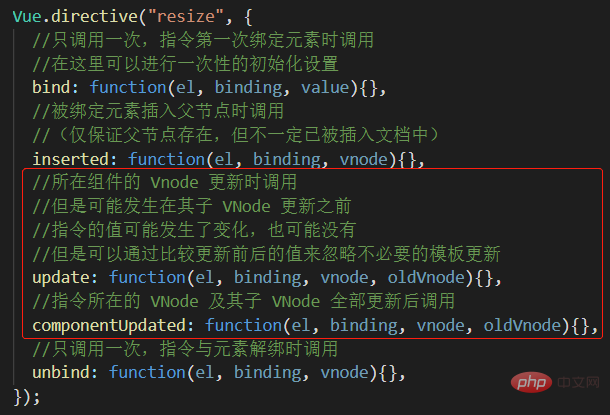
Vue.directive("resize", {
//只调用一次,指令第一次绑定元素时调用
//在这里可以进行一次性的初始化设置
bind: function(el, binding, value){},
//被绑定元素插入父节点时调用
//(仅保证父节点存在,但不一定已被插入文档中)
inserted: function(el, binding, vnode){},
//所在组件的 Vnode 更新时调用
//但是可能发生在其子 VNode 更新之前
//指令的值可能发生了变化,也可能没有
//但是可以通过比较更新前后的值来忽略不必要的模板更新
update: function(el, binding, vnode, oldVnode){},
//指令所在的 VNode 及其子 VNode 全部更新后调用
componentUpdated: function(el, binding, vnode, oldVnode){},
//只调用一次,指令与元素解绑时调用
unbind: function(el, binding, vnode){},
});Hook function example
Let’s first look at the first pair of hook functions, bind and unbind functions. As the names suggest, these two hook functions It is called when the element declared by this directive is bound and unbound, and it should be remembered that both bind and unbind will only be called once.

Next, look at the hook function inserted. Normally, inserted is called after bind.
The difference between bind and inserted is: the parameter el.parentNode in bind is null, and the parent node of the current node can be accessed through el.parentNode in inserted. When there is information that needs to be stored on the parent node and the parent node needs to be accessed, inserted is used more frequently than bind .

Let’s look at the last set of hook functions update and componentUpdate. This pair of hook functions will be called before and after the vnode is updated. .
Compared with other hook functions, update and componentUpdate pass in one more parameter, oldVnode. oldVnode represents the previous Virtual DOM node information, and vnode represents the current Virtual DOM node information. You can determine whether the template needs to be updated by comparing the difference between oldVnode and vnode to reduce unnecessary template updates and thereby improve component performance to a certain extent.
2. 钩子函数参数
function(
// 指令所绑定的元素,可以用来直接操作 DOM
el,
// binding 一个对象,包含以下属性
{
// 指令名,不包括 -v 前缀
name,
// 指令的绑定值,例如:v-my-directive="1+1"中,绑定值为 2
value,
// 指令绑定的前一个值
// 仅在 update 和 componentUpdated 钩子中可用
oldValue,
//字符串形式的指令表达式
//例如 v-my-directive="1+1" 中,表达式为 "1+1"
expression,
//例如指令的参数,可选。
//例如 v-my-directive:foo 中,参数为 "foo"
arg,
//一个包含修饰符的对象
//例如:v-my-directive.foo.bar 中,
//修饰符对象为 {foo: true, bar: true}
modifiers
},
//Vue 编译生成的虚拟节点
vnode,
//上一个虚拟节点,仅在 update 和 componentUpdated 钩子中可用
oldVnode
)钩子函数参数
除了 el 之后,其它参数都应该是只读的,切勿进行修改。如果需要在钩子之间共享数据,建议通过元素的 dataset 来进行。

【相关推荐:《vue.js教程》】
The above is the detailed content of When can I use custom instructions in Vue?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
You can query the Vue version by using Vue Devtools to view the Vue tab in the browser's console. Use npm to run the "npm list -g vue" command. Find the Vue item in the "dependencies" object of the package.json file. For Vue CLI projects, run the "vue --version" command. Check the version information in the <script> tag in the HTML file that refers to the Vue file.
 How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
There are three common methods for Vue.js to traverse arrays and objects: the v-for directive is used to traverse each element and render templates; the v-bind directive can be used with v-for to dynamically set attribute values for each element; and the .map method can convert array elements into new arrays.




