
This article brings you relevant knowledge about mysql database commands. It lists many commonly used commands. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

1.Connect to database
mysql -u username -p password
2. Show existing databases
show databases;
3.Create database
create database sqlname;
4.Select database
use database sqlname;
5. Display the tables in the database (select the database first)
show tables;
6. Display the version information of the current database and the connecting user Name
select version(),user();
7. Delete the database (deletion without prompt when deleting)
drop database sqlname;
1. Create table
(1) Syntax:
create table tablename(
Field 1 Data type field Attribute
…
Field n
);
(2) Note:
1. To prevent conflicts with reserved words when creating a table, enclose it with ''
2. Single-line comments : #…
Multi-line comments: /…/
3. When creating a table, separate multiple fields with English commas, and do not use commas in the last line.
(3) Field constraints and attributes
1. Non-null constraintsnot null (fields are not allowed to be empty)
2.Default constraintsdefault(set default value)
3. Unique constraintunique key(uk)(The value of the set field is unique and can be empty, but there can only be one empty value)
4. Primary key constraintprimary key(pk)(as the unique identifier of table records)
5. Foreign key constraintsforeign key(fk)(used to establish a relationship between two tables, a reference needs to be specified Which field in the main table. InnoDB supports foreign keys in the database storage engine, but MyISAM does not support foreign keys.
The field used as a foreign key must be the primary key in the main table (single field primary key))
Add foreign key constraints:
CONSTRAINT FK_Foreign key name FOREIGN KEY (foreign key field in the word table) REFERENCES associated table name (associated field).
Explosive collection of MySQL database commands (summary sharing) is used as the foreign key of the word table 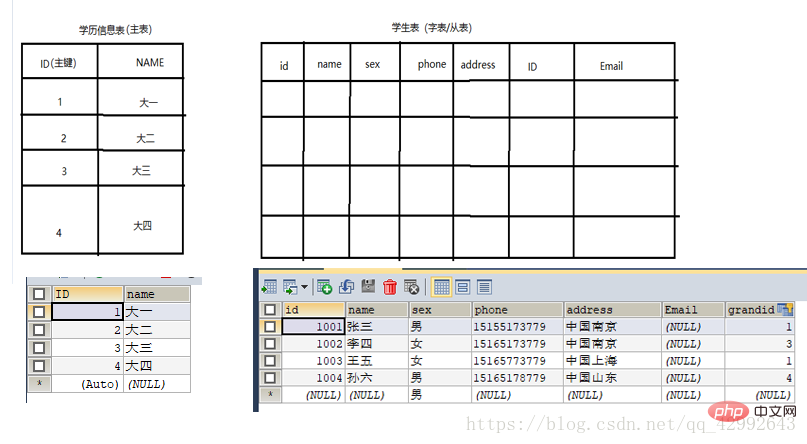
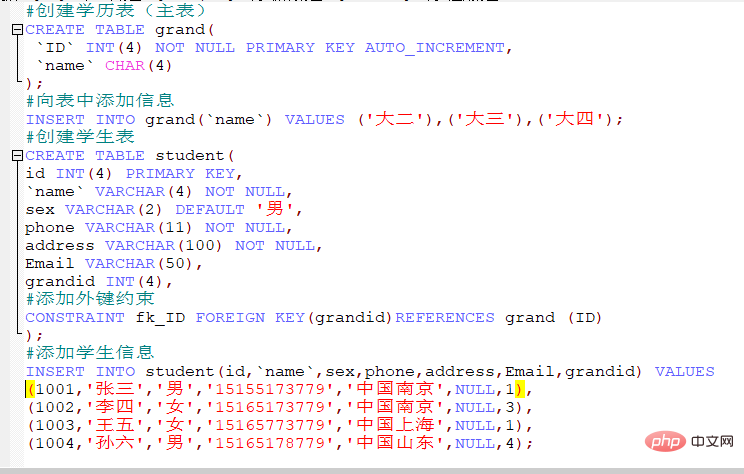
1.Set auto_increment=n, starting from n.
2.Set auto-increment set @@ auto_increment_increment=m, the step size is m. 
3. Multi-field setting primary key: primary key (Field 1, Field 2...Field n)
4. Comments/explanatory text in the table :)comment="Description";
5. Set the character set:)charset="Character set";
6. View the structure of the table:describe'table name'/desc table name
7. View the database definition: show create database sqlname;
8. View the data table definition: show create table tablename ;
9. View the default storage engine: show variables like'storage_engine%';
11. Specify the storage engine of the table:)engine=storage engine;
10. Delete table: drop table 'tablename';
11. Get current date: now();
12. Modify table:
(1) Modify table name: alter table old table name rename new table name;
(2) Add fields: alter table table name add field name data type...;(Add new Fields)
(3) Modify fields: alter table table name change original field name new field name data type...;
(4) Delete fields: alter table Table name drop field name;
(5) Add primary key constraints after creating the table:
alter table table name add constraint primary key name primary key table name (primary key field);
(6) After creating the table, add a foreign key constraint (the field used as a foreign key must be the primary key in the main table (single field primary key)):
alter table table name add constraint foreign key name foreign key (foreign key field) references associated table name (associated field);
1. Insert a single row of data:
insert into table name (field Name list (comma separated)) values (value list (comma separated));
2. Insert multiple rows of data:
insert into table name (field name list) values (value List 1), … ,(value list n);
3. Insert the query results into the new table:
create table new table (select field 1, … ,from original table) ;
查询student表中的id,name,sex,phone数据插入到newstudent表中: CREATE TABLE newstudent(SELECT id,`name`,sex,phone FROM student);
3. Update data (modify data):
update table name set column name = update value where update condition;
修改newstudent表中id=1001的数据名字为tom: UPDATE newstudent SET `name`='tom' WHERE id=1001;
4 .Delete data
(1)delete from table name where deletion condition;
delete deletes the entire data, not just a single column.
删除newstudent表中名字为tom的数据: DELETE FROM newstudent WHERE `name`='tom';
(2) Truncate table deletes data:
truncate table deletes all rows in the table, but the structure, columns, constraints, indexes, etc. of the table will not change. Cannot be used for tables with foreign key constraints. Deleted data cannot be recovered.
truncate table table name where deletion condition;
1.使用select查询
select 列名/表达式/函数/常量 from 表名 where 查询条件 order by 排序的列名asc/desc;
(1)查询所有的数据行和列:
select * from 表名;
(2)查询部分行和列:
select 列名… from 表名 where 查询条件;
(3)在查询中使用列的别名:
select 列名 AS 新列名 form 表名 where 查询条件;
计算,合并得到新的列名:
select 列名1+’.’+列名2 AS 新列名 from 表名;
(4)查询空值:
通过is null 或者 is not null 判断列值是否为空
查询student表中Email为空的学生姓名: SELECT `name` FROM student WHERE Email IS NULL;
2.分组查询
#查询不同课程的平均分,最低分,最高分,并查询出平均分大于80分的课程 SELECT r.subjectno,sub.`SubjectName` 课程名称,AVG(StudentResult) 平均分, MAX(StudentResult) 最高分,MIN(StudentResult) 最低分 FROM result r INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON r.`SubjectNo`=sub.`SubjectNo` GROUP BY r.subjectno #where AVG(StudentResult)>=80出现错误, #分组查询group by 在where语句后, #group by 约束条件使用having语句 HAVING AVG(StudentResult)>=80;
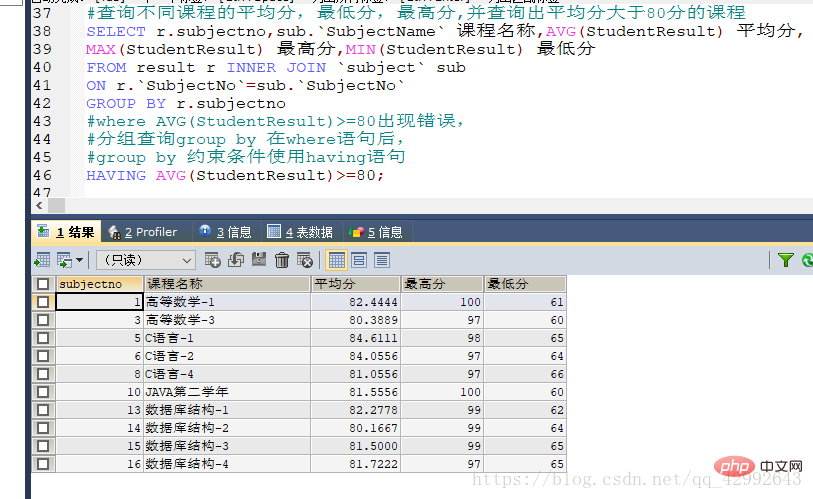
1.聚合函数:
(1)AVG (平均值):select avg(列名)from 表名
假设列名为成绩 则查询到的是表中所有成绩的平均值。
(2)count 返回某字段的行数
(3)max 返回某字段的最大数
(4)min 返回某字段的最小值
(5)sum 返回某字段的和。
2.字符串函数:
(1)concat() 连接字符串s1,s2…sn为一个完整的字符串。
(2)insert(s1,p1,n,news)将字符串s1从p1位置开始,n个字符长的字串替换为字符串news。
(3)lower(s)将字符串s中的所有字符改为小写。
(4)upper(s)将字符串s中的所有字符改为大写。
(5)substring(s,num,len)返回字符串s的第num个位置开始长度为len的子字符串。
3.时间日期函数:
(1)获取当前日期:curdate();
(2)获取当前时间:curtime();
(3)获取当前日期和时间:now();
(4)返回日期date为一年中的第几周:week(date);
(5)返回日期date的年份:year(date);
(6)返回时间time的小时值:hour(time);
(7)返回时间time的分钟值:minute(time);
(8)返回日期参数(date1和date2之间相隔的天数):datediff(date1,date2);
(9)计算日期参数date加上n天后的日期:adddate(date,n);
4.数学函数
(1)返回大于或等于数值x的最小整数:ceil(x);
(2)返回小于或等于数值x的最大整数:floor(x);
(3)返回0~1之间的随机数:rand();
order by 子句
order by子句按照一定的顺序排列查询结果,asc升序排列,desc降序排列。
limit子句
显示指定位置指定行数的记录。
select 字段名列表 form 表名 where 约束条件 group by分组的字段名 order by 排序列名 limit 位置偏移量,行数;
#查询学生信息里gid=1按学号升序排列前四条记录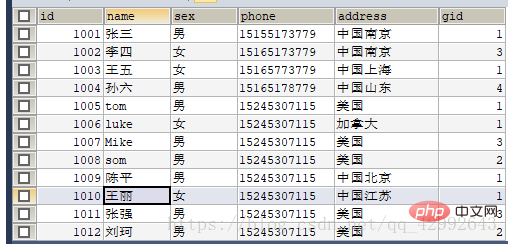
#查询学生信息里gid=1按学号升序排列前四条记录(步长) SELECT id,`name` FROM `student1` WHERE gid=1 ORDER BY id LIMIT 4; (查询表里全部信息中gid=1的前四个学生)
查询结果: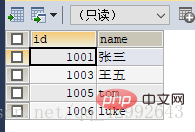
#查询学生信息里gid=1按学号升序排列前四条记录(位置偏移量,步长) SELECT id,`name` FROM `student1` WHERE gid=1 ORDER BY id LIMIT 4,4; (查询表中全部信息gid=1前四条以后的全部信息中的前四条学生信息)
查询结果: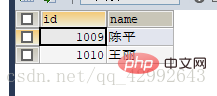
in子查询******not in 子查询
使用in关键字可以使父查询匹配子查询返回的多个单字段值。
解决使用比较运算符(=,>等),子查询返回值不唯一错误信息。
like模糊查询
LIKE语句语法格式:select * from 表名 where 字段名 like 对应值(子串)。
它主要是针对字符型字段的,它的作用是在一个字符型字段列中检索包含对应子串的。
A:% 包含零个或多个字符的任意字符串: 1、LIKE’Mc%’ 将搜索以字母 Mc 开头的所有字符串(如 McBadden)。
2、LIKE’%inger’ 将搜索以字母 inger 结尾的所有字符串(如 Ringer、Stringer)。
3、LIKE’%en%’ 将搜索在任何位置包含字母 en 的所有字符串(如 Bennet、Green、McBadden)。
B:_(下划线) 任何单个字符:LIKE’_heryl’ 将搜索以字母 heryl 结尾的所有六个字母的名称(如 Cheryl、Sheryl)。
C:[ ] 指定范围 ([a-f]) 或集合 ([abcdef]) 中的任何单个字符:、
1,LIKE’[CK]ars[eo]n’ 将搜索下列字符串:Carsen、Karsen、Carson 和 Karson(如 Carson)。
2、LIKE’[M-Z]inger’ 将搜索以字符串 inger 结尾、以从 M 到 Z 的任何单个字母开头的所有名称(如 Ringer)
***D:[^] 不属于指定范围 ([a-f]) 或集合 ([abcdef]) 的任何单个字符:LIKE’M[^c]%’ 将搜索以字母 M 开头,并且第二个字母不是 c 的所有名称(如MacFeather)。
E: 它同于DOS命令中的通配符,代表多个字符:cc代表cc,cBc,cbc,cabdfec等多个字符。
F:?同于DOS命令中的?通配符,代表单个字符 :b?b代表brb,bFb等
G:# 大致同上,不同的是代只能代表单个数字。k#k代表k1k,k8k,k0k 。
F:[!] 排除 它只代表单个字符
下面我们来举例说明一下:
例1,查询name字段中包含有“明”字的。
select * from table1 where name like ‘%明%’
例2,查询name字段中以“李”字开头。
select * from table1 where name like '李’
例3,查询name字段中含有数字的。
select * from table1 where name like ‘%[0-9]%’
例4,查询name字段中含有小写字母的。
select * from table1 where name like ‘%[a-z]%’
例5,查询name字段中不含有数字的。
select * from table1 where name like ‘%[!0-9]%’
可以自定义转移符----》escape’自定义转移符’
distinct------》去除重复项
between*and模糊查询
操作符 BETWEEN … AND 会选取介于两个值之间的数据范围。这些值可以是数值、文本或者日期。
null ,not null查询
-- 查询手机号不为null的用户数据 SELECT * from user where phone is not null; -- 查询手机号为null的用户数据 SELECT * from user where phone is null;
exists 子查询 not exists子查询
exists子查询用来确认后边的查询是否继续进行
drop table if exists test—>判断是否存在表test,如果存在就删除。
not exists实现取反操作。对不存在对应查询条件的记录。
多表连接查询是通过各个表之间共同列的关联性来查询数据。
1.内连接查询
内连接查询根据表中共同的列进行匹配。取两个的表的交集。两个表存在主外键关系是通常使用内连接查询。
内连接使用inner join…on 关键字或者where子句来进行表之间的关联。
inner 可省略 on 用来设置条件。
(1)在where子句中指定连接条件
(2)在from中使用inner join…on关键字
#查询学生姓名和成绩 SELECT studentname,studentresult FROM student s,result r WHERE s.`StudentNo`=r.`StudentNo`
#在from中使用inner join....on关键字 SELECT s.`StudentName`,r.`StudentResult` ,r.`SubjectNo`FROM student s INNER JOIN result r ON s.`StudentNo`=r.`StudentNo`
两种方法查询结果相同。
2.外连接查询
外连接查询中参与连接的表有主从之分,已主表的每行数据匹配从表的数据列,将符合连接条件的数据直接返回到结果集中,对不符合连接条件的列,将被填上null值再返回到结果集中。
(1)左外连接查询
left join…on 或者left outer join…on关键字进行表之间的关联。
SELECT s.`StudentName`,r.`StudentResult` ,r.`SubjectNo`FROM student s LEFT JOIN result r ON s.`StudentNo`=r.`StudentNo`
将没有成绩的学生成绩查出。
(2)右外连接查询
右外连接包含右表中所有的匹配行,右表中有的项在左表中没有对应的项将以null值填充。
right join…on 或right outer join…on关键字进行表之间的关联。
(3)自连接
把一个表作为两个表使用。
#创建一个表 CREATE TABLE book( id INT(10), sort INT(10), books VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL ); #插入数据 INSERT INTO book VALUES (2,1,'古文书'), (3,1,'现代书'), (4,2,'《三字经》'), (5,2,'《唐诗三百首》'), (6,3,'《我与地坛》'), (7,2,'《游大林寺》'), (8,2,'《王右军年减十岁时》'), (9,3,'《致橡树》'); #查询结果为: #书籍类型 书籍名 #古文书 三字经.... #现代书 我与地坛.... SELECT a.books 书籍类型, b.books 书籍名 FROM book a,book b WHERE a.id=b.sort;
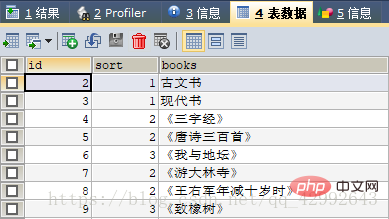
自连接查询结果: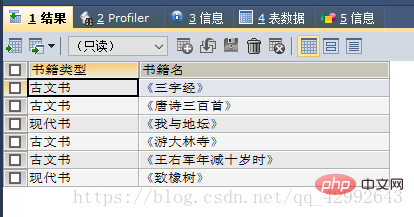
1. Transaction
Transaction refers to bundling a series of data operations into a whole for unified management.
Submit or cancel the creation request to the system together with all commands as a whole.
Transaction properties: atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability.
The myISA storage engine does not support transactions.
Turn off automatic transaction submission: set autocommit=0;
(1) Start transaction: begin/start transaction;
(2) Submit transaction: commit;
(3) Rollback/ Undo transaction: rollback;
Resume automatic submission: set autocommit=1;
Set the result set to? ? Encoding format display: set names? ? ;
2. View
A view is a method of viewing data in one or more tables in a database. A view is a virtual table created as a subset of rows or columns from one or more tables. Views act as table filters in queries.
(1) Create a view: create view view name as
Create index:
create [Index type] index index name on table name (column to create index);
Or add after the column when creating the table Index type.
Or modify the table alter table table name add index index name (index column);
Delete index: drop index index name;
View index: show index from table name;
4. Database backup and recovery
1. Use the mysqldump command to back up the database
mysqldump -u -p database name>Backup database location and name;
Table data export To the text file
select *from table name where query conditions into outfile backup database location and name;
2. Use the mysql command to restore the database (create a new database first )
mysql -u -p Newly created database name
source database backup file;
Create new user
#Create local user
CREATE USER `user`@`localhost` IDENTIFIED BY '123123';
#Users can log in to any Remote host, use wildcard %
CREATE USER `user2`@`123%` IDENTIFIED BY '123123';
#authorize all permissions to the user
GRANT ALL ON mysql.`user` TO `user2`@`123%`;
#Authorize the created user
GRANT SELECT,INSERT ON mysql.`user` TO `user2`@` 123%`;
#Authorization when creating a user
GRANT SELECT,INSERT ON mysql.`user` TO `user_2`@`123%` IDENTIFIED BY '123123';
#Delete user user2 (you must have database global permissions or select permissions when using the delete statement)
DROP USER `user2`@`123%`;
DROP USER `user_2`@` 123%`;
DROP USER `user`@`localhost`;
#mysqladmin changes the super user user2 account password (the mysqladmin command is used in cmd and can only change the super user password)
mysqladmin -u root -p PASSWORD "123456";
#Modify the current login user password
SET PASSWORD =PASSWORD("123456");
#Modify other user passwords
SET PASSWORD FOR `user2`@`123%`=PASSWORD("123456");
Recommended learning: mysql video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Explosive collection of MySQL database commands (summary sharing). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!