 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 Linux installation of docker and summary of basic operations of docker
Linux installation of docker and summary of basic operations of docker
Linux installation of docker and summary of basic operations of docker
This article brings you how to install docker on Linux and the basic operations of docker. I hope it will be helpful to you.

1. Install docker
Docker is required to run on Centos 7, the system is required to be 64-bit, and the system kernel version is 3.10 or above
1.uname -an View the current system version
2.yum -y install docker Download and install docker
3.service docker start Start the docker service
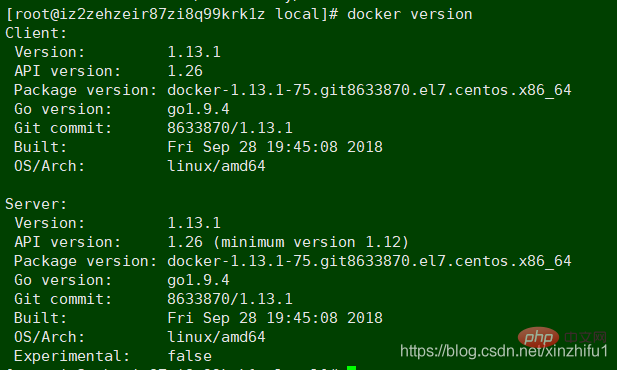
4.docker version Check whether docker is installed successfully
When you see the information in the picture below, it means The local docker has been installed successfully, it is very simple
2. Mirror operation
Creating a container must be based on the image, so first Let’s talk about the operation of docker images
Search for images
docker images ll Check whether the local machine already has an image
Currently there is no image in the machine, go to Docker Hub to download (the image can also be customized, I won’t go into details here)
docker search java , you can also specify a specific version to download,
For example: docker search Ubuntu: 1.2.5.4, you can search docker Hub and many images will be listed
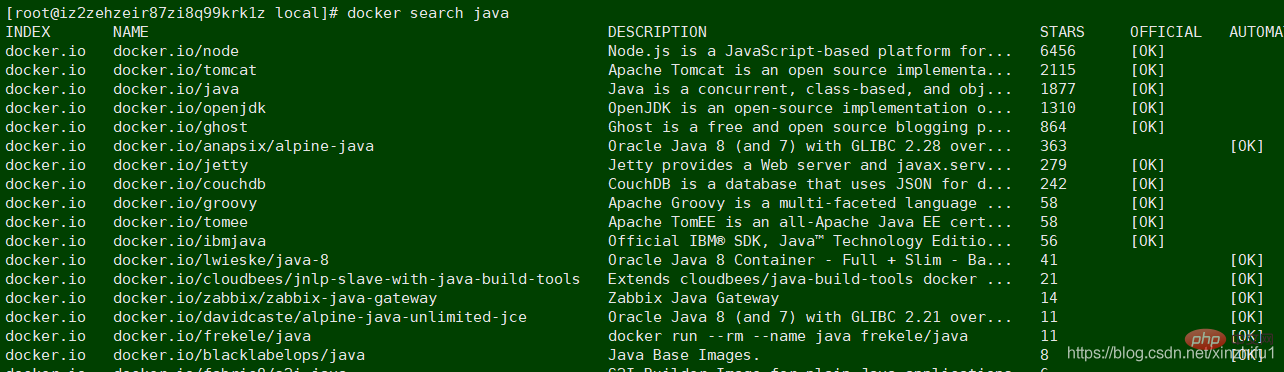
Download the image
docker pull docker.io/nginx to download
The image downloaded locally is larger than the one searched on docker Hub because it is automatically decompressed during the download process , when viewing the image list, you will see the image you just downloaded
The list includes the warehouse name, version label, image ID, creation time and occupied space

##Delete image
Delete useless image docker rmi image id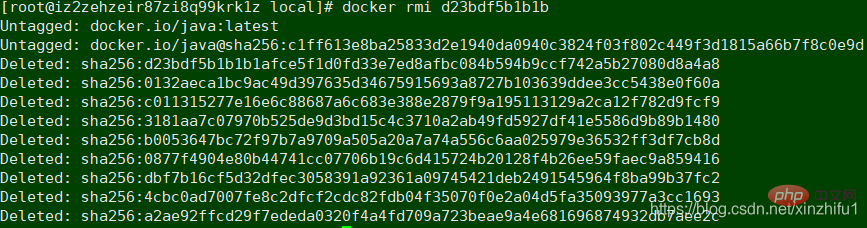
We have downloaded the Nginx image earlier, and then we will create a container with only Nginx application docker run -i -t
docker run -idt --name container_nginx -p 8080:80 docker.io/nginx
Note: There are two - in front of the name, -p in front of the port, docker.io/nginx is the image name, 8080 is the port of the host, and 80 is the port of the Nginx application
A port on the host can only be mapped to one container port, and multiple container ports cannot correspond to one host port (if the container is installed on a centos-like system, the container port can be set casually, but if the container is It is just a simple application, then the container port should be the port of the application itself)

exit 退出容器 docker ps 查看运行中的容器 docker ps -a 查看运行中和非运行中的所有容器 docker exec -it container_nginx /bin/bash 进入容器 如果容器还未启动 执行docker start container_nginx
whereis nginx 找Nginx的启动目录 [root@iz2zehzeir87zi8q99krk1z ~]# docker start container_nginx container_nginx [root@iz2zehzeir87zi8q99krk1z ~]# docker exec -it container_nginx /bin/bash root@84683e425116:/# whereis nginx nginx: /usr/sbin/nginx /usr/lib/nginx /etc/nginx /usr/share/nginx root@84683e425116:/# /usr/sbin/nginx
/ sbin / iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 8080 -j ACCEPT
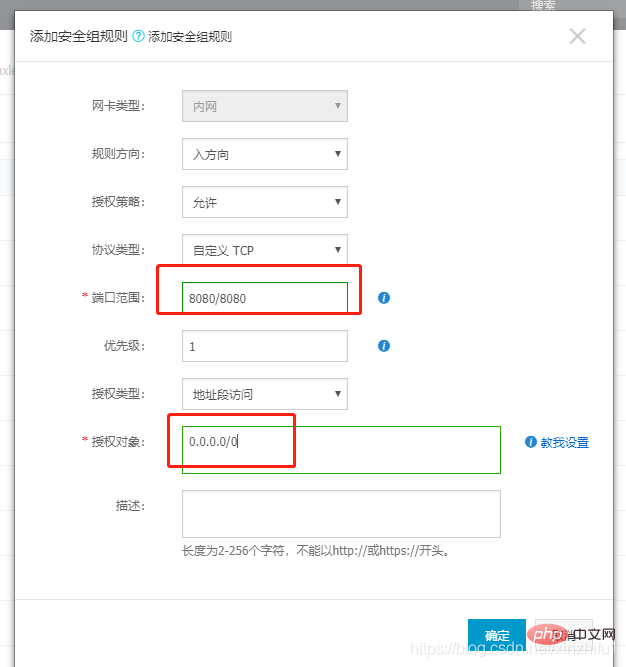
Delete container
容器删除之前先将容器停止 docker stop container_nginx 或者是容器的id docker rm -f container_nginx 容器删除
The difference between docker start and docker run
docker start name 启动一个已经创建的容器 docker run 创建并启动一个容器
从主机复制到容器 sudo docker cp host_path containerID:container_path
从容器复制到主机 sudo docker cp containerID:container_path host_path
docker cp container_nginx:/usr/local/xin.txt /usr/local/software/ 容器向主机复制文件 这样一个基础的docker容器就创建完了 。。。。。。。。。。。。 反过来大家再看一看docker的容器与镜像的区别 https://www.cnblogs.com/linjiaxin/p/7381421.html 那么其实镜像与容器的本质区别并不大,那么镜像可以生成容器 ,容器是否可以做成镜像呢? 用当前的容器生成了redis镜像 例如:A、B两台机器都想安装redis,A机器上创建容器并在容器中做好redis的一切配置,让后将这个容器docker commit 成镜像image_redis,B机器也想要安装redis,直接用镜像image_redis创建容器就行了,docker就是做这样一劳永逸的事情。 而且传统方式得在每台机器上安装配置redis非常麻烦 镜像压缩打包 (主机上进行操作),有两种方式 docker save 与 docker load 和 docker export 与 docker import docker save 是直接将镜像进行打包 docker save <镜像名>或<镜像id>
docker cp /usr/local/xinzhifu.txt container_nginx:/usr/local/ 主机向容器复制文件docket commit container_nginx image_nginx:v1
容器名 自己起一个镜像的名字:版本号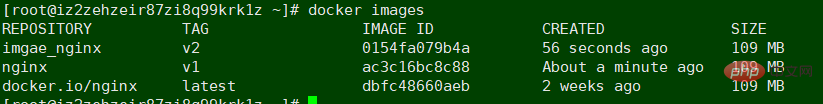
四.镜像的导入与导出
docker save nginx | gzip > nginx_xin_image.tar.gz 将现有的镜像压缩打包
docker load -i nginx_xin_image.tar.gz 压缩的镜像解压
docker images 进行查看
docker export container_nginx> nginx_image.tar
cat nginx_image.tar | sudo docker import - nginx_image:import
docker export 是直接将容器进行打包 docker save <容器名>或<容器id>
需要注意两种方法配套的,切不可混用。虽然导入导出时没问题,但是在创建容器时候会报错
如果使用import导入save产生的文件,虽然导入不提示错误,但是启动容器时会提示失败,
会出现类似"docker: Error response from daemon: Container command not found or does not exist"的错误。
类似,使用load载入export产生的文件,也会出现问题。
相关推荐:《Linux视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of Linux installation of docker and summary of basic operations of docker. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Android TV Box gets unofficial Ubuntu 24.04 upgrade
Sep 05, 2024 am 06:33 AM
Android TV Box gets unofficial Ubuntu 24.04 upgrade
Sep 05, 2024 am 06:33 AM
For many users, hacking an Android TV box sounds daunting. However, developer Murray R. Van Luyn faced the challenge of looking for suitable alternatives to the Raspberry Pi during the Broadcom chip shortage. His collaborative efforts with the Armbia
 deepseek web version entrance deepseek official website entrance
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
deepseek web version entrance deepseek official website entrance
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
DeepSeek is a powerful intelligent search and analysis tool that provides two access methods: web version and official website. The web version is convenient and efficient, and can be used without installation; the official website provides comprehensive product information, download resources and support services. Whether individuals or corporate users, they can easily obtain and analyze massive data through DeepSeek to improve work efficiency, assist decision-making and promote innovation.
 How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
There are many ways to install DeepSeek, including: compile from source (for experienced developers) using precompiled packages (for Windows users) using Docker containers (for most convenient, no need to worry about compatibility) No matter which method you choose, Please read the official documents carefully and prepare them fully to avoid unnecessary trouble.
 BitPie Bitpie wallet app download address
Sep 10, 2024 pm 12:10 PM
BitPie Bitpie wallet app download address
Sep 10, 2024 pm 12:10 PM
How to download BitPie Bitpie Wallet App? The steps are as follows: Search for "BitPie Bitpie Wallet" in the AppStore (Apple devices) or Google Play Store (Android devices). Click the "Get" or "Install" button to download the app. For the computer version, visit the official BitPie wallet website and download the corresponding software package.
 BITGet official website installation (2025 beginner's guide)
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
BITGet official website installation (2025 beginner's guide)
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
BITGet is a cryptocurrency exchange that provides a variety of trading services including spot trading, contract trading and derivatives. Founded in 2018, the exchange is headquartered in Singapore and is committed to providing users with a safe and reliable trading platform. BITGet offers a variety of trading pairs, including BTC/USDT, ETH/USDT and XRP/USDT. Additionally, the exchange has a reputation for security and liquidity and offers a variety of features such as premium order types, leveraged trading and 24/7 customer support.
 Detailed explanation: Shell script variable judgment parameter command
Sep 02, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
Detailed explanation: Shell script variable judgment parameter command
Sep 02, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
The system variable $n is the parameter passed to the script or function. n is a number indicating the number of parameters. For example, the first parameter is $1, and the second parameter is $2$? The exit status of the previous command, or the return value of the function. Returns 0 on success, 1 on failure $#Number of parameters passed to the script or function $* All these parameters are enclosed in double quotes. If a script receives two parameters, $* is equal to $1$2$0The name of the command being executed. For shell scripts, this is the path to the activated command. When $@ is enclosed in double quotes (""), it is slightly different from $*. If a script receives two parameters, $@ is equivalent to $1$2$$the process number of the current shell. For a shell script, this is the process I when it is executing
 Zabbix 3.4 Source code compilation installation
Sep 04, 2024 am 07:32 AM
Zabbix 3.4 Source code compilation installation
Sep 04, 2024 am 07:32 AM
1. Installation environment (Hyper-V virtual machine): $hostnamectlStatichostname:localhost.localdomainIconname:computer-vmChassis:vmMachineID:renwoles1d8743989a40cb81db696400BootID:renwoles272f4aa59935dcdd0d456501Virtualization:microsoftOperatingSystem:CentOS Linux7(Core)CPEOSName:cpe:
 Ouyi okx installation package is directly included
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Ouyi okx installation package is directly included
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Ouyi OKX, the world's leading digital asset exchange, has now launched an official installation package to provide a safe and convenient trading experience. The OKX installation package of Ouyi does not need to be accessed through a browser. It can directly install independent applications on the device, creating a stable and efficient trading platform for users. The installation process is simple and easy to understand. Users only need to download the latest version of the installation package and follow the prompts to complete the installation step by step.





