How to add extensions to yum php7.1
Yum php7.1 method to add extensions: 1. Install php7.1 through yum; 2. Add through the "yum -y install php-mysql php-gd php-ldap php-odbc..." command Common PHP extensions are enough.

The operating environment of this article: centos7 system, PHP7.1 version, DELL G3 computer
How to add extensions to yum php7.1?
Tutorial on how to deploy php7.1 under CentOS 7 and enable MySQL extension
Preface
Previously installed php7.1 on CentOS7 Sometimes I encountered the problem that the PHP source and PHP7.1 did not support the MySQL extension. I took the time to install it in the morning and finally solved these two problems. I hereby record the memo.
Simple installation (yum method)
Install software source
Add epel source
[root@opstrip.com opt]# rpm --import /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY* [root@opstrip.com opt]# rpm -Uvh http://mirrors.rit.edu/fedora/epel//7/x86_64/e/epel-release-7-9.noarch.rpm
Add remi source
[root@opstrip.com opt]# rpm -Uvh http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm
Install and update Software
Install the yum-config-manager utility
[root@opstrip.com opt]# yum -y install yum-utils
Update the current software version of the system
[root@opstrip.com opt]# yum -y update
After the update is completed, you can install the required PHP version.
Install PHP
After the above preparations are completed, you can install the required PHP version.
For PHP5.4
[root@opstrip.com opt]# yum -y install php
Before installation, you can try yum search php54 to search for installable software packages.
For PHP7.0
[root@opstrip.com opt]# yum-config-manager --enable remi-php70 [root@opstrip.com opt]# yum -y install php php-opcache
Before installation, you can try yum search php70 to search for installable software packages.
For PHP7.1
[root@opstrip.com opt]# yum-config-manager --enable remi-php71 [root@opstrip.com opt]# yum -y install php php-opcache
Before installation, you can try yum search php71 to search for installable software packages.
After completion, you need to add common PHP extensions:
[root@opstrip.com opt]# yum -y install php-mysql php-gd php-ldap php-odbc php-pear php-xml php-xmlrpc php-mbstring php-soap curl curl-devel
For Nginx
[root@opstrip.com opt]# yum -y install nginx nginx-mod-http-perl nginx-mod-stream nginx-filesystem nginx-mod-mail nginx-mod-http-image-filter nginx-all-modules nginx-mod-http-geoip nginx-mod-http-xslt-filter
It is still recommended to try yum search nginx to search for installable software packages before installation.
After the installation is complete, configure PHP and Nginx and start it to test the phpinfo page. It should be displayed normally at this time.
Source code compilation and installation
Preparation before installation
Download PHP installation package
[root@opstrip.com opt]# wget -O php-7.1.5.tar.gz http://cn2.php.net/distributions/php-7.1.5.tar.gz
Unzip
[root@opstrip.com opt]# tar xf php-7.1.5.tar.gz
Install dependency package
[root@opstrip.com php-7.1.5]# yum install -y libxml2 libxml2-devel openssl openssl-devel bzip2 bzip2-devel libcurl libcurl-devel libjpeg libjpeg-devel libpng libpng-devel freetype freetype-devel gmp gmp-devel libmcrypt libmcrypt-devel readline readline-devel libxslt libxslt-devel
Configuration and installation
Compilation configuration
[root@opstrip.com opt]# cd php-7.1.5 [root@opstrip.com php-7.1.5]# ./configure \ --prefix=/usr/local/php \ --with-config-file-path=/etc \ --enable-fpm \ --with-fpm-user=nginx \ --with-fpm-group=nginx \ --enable-inline-optimization \ --disable-debug \ --disable-rpath \ --enable-shared \ --enable-soap \ --with-libxml-dir \ --with-xmlrpc \ --with-openssl \ --with-mcrypt \ --with-mhash \ --with-pcre-regex \ --with-sqlite3 \ --with-zlib \ --enable-bcmath \ --with-iconv \ --with-bz2 \ --enable-calendar \ --with-curl \ --with-cdb \ --enable-dom \ --enable-exif \ --enable-fileinfo \ --enable-filter \ --with-pcre-dir \ --enable-ftp \ --with-gd \ --with-openssl-dir \ --with-jpeg-dir \ --with-png-dir \ --with-zlib-dir \ --with-freetype-dir \ --enable-gd-native-ttf \ --enable-gd-jis-conv \ --with-gettext \ --with-gmp \ --with-mhash \ --enable-json \ --enable-mbstring \ --enable-mbregex \ --enable-mbregex-backtrack \ --with-libmbfl \ --with-onig \ --enable-pdo \ --with-mysqli=mysqlnd \ --with-pdo-mysql=mysqlnd \ --with-zlib-dir \ --with-pdo-sqlite \ --with-readline \ --enable-session \ --enable-shmop \ --enable-simplexml \ --enable-sockets \ --enable-sysvmsg \ --enable-sysvsem \ --enable-sysvshm \ --enable-wddx \ --with-libxml-dir \ --with-xsl \ --enable-zip \ --enable-mysqlnd-compression-support \ --with-pear \ --enable-opcache
For details, please refer to the official PHP installation instructions document: http://php.net/manual/zh/install.unix.nginx.php
Compile and install
[root@opstrip.com php-7.1.5]# make && make install
Configure environment variables:
Append export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/php/bin at the end of /etc/profile, and then execute source / Check the php version after etc/profile takes effect:
[root@opstrip.com php-7.1.5]# php -v PHP 7.1.5 (cli) (built: May 31 2017 16:12:38) ( NTS ) Copyright (c) 1997-2017 The PHP Group Zend Engine v3.1.0, Copyright (c) 1998-2017 Zend Technologies
Configuration after installation
Configuration php-fpm
After the installation is completed, you can use sapi/fpm/php-fpm.server Let’s start php-fpm. However, for the convenience of future management, it is usually necessary to place the configuration files in the /etc directory and add php-fpm.server to the systemctl service. As follows:
[root@opstrip.com php-7.1.5]# mkdir -p /etc/php-fpm.d [root@opstrip.com php-7.1.5]# cp php.ini-production /etc/php.ini [root@opstrip.com php-7.1.5]# cp sapi/fpm/php-fpm.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/ [root@opstrip.com php-7.1.5]# cp sapi/fpm/www.conf /etc/php-fpm.d/
Then change the /usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service file to execute the correct path, as follows:
[root@opstrip.com php-7.1.5]# vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service # It's not recommended to modify this file in-place, because it # will be overwritten during upgrades. If you want to customize, # the best way is to use the "systemctl edit" command. [Unit] Description=The PHP FastCGI Process Manager After=network.target [Service] Type=simple PIDFile=/var/run/php-fpm.pid ExecStart=/usr/local/php/sbin/php-fpm --nodaemonize --fpm-config /etc/php-fpm.conf ExecReload=/bin/kill -USR2 $MAINPID PrivateTmp=true [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Start php-fpm
When starting the PHP service through systemctl for the first time, you need to enable the php-fpm service first:
[root@opstrip.com php-7.1.5]# systemctl enable php-fpm.service [root@opstrip.com php-7.1.5]# systemctl start php-fpm.service
Compile and install Nginx
See this article for details, and configure and start Nginx as needed. I won’t write it down here.
Enable MySQL extension (only compile and install)
Since PHP7 has completely removed MySQL extension support (replaced by mysqli and mysqlnd), some old software will If an error similar to that the mysql_connect() function is not defined is reported, it is generally recommended to use the new PHPmysqli or pdo extension to replace it. Of course, you can also check out the legacy version of the PHP7 code that supports the MySQL extension and compile and install it yourself. However, it should be noted that the MySQL extension has no subsequent updates at all.
Preparation before installation
View the current extension
Check the current PHP7.1 built-in extension:
[root@opstrip.com php-7.1.5]# ls ext bcmath dom gd json oci8 pdo_firebird posix skeleton sysvsem xmlwriter bz2 enchant gettext ldap odbc pdo_mysql pspell snmp sysvshm xsl calendar exif gmp libxml opcache pdo_oci readline soap tidy zip com_dotnet ext_skel hash mbstring openssl pdo_odbc recode sockets tokenizer zlib ctype ext_skel_win32.php iconv mcrypt pcntl pdo_pgsql reflection spl wddx curl fileinfo imap mysql pcre pdo_sqlite session sqlite3 xml date filter interbase mysqli pdo pgsql shmop standard xmlreader dba ftp intl mysqlnd pdo_dblib phar simplexml sysvmsg xmlrpc
You can see that the MySQL extension has indeed been removed Now, we can directly check out the old PHP MySQL extension code in the ext directory.
Get the PHP MySQL extension source code
[root@opstrip.com ext]# git clone https://github.com/php/pecl-database-mysql mysql --recursive Cloning into 'mysql'... remote: Counting objects: 145, done. remote: Total 145 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 145 Receiving objects: 100% (145/145), 88.41 KiB | 0 bytes/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (65/65), done. Checking connectivity... done.
Compile and install the MySQL extension
Compile using phpize
[root@opstrip.com ext]# cd mysql [root@opstrip.com mysql]# ls config.m4 config.w32 CREDITS LICENSE mysql.mak mysql_mysqlnd.h package.xml php_mysql.c php_mysql.h php_mysql_structs.h README.md tests [root@opstrip.com mysql]# /usr/local/php/bin/phpize Configuring for: PHP Api Version: 20151012 Zend Module Api No: 20151012 Zend Extension Api No: 320151012 [root@opstrip.com mysql]# ./configure --with-php-config=/usr/local/php/bin/php-config
Installation
[root@opstrip.com mysql]# make && make install [root@opstrip.com mysql]# ls /usr/local/php/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20160303/ mysql.so opcache.a opcache.so
Required after the installation is complete Confirm whether the MySQL extension is installed correctly.
Finally modify the php.ini configuration file and add a line:
extension = "mysql.so"
Restart the php-fpm service and you will see the MySQL extension in phpinfo:
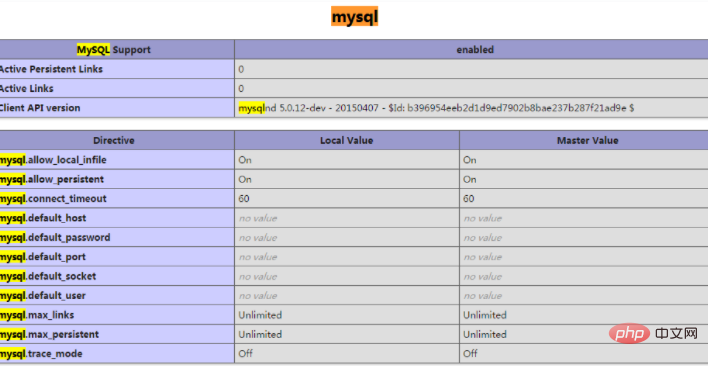
–This configuration is complete.
Recommended learning: "PHP Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of How to add extensions to yum php7.1. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Detailed explanation of the steps to upgrade gcc using yum on CentOS6.5
Dec 31, 2023 am 10:59 AM
Detailed explanation of the steps to upgrade gcc using yum on CentOS6.5
Dec 31, 2023 am 10:59 AM
Because C++11 needs to be used, but the gcc4.4.7 that comes with CentOS does not support it, I decided to upgrade gcc. The operation is as follows: #Backup mv/etc/yum.repos.d/devtools-2.repo/etc/yum.repos.d/devtools-2.repo.bakwgethttp://people.centos.org/tru/devtools-2 /devtools-2.repo-O/etc/yum.repos.d/devtools-2.repoyuminstalldevtoolset-2-gccdevtoolse
 Centos offline installation of Chinese version of GitLab
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:36 AM
Centos offline installation of Chinese version of GitLab
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:36 AM
1. Download the gitlab installation package. Download the latest Chinese version of the gitlab installation package from [Tsinghua University Open Source Software Mirror Station]. The installation package comes with a simplified Chinese localization package. Download the latest gitlab installation package from [gitlab official website]. 2. Install gitlab, take gitlab-ce-14.9.4-ce.0.el7.x86_64 as an example, upload it to the centos server and use yum to install gitlabyum-yinstallgitlab-ce-14.3.2-ce.0.el7.x86_64. rpm uses yum to install gityum-yinstallgit#Install git and modify the gitlab configuration file vi
 What is the difference between Linux package management tools yum and apt?
May 30, 2023 am 09:53 AM
What is the difference between Linux package management tools yum and apt?
May 30, 2023 am 09:53 AM
Generally speaking, famous Linux systems are basically divided into two categories: RedHat series: Redhat, Centos, Fedora, etc.; Debian series: Debian, Ubuntu, etc. yum (YellowdogUpdater, Modified) is a Shell front-end package manager in Fedora, RedHat and SUSE. apt (AdvancedPackagingTool) is a shell front-end package manager in Debian and Ubuntu. Overview Generally speaking, the famous Linux systems are basically divided into two categories: RedHat series: Redhat, Cento
 How to delete php in centos7+yum
Jan 19, 2023 am 10:00 AM
How to delete php in centos7+yum
Jan 19, 2023 am 10:00 AM
How to delete php in centos7 yum: 1. Check the PHP version through "php -v"; 2. Use "rpm -qa|grep php" to check the installed PHP related extensions; 3. Uninstall php by executing the "yum remove php" command That’s it.
 How to use yum to install php on linux
Jan 29, 2023 am 09:46 AM
How to use yum to install php on linux
Jan 29, 2023 am 09:46 AM
How to install php using yum on Linux: 1. Execute the "mkdir /usr/local/php" command; 2. Download the updated installation package of the yum source; 3. Install the relevant yum source installation package; 4. Install through the "yum install" command php is enough.
 What tool is linux yum?
Feb 10, 2023 am 10:09 AM
What tool is linux yum?
Feb 10, 2023 am 10:09 AM
In Linux, yum is a software package manager that exists specifically to solve package dependencies; yum is an improved RPM software manager, which solves the package dependency problems faced by RPM. When the administrator uses yum to install an RPM package, yum will first download the dependency file of the package from the server side, and then download and install all related RPM packages from the server side at once by analyzing this file.
![[Linux Tools]-yum/gdb usage tutorial!](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/887/227/170978100851477.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) [Linux Tools]-yum/gdb usage tutorial!
Mar 07, 2024 am 11:10 AM
[Linux Tools]-yum/gdb usage tutorial!
Mar 07, 2024 am 11:10 AM
yum is a commonly used software package management tool, and gdb is a powerful debugging tool. The following are their usage tutorials: yum usage tutorial: Install software packages: Use the yuminstall command to install software packages. For example, to install the Apache web server, you can run yuminstallhttpd. Upgrade software packages: Use the yumupdate command to upgrade installed software packages. For example, running yumupdate will upgrade all packages in the system. Delete a software package: Use the yumremove command to delete a software package. For example, to remove the Apache Web server, you can run yumremovehttpd. Search for packages: use yumsear
 Exploring Linux Yum Tools: A Brief Introduction and Practical Guide
Feb 26, 2024 am 10:00 AM
Exploring Linux Yum Tools: A Brief Introduction and Practical Guide
Feb 26, 2024 am 10:00 AM
In today's digital era, technology in the field of computer science is changing with each passing day, and operating systems, as the core of computer software systems, are also constantly evolving and innovating. Among them, Linux, as an open source operating system, has received widespread attention and application. In Linux systems, the Yum tool serves as a package manager and plays a vital role in the installation, deletion and update of software. This article will briefly introduce the Yum tool and provide usage guidelines to help readers better utilize this tool to manage Linux systems.




