What is the skeleton screen in vue
In vue, the skeleton screen shows the user the general structure of the page before the page data is loaded, and then renders the page after the requested data is returned, adding the data content that needs to be displayed; the skeleton screen can be understood This is a blank version of the page before the data is loaded, a simple critical rendering path.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, vue2.9.6 version, DELL G3 computer.
Compared with the early days when back-end code was tightly coupled and back-end engineers had to write front-end code, it has now developed to the point where front-end and back-end are separated. This development method has greatly improved the maintainability of front-end and back-end projects. stability and development efficiency, allowing front-end and back-end engineers to focus on their main business. However, while bringing convenience, it also brings some disadvantages, such as the first screen rendering time (FCP) because the first screen needs to request more content, which requires more HTTP round-trip time (RTT) than before, which results in white If the screen remains blank for too long, the user experience will be greatly compromised. If the user's network speed is poor, the FCP will be longer.
This led to a series of optimization methods, and the skeleton screen was also proposed.
1. FCP optimization
Among the four user-centered page performance measurement indicators proposed by Google, FP/FCP may be the most familiar to developers:
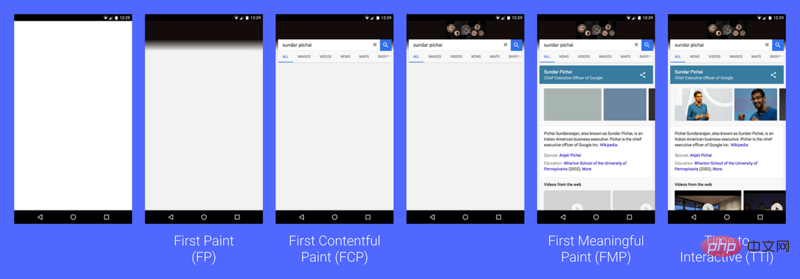
In order to optimize the first screen rendering time indicator and reduce the white screen time, the front-end guys have thought of many ways:
Accelerate or reduce HTTP requests Loss: Use CDN to load public libraries, use strong caching and negotiated caching, use domain name convergence, use Base64 instead of small pictures, use Get requests instead of Post requests, set Access-Control-Max-Age to reduce preflight requests, and jump to others within the page Use browser prefetch to pre-parse domain names or request resources from other domain names;
Delayed loading: non-important libraries, delayed loading of non-first-screen images, lazy loading of SPA components, etc.;
Reduce the size of the requested content: enable server Gzip compression, JS and CSS file compression and merging, reduce cookie size, SSR directly outputs the rendered HTML, etc.;
Principle of browser rendering: optimize the key rendering path and minimize JS and CSS that block rendering;
Optimize user waiting experience: use loading progress bar, chrysanthemum on white screen Picture, skeleton screen replacement, etc.;
What I want to introduce here is the skeleton screen that optimizes the user’s waiting experience. It can be regarded as an upgraded version of the original loading chrysanthemum picture, combined with the traditional The first screen optimization method can achieve good results by optimizing the application.
2. Skeleton screen
The skeleton screen shows the user the general structure of the page before the page data is loaded, and then renders the page until the requested data is returned to supplement the data that needs to be displayed. content. It is often used for relatively regular list pages such as article lists and dynamic list pages.
The skeleton screen can be understood as before the data is loaded in, a blank version of the page, a simple critical rendering path. You can take a look at Facebook's skeleton screen implementation below. You can see that before the page is fully rendered, the user will see a skeleton screen page with a simple style that depicts the general frame of the current page. Then each placeholder part in the skeleton screen is actually The resource is completely replaced. During this process, the user will feel that the content is gradually loading and about to be presented, which reduces the user's anxiety and makes the loading process subjectively smooth.

You can take a look at the example pictures below. The first one is a skeleton screen, the second one is a chrysanthemum picture, and the third one is without optimization. You can see that compared to The traditional chrysanthemum picture will make the content appear smooth and unobtrusive to the senses, and the experience will be better.
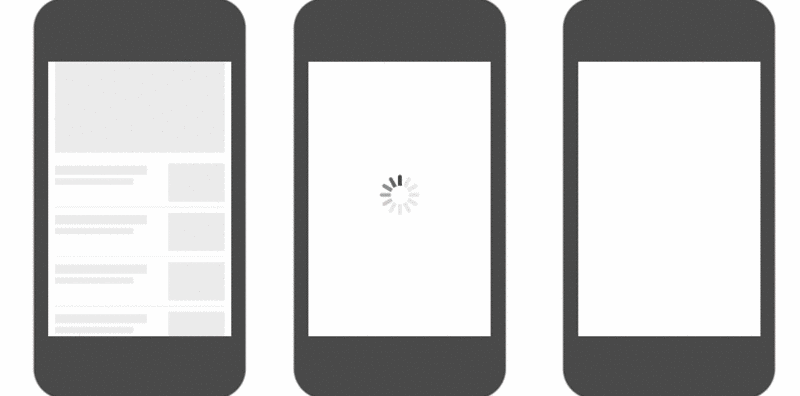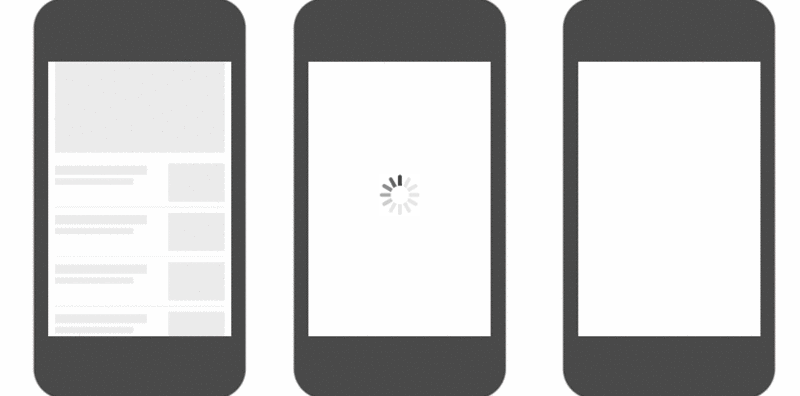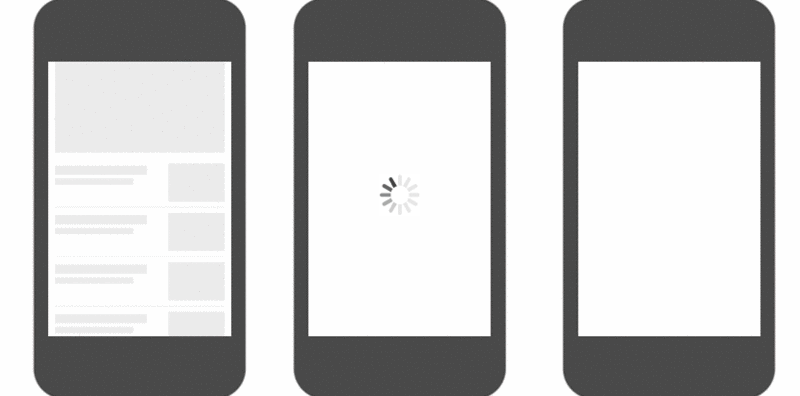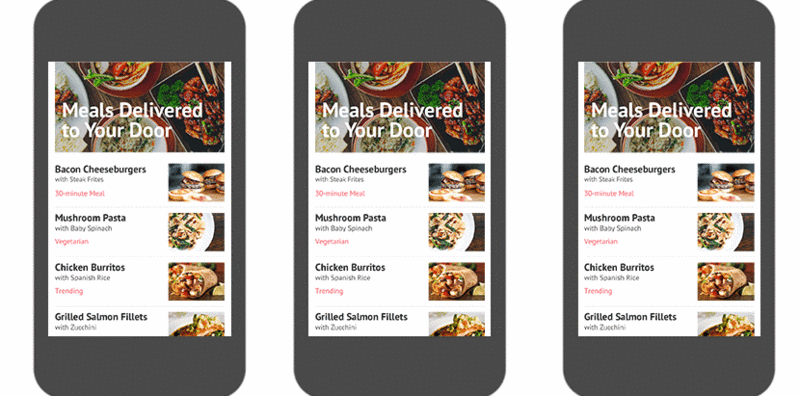
3. Methods of generating skeleton screens
The main methods of generating skeleton screens are:
- To customize the skeleton screen for the target page by handwriting HTML and CSS, you can refer to "Vue Page Skeleton Screen Injection Practice". The main idea is to use vue-server-renderer, a plug-in originally used for server-side rendering. , used to process the
.vuefile we wrote intoHTML, insert it into the mount point of the page template, and complete the injection of the skeleton screen. This method is not very civilized. If the page style changes, the skeleton screen must be changed again, which increases maintenance costs. For the style implementation of the skeleton screen, please refer to CodePen - Use pictures as the skeleton screen; It is simple and violent, let the UI students spend some effort haha; the mobile page of Xiaomi Mall uses this method, it uses a Base64 The picture is used as the skeleton screen.
- Automatically generate and automatically insert a static skeleton screen. This method is similar to the first method, but it automatically generates a skeleton screen. You can pay attention to the Ele.me open source plug-in page-skeleton-webpack-plugin, which is based on Different routing pages in the project generate corresponding skeleton screen pages, and the skeleton screen pages are packaged into the corresponding static routing pages through webpack. However, it should be noted that this plug-in currently only supports history routing, and does not support hash routing. Currently, only the skeleton screen on the homepage is supported, and there is no partial skeleton screen implementation at the component level. The author said that there will be plans to implement it in the future (issue 9).
There is also a plug-in vue-skeleton-webpack-plugin, which changes the way of inserting the skeleton screen from manual to automatic. The principle is to use the Vue pre-rendering function during construction to convert the skeleton screen component. The HTML fragment of the rendering result is inserted into the mount point of the HTML page template, and the style is inlined into the head tag. This plug-in can set different skeleton screens for different routes on a single page, or for multiple pages. At the same time, for the convenience of debugging during development, the skeleton screen will be written into the router as a route, which is quite considerate.
vue-skeleton-webpack-plugin For specific usage, refer to vue-style-codebase, mainly focusing on several files in the build directory. For the online demo, use the network in Chrome's DevTools. Set the speed to Gast 3G / Slow 3G and you will see the effect~
[Related recommendations: vue.js tutorial]
The above is the detailed content of What is the skeleton screen in vue. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
There are three common methods for Vue.js to traverse arrays and objects: the v-for directive is used to traverse each element and render templates; the v-bind directive can be used with v-for to dynamically set attribute values for each element; and the .map method can convert array elements into new arrays.
 How to jump to the div of vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:18 AM
How to jump to the div of vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:18 AM
There are two ways to jump div elements in Vue: use Vue Router and add router-link component. Add the @click event listener and call this.$router.push() method to jump.






