 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 How to implement HTTP transfer of large files based on nodejs? (Sharing of practical methods)
How to implement HTTP transfer of large files based on nodejs? (Sharing of practical methods)
How to implement HTTP transfer of large files based on nodejs? (Sharing of practical methods)
Based on nodeHow to implement http transmission of large files? The following article will introduce to you several practical http file transfer solutions based on nodejs. I hope it will be helpful to you!

The http file transfer solution based on nodejs plays an important role in the current front-end and back-end full-stack development. In this article, I will go through several A solution to implement HTTP transfer of large files. Before implementing the function, we first write a large file through the fs module of nodejs and generate a local file in the project:
const fs = require('fs');
const writeStream = fs.createWriteStream(__dirname + "/file.txt");
for(let i = 0;i <= 100000; i++) {
writeStream.write(`${i} —— 我是${i}号文件\n`, "utf-8");
}
writeStream.end();
After the above code runs successfully, A text file with a size of 3.2MB will be generated in the current execution directory, which will be used as the "large file material" for the following program. Before listing the large file transfer scheme, we first encapsulate the two public methods that will be used later: File reading method and File compression method:
// 封装读取文件的方法
const readFile = async (paramsData) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile(paramsData, (err, data) => {
if(err) {
reject('文件读取错误');
} else {
resolve(data);
}
})
})
}
// 封装文件压缩方法
const gzip = async (paramsData) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
zlib.gzip(paramsData, (err, result) => {
if(err) {
reject('文件压缩错误');
} else {
resolve(result);
}
})
})
}1. Transmit through large files after data compression
When the browser sends a request, it will carry accept and accept- * Request header information, used to tell the server the file types supported by the current browser, the supported compression format list and the supported languages. The Accept-Encoding field in the request header is used to tell the server the content encoding method (usually a certain compression algorithm) that the client can understand. The server will choose a method supported by the client and notify the client of the choice through the response header Content-Encoding. The response header tells the browser that the JS script returned is passed gzip Compression algorithm processed
// 请求头 accept-encoding: gzip, deflate, br
// 响应头 cache-control: max-age=2592000 content-encoding: gzip content-type: application/x-javascript
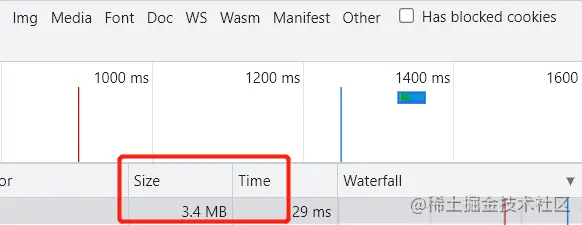
Based on the understanding of Accept-Encoding and Content-Encoding fields, let’s verify that it is not turned on gzip And the effect of turning on gzip.
// 实现一个简单的文件读取服务器(没有开启gzip)
const server = http.createServer(async (req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {
"Content-Type": "text/plain;charset=utf-8",
});
const buffer = await readFile(__dirname + '/file.txt');
res.write(buffer);
res.end();
})
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log(`server启动成功`)
})
// 实现一个简单的文件读取服务器(开启gzip)
const server = http.createServer(async(req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {
"Content-Type": "text/plain;charset=utf-8",
"Content-Encoding": "gzip"
});
const buffer = await readFile(__dirname + '/file.txt');
const gzipData = await gzip(buffer);
res.write(gzipData);
res.end();
})
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log(`server启动成功`)
})2. Transmission through data chunking
When there is a scenario where a large HTML table needs to be generated using the data obtained from the database query, or when a large number of images need to be transmitted, this can be achieved through block transmission.
Transfer-Encoding: chunked Transfer-Encoding: gzip, chunked
The value of the Transfer-Encoding field in the response header is chunked, which indicates that the data is sent in a series of chunks. It should be noted that the two fields Transfer-Encoding and Content-Length are mutually exclusive, which means that these two fields cannot appear at the same time in the response message.
// 数据分块传输
const spilitChunks = async () =>{
const buffer = await readFile(__dirname + '/file.txt');
const lines = buffer.toString('utf-8').split('\n');
let [chunks, i, n] = [[], 0, lines.length];
while(i < n) {
chunks.push(lines.slice(i, i+= 10));
};
return chunks;
}
const server = http.createServer(async(req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {
"Content-Type": "text/plain;charset=utf-8",
"Transfer-Encoding": "chunked",
"Access-Control-Allow-Origin": "*",
});
const chunks = await spilitChunks();
for(let i =0; i< chunks.length; i++) {
setTimeout(() => {
let content = chunks[i].join("&");
res.write(`${content.length.toString(16)}\r\n${content}\r\n`);
}, i * 1000);
}
setTimeout(() => {
res.end();
}, chunks.length * 1000);
})
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log(`server启动成功`)
})3. Transmit through data stream
When using Node.js Return large files to the client When using a stream to return a file stream, you can avoid taking up too much memory when processing large files. The specific implementation is as follows. When using stream form to return file data, the value of the HTTP response header Transfer-Encoding field is chunked, indicating that the data is sent in a series of chunks.
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {
"Content-Type": "text/plain;charset=utf-8",
"Content-Encoding": "gzip",
"Transfer-Encoding": "chunked"
});
fs.createReadStream(__dirname + "/file.txt")
.setEncoding("utf-8")
.pipe(zlib.createGzip())
.pipe(res);
})
server.listen(3000, () => {
console.log(`server启动成功`)
})For more node-related knowledge, please visit: nodejs tutorial! !
The above is the detailed content of How to implement HTTP transfer of large files based on nodejs? (Sharing of practical methods). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a backend framework?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Node.js can be used as a backend framework as it offers features such as high performance, scalability, cross-platform support, rich ecosystem, and ease of development.
 What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
What is the difference between npm and npm.cmd files in the nodejs installation directory?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:18 AM
There are two npm-related files in the Node.js installation directory: npm and npm.cmd. The differences are as follows: different extensions: npm is an executable file, and npm.cmd is a command window shortcut. Windows users: npm.cmd can be used from the command prompt, npm can only be run from the command line. Compatibility: npm.cmd is specific to Windows systems, npm is available cross-platform. Usage recommendations: Windows users use npm.cmd, other operating systems use npm.
 Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Is nodejs a back-end development language?
Apr 21, 2024 am 05:09 AM
Yes, Node.js is a backend development language. It is used for back-end development, including handling server-side business logic, managing database connections, and providing APIs.
 What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
What are the global variables in nodejs
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:54 AM
The following global variables exist in Node.js: Global object: global Core module: process, console, require Runtime environment variables: __dirname, __filename, __line, __column Constants: undefined, null, NaN, Infinity, -Infinity
 How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
How to connect nodejs to mysql database
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:13 AM
To connect to a MySQL database, you need to follow these steps: Install the mysql2 driver. Use mysql2.createConnection() to create a connection object that contains the host address, port, username, password, and database name. Use connection.query() to perform queries. Finally use connection.end() to end the connection.
 Which one to choose between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Which one to choose between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Node.js and Java each have their pros and cons in web development, and the choice depends on project requirements. Node.js excels in real-time applications, rapid development, and microservices architecture, while Java excels in enterprise-grade support, performance, and security.
 Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
Is there a big difference between nodejs and java?
Apr 21, 2024 am 06:12 AM
The main differences between Node.js and Java are design and features: Event-driven vs. thread-driven: Node.js is event-driven and Java is thread-driven. Single-threaded vs. multi-threaded: Node.js uses a single-threaded event loop, and Java uses a multi-threaded architecture. Runtime environment: Node.js runs on the V8 JavaScript engine, while Java runs on the JVM. Syntax: Node.js uses JavaScript syntax, while Java uses Java syntax. Purpose: Node.js is suitable for I/O-intensive tasks, while Java is suitable for large enterprise applications.
 How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
How to deploy nodejs project to server
Apr 21, 2024 am 04:40 AM
Server deployment steps for a Node.js project: Prepare the deployment environment: obtain server access, install Node.js, set up a Git repository. Build the application: Use npm run build to generate deployable code and dependencies. Upload code to the server: via Git or File Transfer Protocol. Install dependencies: SSH into the server and use npm install to install application dependencies. Start the application: Use a command such as node index.js to start the application, or use a process manager such as pm2. Configure a reverse proxy (optional): Use a reverse proxy such as Nginx or Apache to route traffic to your application



)


