 Database
Database
 Mysql Tutorial
Mysql Tutorial
 Let's talk about the basics of MySQL custom variables and statement end delimiters
Let's talk about the basics of MySQL custom variables and statement end delimiters
Let's talk about the basics of MySQL custom variables and statement end delimiters
This article brings you relevant knowledge about custom variables and statement end delimiters in mysql. I hope it will be helpful to you.

Stored Program
Sometimes in order to complete a common function, you need to execute many statements, and each time you enter these statements one by one in the client. Multiple statements are annoying. The uncle who designed MySQL very thoughtfully provided us with something called stored program. This so-called stored program can encapsulate some statements. Then provide the user with a simple way to call this stored procedure to execute these statements indirectly. Depending on the calling method, we can divide stored procedures into the following types: stored routines, triggers and events. Among them, Stored routines can be subdivided into Stored functions and Stored procedures. Let’s draw a picture to show it:
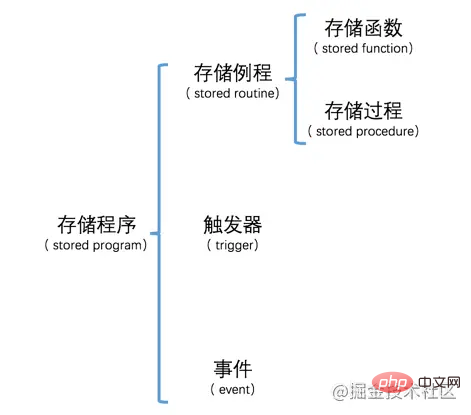
Don’t be afraid that there are many unfamiliar concepts, we will break them down later. However, before formally introducing stored procedures, we need to first understand the concepts of custom variables and statement end delimiters in MySQL.
Introduction to custom variables
In life we often encounter some fixed values, such as numbers 100, strings 'Hello' , we call these things with fixed values constants. But sometimes for convenience, we will use a certain symbol to represent a value, and the value it represents can change. For example, we stipulate that the symbol a represents the number 1, and then we can let the symbol a represent the number 2. We can make this value happen The changed stuff is called variable, and the symbol a is called the variable name of this variable. In MySQL, we can customize some of our own variables through the SET statement, for example:
mysql> SET @a = 1; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql>
The above statement indicates that we have defined a name It is a variable of a, and the integer 1 is assigned to this variable. However, everyone needs to pay attention to the fact that the uncle who designed MySQL stipulated that we must add a @ symbol in front of our custom variables (although it is a bit strange, this is what others stipulated, so everyone should just abide by it).
If we want to check the value of this variable later, just use the SELECT statement, but we still need to add a @ symbol before the variable name:
mysql> SELECT @a; +------+ | @a | +------+ | 1 | +------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
The same variable can also store different types of values. For example, we assign a string value to the variable a:
mysql> SET @a = '哈哈哈'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) mysql> SELECT @a; +-----------+ | @a | +-----------+ | 哈哈哈 | +-----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
In addition to assigning a constant to a In addition to variables, we can also assign one variable to another variable:
mysql> SET @b = @a; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select @b; +-----------+ | @b | +-----------+ | 哈哈哈 | +-----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
In this way, variables a and b will have the same value'Wahaha' !
We can also assign the result of a certain query to a variable, provided that the result of the query has only one value:
mysql> SET @a = (SELECT m1 FROM t1 LIMIT 1); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql>
We can also use another form of statement to assign the query result The result is assigned to a variable:
mysql> SELECT n1 FROM t1 LIMIT 1 INTO @b; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql>
Because the query results of the statements SELECT m1 FROM t1 LIMIT 1 and SELECT n1 FROM t1 LIMIT 1 have only one value, so they It can be directly assigned to variable a or b. Let’s check the values of these two variables:
mysql> SELECT @a, @b; +------+------+ | @a | @b | +------+------+ | 1 | a | +------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
If our query result is a record with multiple column values in the record, we want to assign these values to different variables. , only the INTO statement can be used:
mysql> SELECT m1, n1 FROM t1 LIMIT 1 INTO @a, @b; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql>
The result set of this query statement only contains one record, we put the value of the m1 column of this record The value is assigned to variable a, and the value of column n1 is assigned to variable b.
End of statement delimiter
At the interactive interface of the MySQL client, when we complete the keyboard input and press the Enter key, MySQL The client will detect whether the content we input contains one of the three symbols ;, \g or \G. If so, it will input us. content is sent to the server. In this way, if we want to send multiple statements to the server at once, we need to write these statements in one line, such as this:
mysql> SELECT * FROM t1 LIMIT 1;SELECT * FROM t2 LIMIT 1;SELECT * FROM t3 LIMIT 1; +------+------+ | m1 | n1 | +------+------+ | 1 | a | +------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) +------+------+ | m2 | n2 | +------+------+ | 2 | b | +------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) +------+------+ | m3 | n3 | +------+------+ | 3 | c | +------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
The reason for this inconvenience is that, MySQLThe symbol used by the client to detect the end of input is the same as the symbol that separates each statement! In fact, we can also use the delimiter command to customize the symbol at the end of the MySQL detection statement input, which is the so-called statement end delimiter , such as this:
mysql> delimiter $ mysql> SELECT * FROM t1 LIMIT 1; -> SELECT * FROM t2 LIMIT 1; -> SELECT * FROM t3 LIMIT 1; -> $ +------+------+ | m1 | n1 | +------+------+ | 1 | a | +------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) +------+------+ | m2 | n2 | +------+------+ | 2 | b | +------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) +------+------+ | m3 | n3 | +------+------+ | 3 | c | +------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
delimiter $命令意味着修改语句结束分隔符为$,也就是说之后MySQL客户端检测用户语句输入结束的符号为$。上边例子中我们虽然连续输入了3个以分号;结尾的查询语句并且按了回车键,但是输入的内容并没有被提交,直到敲下$符号并回车,MySQL客户端才会将我们输入的内容提交到服务器,此时我们输入的内容里已经包含了3个独立的查询语句了,所以返回了3个结果集。
我们也可以将语句结束分隔符重新定义为$以外的其他包含单个或多个字符的字符串,比方说这样:
mysql> delimiter EOF mysql> SELECT * FROM t1 LIMIT 1; -> SELECT * FROM t2 LIMIT 1; -> SELECT * FROM t3 LIMIT 1; -> EOF +------+------+ | m1 | n1 | +------+------+ | 1 | a | +------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) +------+------+ | m2 | n2 | +------+------+ | 2 | b | +------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) +------+------+ | m3 | n3 | +------+------+ | 3 | c | +------+------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
我们这里采用了EOF作为MySQL客户端检测输入结束的符号,是不是很easy啊!当然,这个只是为了方便我们一次性输入多个语句,在输入完成之后最好还是改回我们常用的分号;吧:
mysql> delimiter ;
小贴士: 我们应该避免使用反斜杠(\)字符作为语句结束分隔符,因为这是MySQL的转义字符。
推荐学习:mysql视频教程
The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about the basics of MySQL custom variables and statement end delimiters. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1379
1379
 52
52
 MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL: Simple Concepts for Easy Learning
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:29 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system. 1) Create database and tables: Use the CREATEDATABASE and CREATETABLE commands. 2) Basic operations: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE and SELECT. 3) Advanced operations: JOIN, subquery and transaction processing. 4) Debugging skills: Check syntax, data type and permissions. 5) Optimization suggestions: Use indexes, avoid SELECT* and use transactions.
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
How to create navicat premium
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Create a database using Navicat Premium: Connect to the database server and enter the connection parameters. Right-click on the server and select Create Database. Enter the name of the new database and the specified character set and collation. Connect to the new database and create the table in the Object Browser. Right-click on the table and select Insert Data to insert the data.
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.
 How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
How to create a new connection to mysql in navicat
Apr 09, 2025 am 07:21 AM
You can create a new MySQL connection in Navicat by following the steps: Open the application and select New Connection (Ctrl N). Select "MySQL" as the connection type. Enter the hostname/IP address, port, username, and password. (Optional) Configure advanced options. Save the connection and enter the connection name.
 Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL is chosen for its performance, reliability, ease of use, and community support. 1.MySQL provides efficient data storage and retrieval functions, supporting multiple data types and advanced query operations. 2. Adopt client-server architecture and multiple storage engines to support transaction and query optimization. 3. Easy to use, supports a variety of operating systems and programming languages. 4. Have strong community support and provide rich resources and solutions.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL: Essential Skills for Developers
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:30 AM
MySQL and SQL are essential skills for developers. 1.MySQL is an open source relational database management system, and SQL is the standard language used to manage and operate databases. 2.MySQL supports multiple storage engines through efficient data storage and retrieval functions, and SQL completes complex data operations through simple statements. 3. Examples of usage include basic queries and advanced queries, such as filtering and sorting by condition. 4. Common errors include syntax errors and performance issues, which can be optimized by checking SQL statements and using EXPLAIN commands. 5. Performance optimization techniques include using indexes, avoiding full table scanning, optimizing JOIN operations and improving code readability.



