Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Docker
Docker
 The most systematic mastery of Docker core technology (summary sharing)
The most systematic mastery of Docker core technology (summary sharing)
The most systematic mastery of Docker core technology (summary sharing)
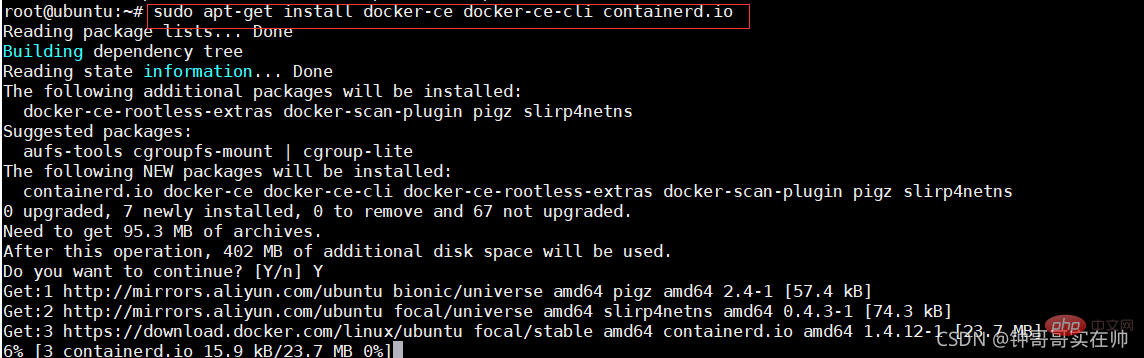
This article brings you some related questions about container operation of docker core technology, detailed explanation of Dockerfile, etc. I hope it will be helpful to you.

1. Docker
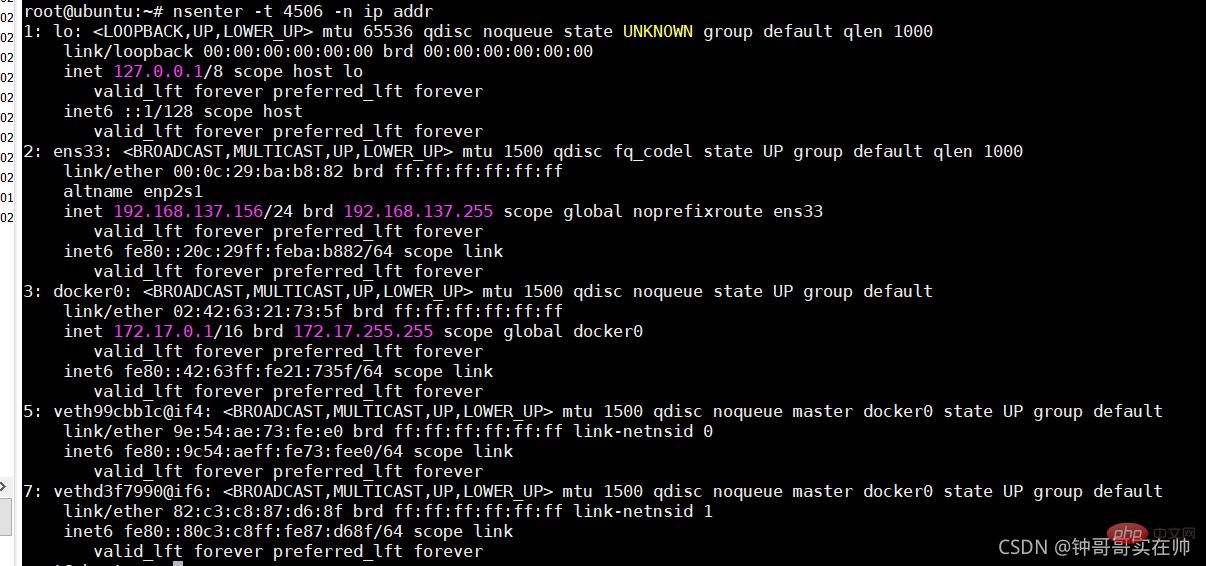
1. Introduction
- Based on the Cgroup, Namespace, and Union FS technologies of the Linux kernel, Encapsulating and isolating processes is a virtual technology at the operating system level. Since the isolated process is independent of the host and other isolated processes, it is called a container.
- The initial implementation was based on LXC. LXC will be removed from 0.7 onwards. Switch to the self-developed Libcontainer. Starting from 1.11, it has further evolved to use runC and Containerd
- Docker has further encapsulated it on the basis of the container, from file system, network interconnection to process isolation, etc. , which greatly simplifies the creation and maintenance of containers, making Docker technology lighter and faster than virtual machine technology
2. Docker advantages
- Use it more efficiently System resources
- Faster startup time
- Consistent operating environment
- Continuous delivery and deployment
- Easier migration
- More Easily maintain and expand
3. Comparison between Docker and virtual machines



 ##3. Container operation
##3. Container operation
- Start:
- docker run:
-It interaction
-d Running
--P port mapping
--V disk hanging
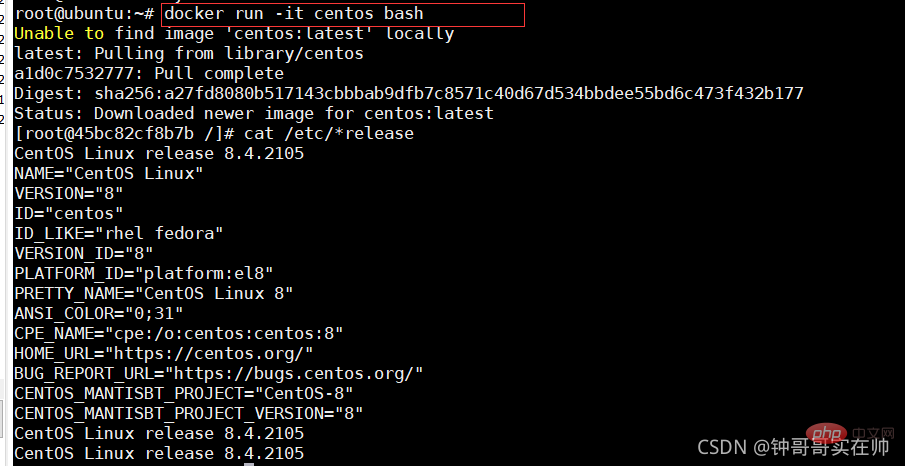
- Start the terminated container
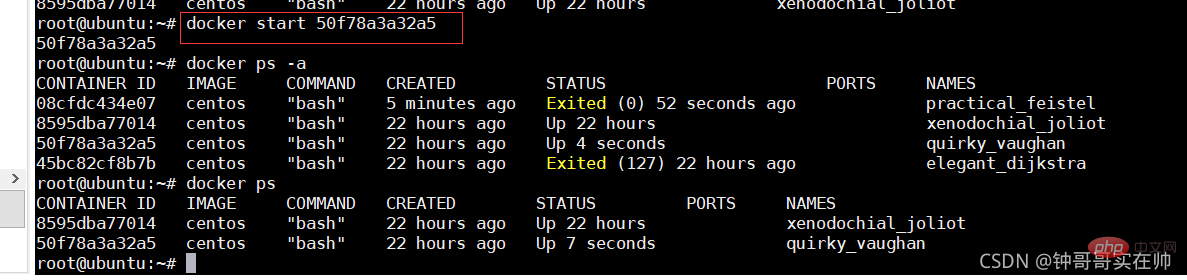
- Stop container
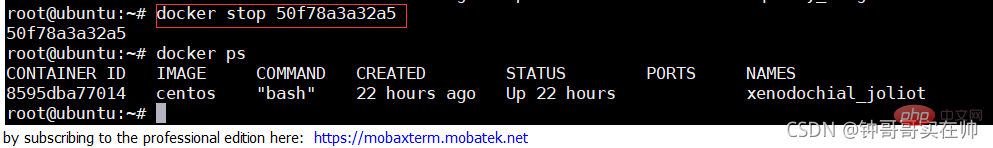
- View container process

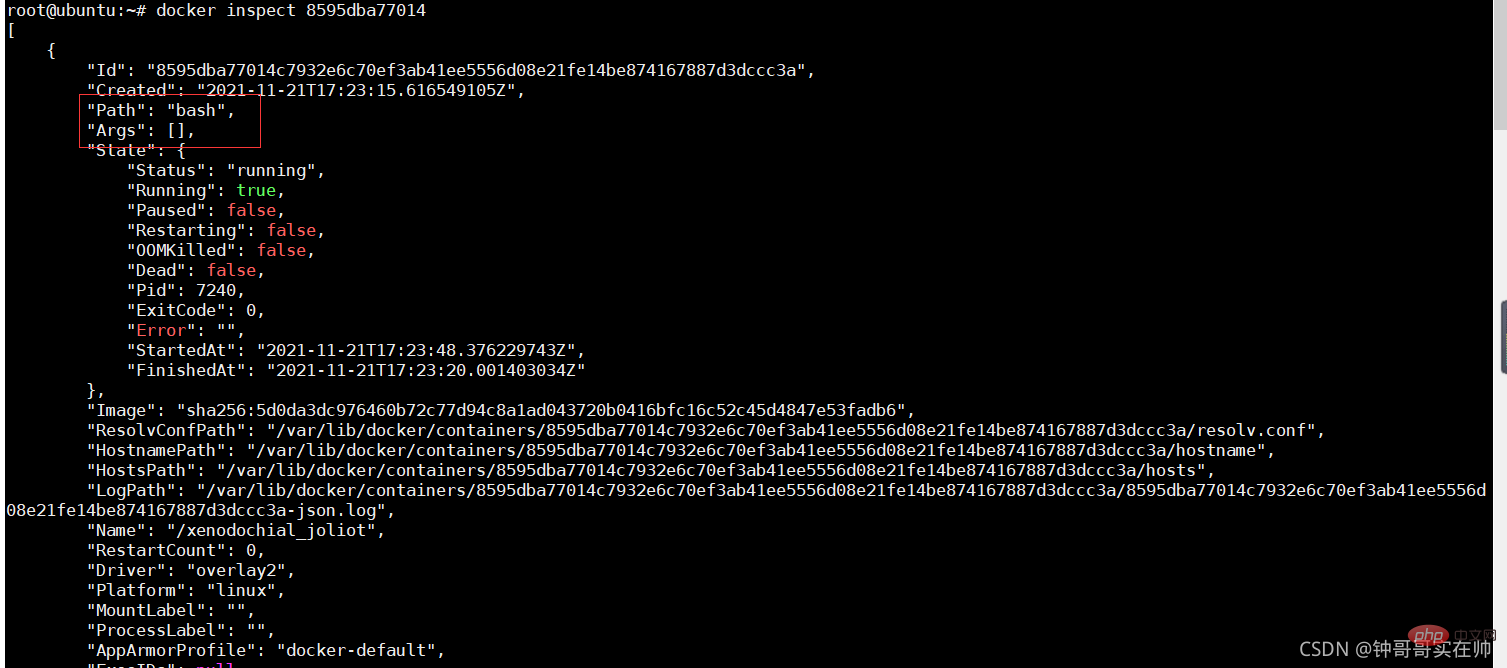
- ##View container details
-
docker inspect
docker cp file1
:/file_to_path
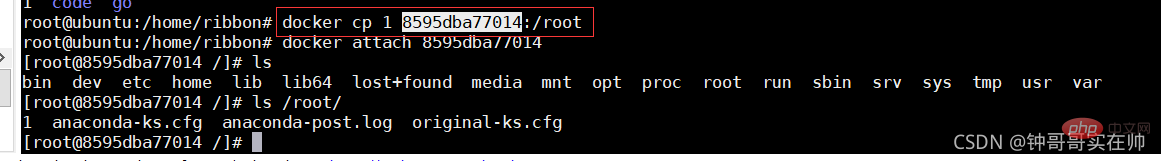 #docker exits the container without closing the container: ctrl q p
#docker exits the container without closing the container: ctrl q p
docker exits the container and closes the container: exit
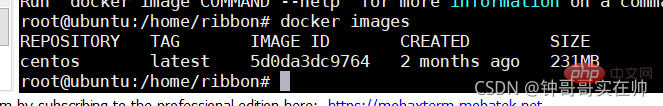
##Query all docker images
docker images
- Docker hub: https://hub.docker.com
Create a private image warehouse: docker run -d -p 5000:5000 registry
Four. Dockerfile Detailed explanation
- From: Specify the basic mirror image, must be the first instructions
- : Format:
From & LT; Image & GT;@& LT; Digest & GT;
## Example:## Ubuntu
AINTAINER: Maintenance Information# This #Format: MAINTAINER
RUN: Command executed when building the image
Format: Shell execution: RUNRUN apt-get update && apt The two commands -get install are always connected with &&, otherwise the apt-get update build layer will be cached, which will cause the new package to fail to be installed
ADD: Add local files to the container, Types such as tar will automatically decompress and you can access network resources, similar to wget
Format: ADDCOPY: The function is similar to ADD, but it does not decompress files and cannot access network resources
Use multi-stage in Dockerfile: multi-stage in Dockerfile (multi-stage build) - sparkdev - Blog Park Format: COPYCMD: Called after the container is built, that is, it is called only when the container starts
Format: CMD ["executable","param1","param2"] (Execute executable file, priority) CMD ["param1","param2"] ( If ENTRYPOINT is set, call ENTRYPOINT directly to add parameters)
CMD command param1 param2 (execute shell internal command)
ENTRTPOINT: Configure the container to make it executable.
Format: ENTRYPOINT ["executable", "param1", "param2"] (executable file, priority) ENTRYPOINT command param1 param2 (shell internal command)
LABAL: Used to add source data to the image
Format: LABELENV: Set environment variables
Format: ENVEXPOSE: Specify external interaction Port
Format: EXPOSEVOLUME: Used to specify the persistence directory
Format: VOLUME [USER: Specify the run The user name or UID of the container, and subsequent RUN will also use the specified user.
Format: USER user
USER user:group
USER uid
USER uid:gid
USER user:gid
USER uid:group
USER www
ARG: Used to specify variables passed to the build runtime
Format: ARG < name>[=
Example:
ARG build_user=ribbon
##
5. Detailed explanation of Linux NameSpace
Detailed explanation of NamesSpace:
Linux NameSpace_Frank_Abagnale's Blog-CSDN Blog This article provides a more detailed introduction. You can refer to this article
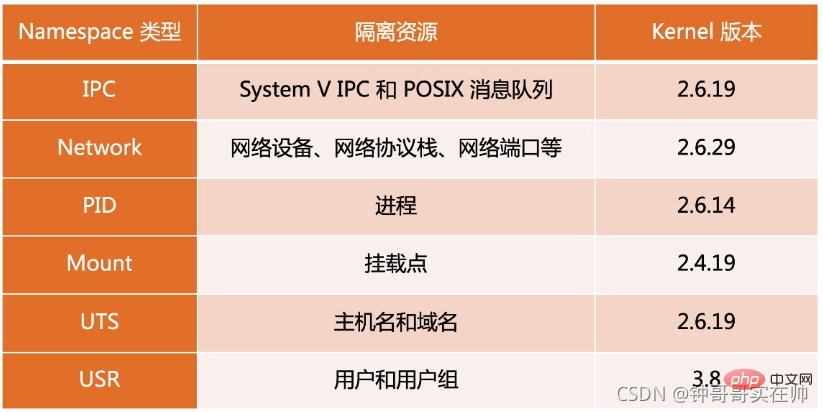
Common operations of NameSpace
- to view the namespace of the current system:
lsns -t
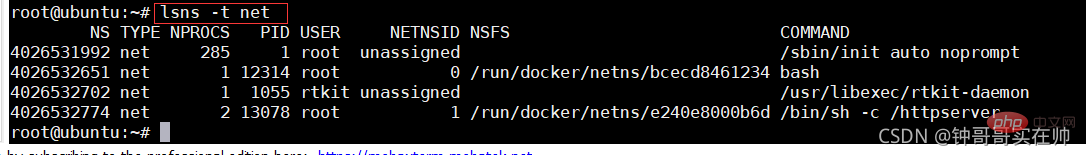
- View the namespace of a process:
ls -la /proc/
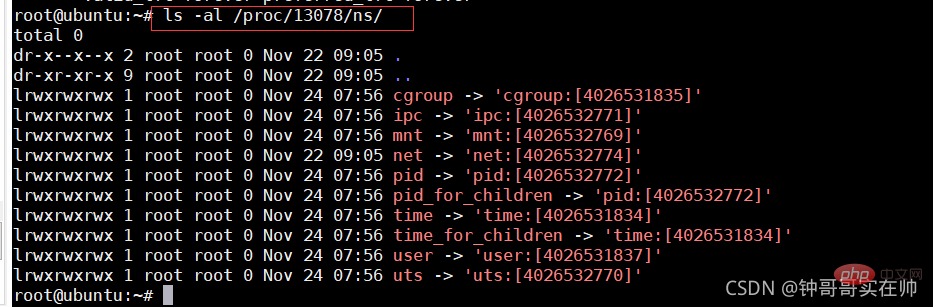
- View a namespace running command
nsenter -t
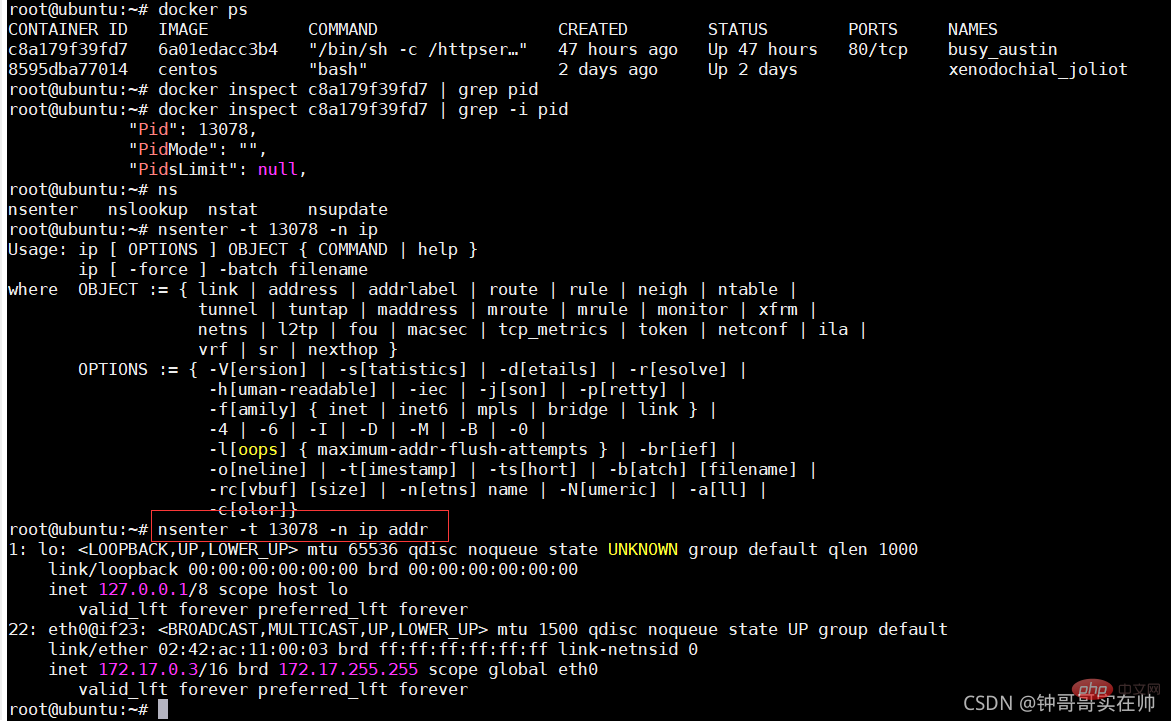
6. Detailed explanation of Linux Cgroups
Detailed explanation of Cgroups
Container Core: cgroups - Brief Book You can refer to this article to learn more
Simulate Cgroups to control CPU resources
Pass Simulate to better familiarize yourself with the effect of Cgroups controlling resources. First create the cpudemo folder
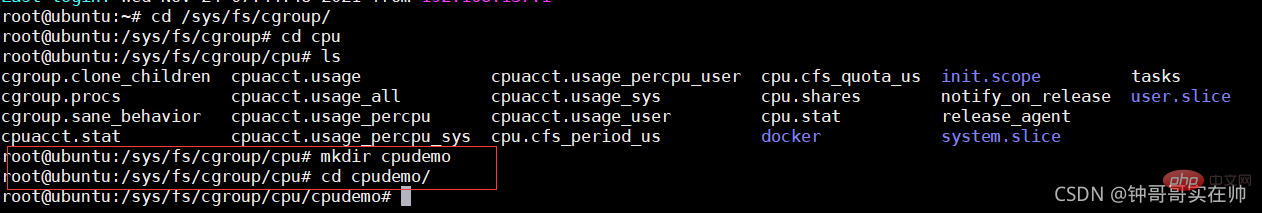
Execute top and you can see that busyloop takes up two CPU resources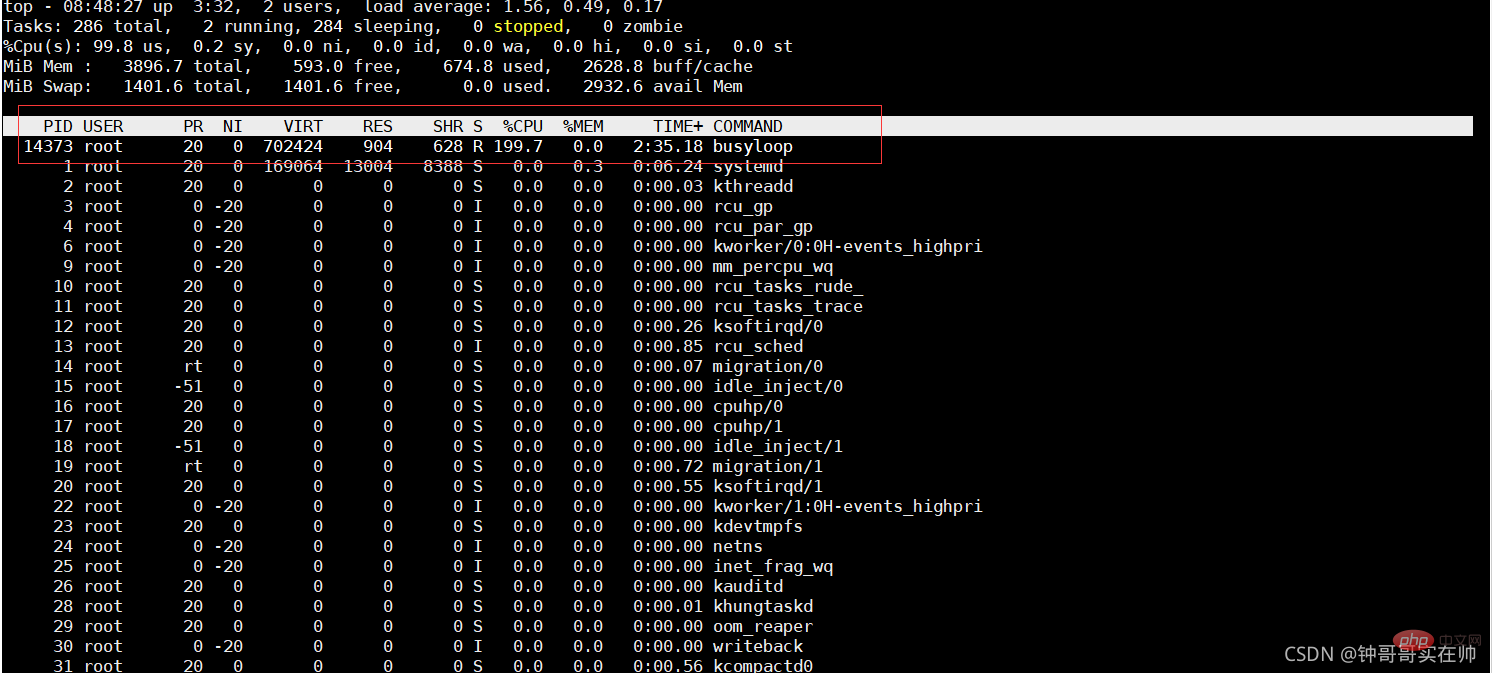
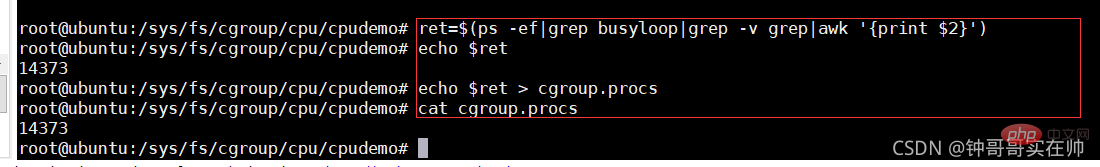
Add the process to the cgroup process configuration group
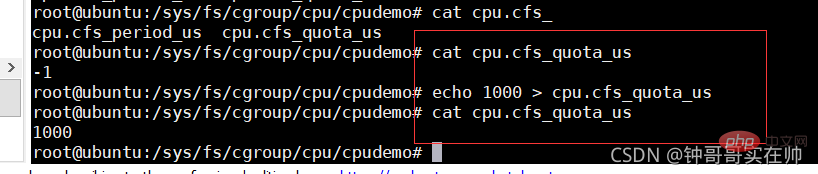
Set cpuquota
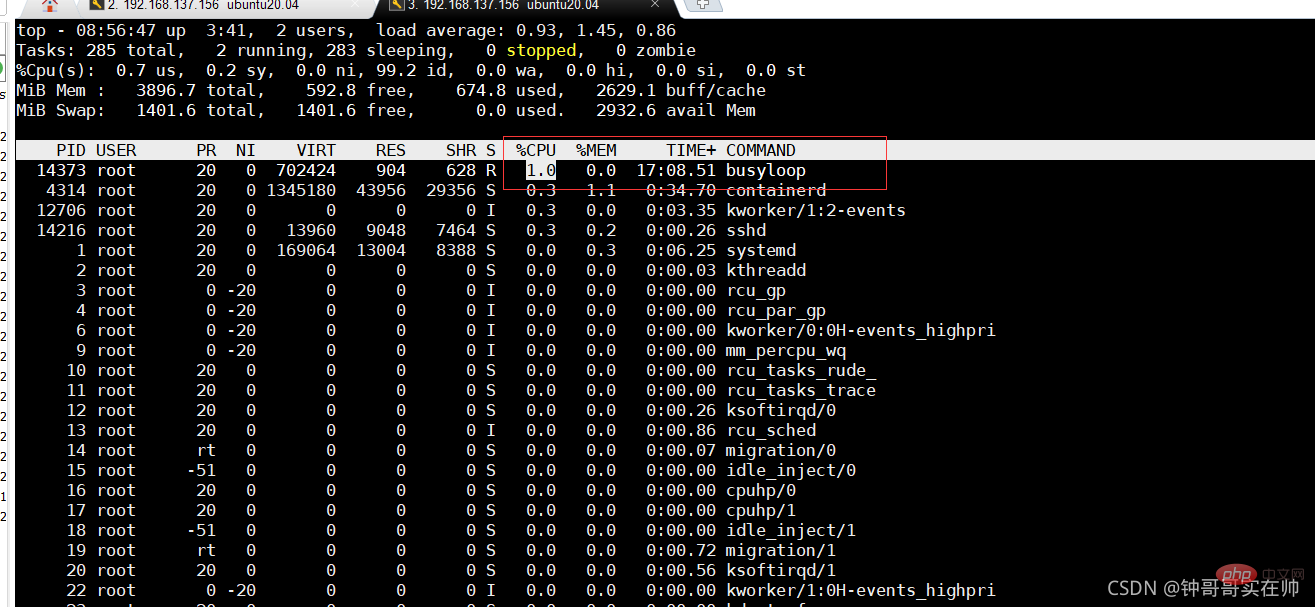
You can see that success will occupy 200% The CPU resources are reduced to 1%
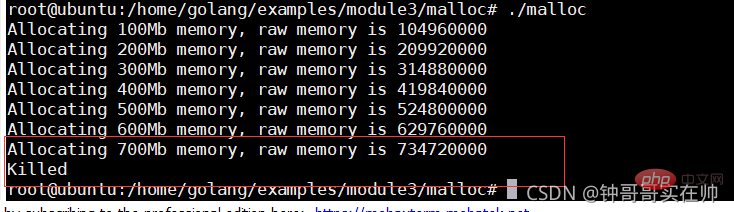
Simulating Cgroups exceeding the limit memory resources and being killed by OOM
/ Create the memorydemo folder in the sys/fs/cgroup/memory directory
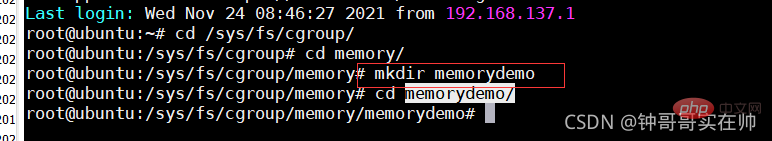
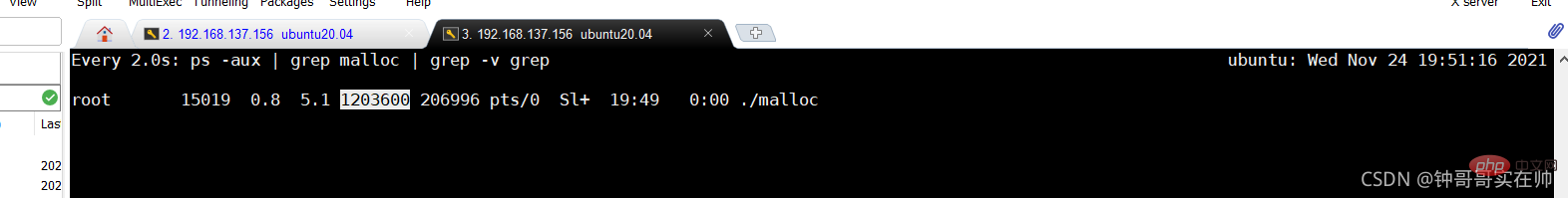
Run the memory-consuming program and use watch to query the memory usage

Configure the process into the cgroups configuration group 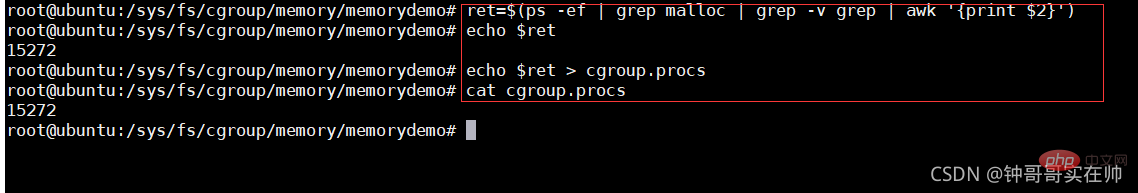
Set the maximum memory size
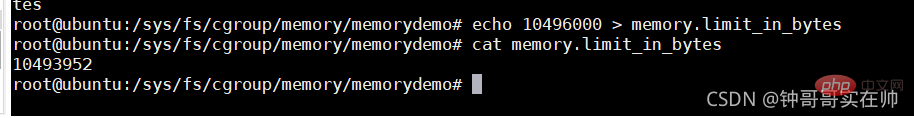
Waiting for the program Killed by OOM, dmesg can see the kill information

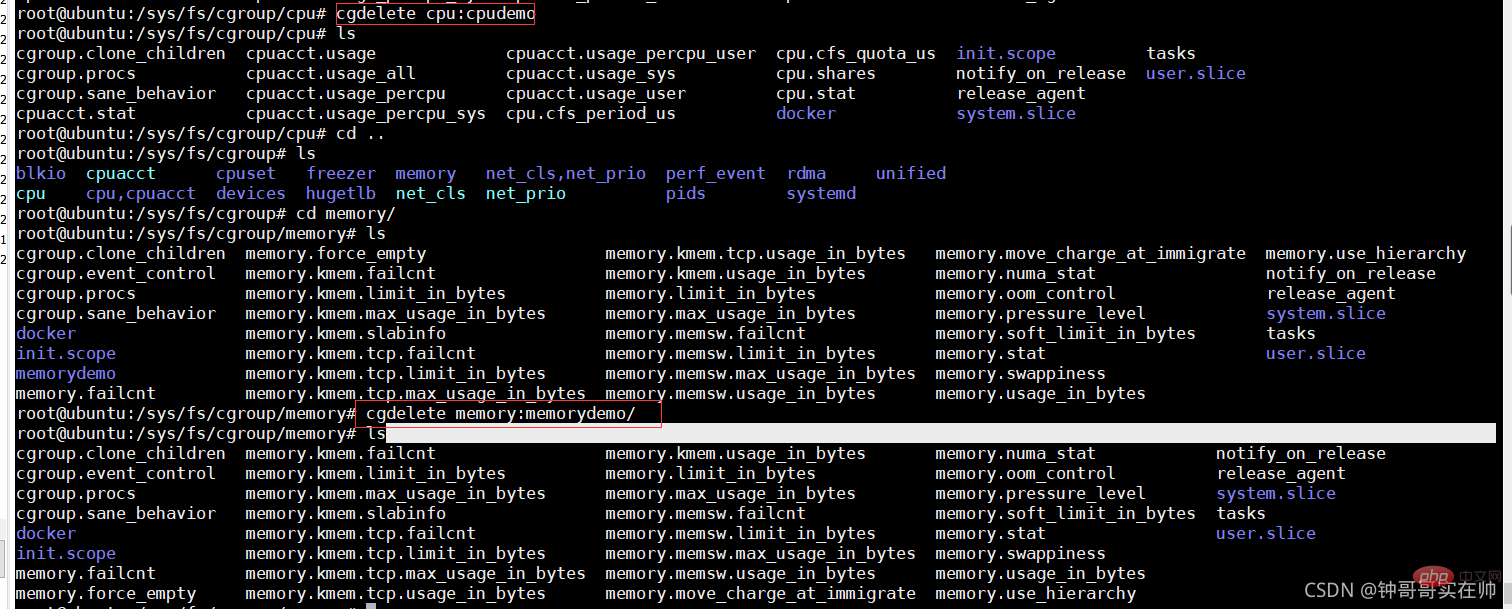
Note: To delete self-created cgroup folders, you need to use cgroup-tools
7. Union FS
The technologies used by Docker are all derived from Linux technologies and are not There is no innovation, and the innovation of Docker is the file system.
1. Concept:
- File system that mounts different directories under the same virtual file system
- Supports setting readonly, readwrite and without for each member directory -able permissions
- File system layering, the directory with readonly permissions can be logically modified. The modifications here are incremental and do not affect the readonly part
- Usual Union FS uses: Multiple disks are mounted to the same directory, and the other is to combine the readonly part and the writeable directory
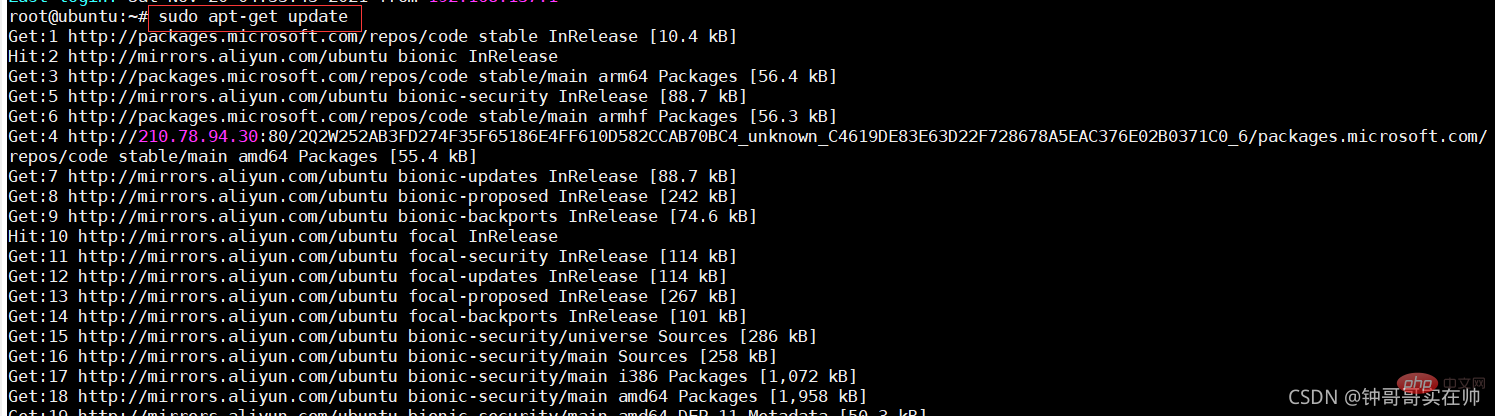
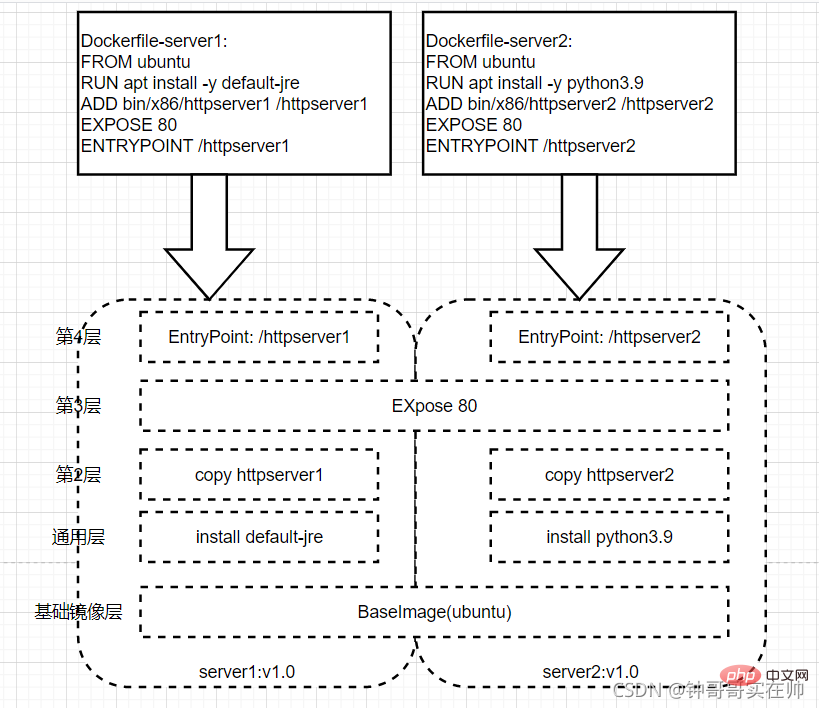
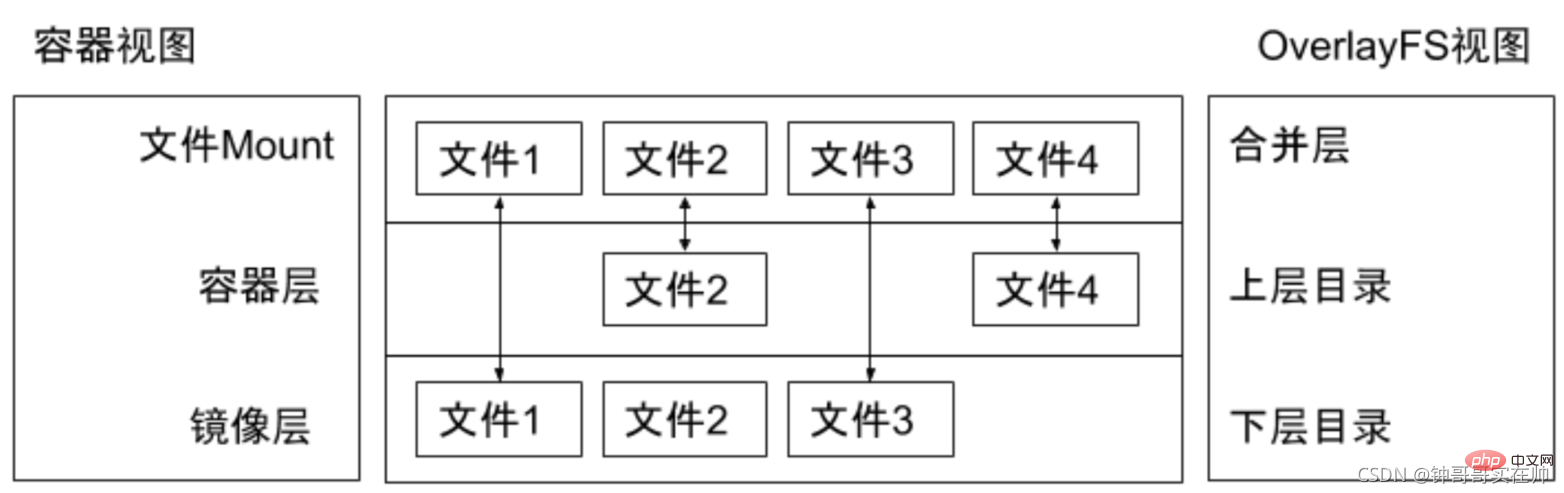
2. Illustration of Union FS
In the design of the Docker image, The concept of layer is introduced, that is to say, every step of the user's image creation operation will generate a layer, that is, an incremental rootfs (a directory), so that the containers where application A and application B are located jointly reference the same The ubuntu operating system layer and the Golang environment layer (as read-only layers) each have their own application layer and writable layer. When starting the container, mount the relevant layers to a directory through UnionFS as the root file system of the container.
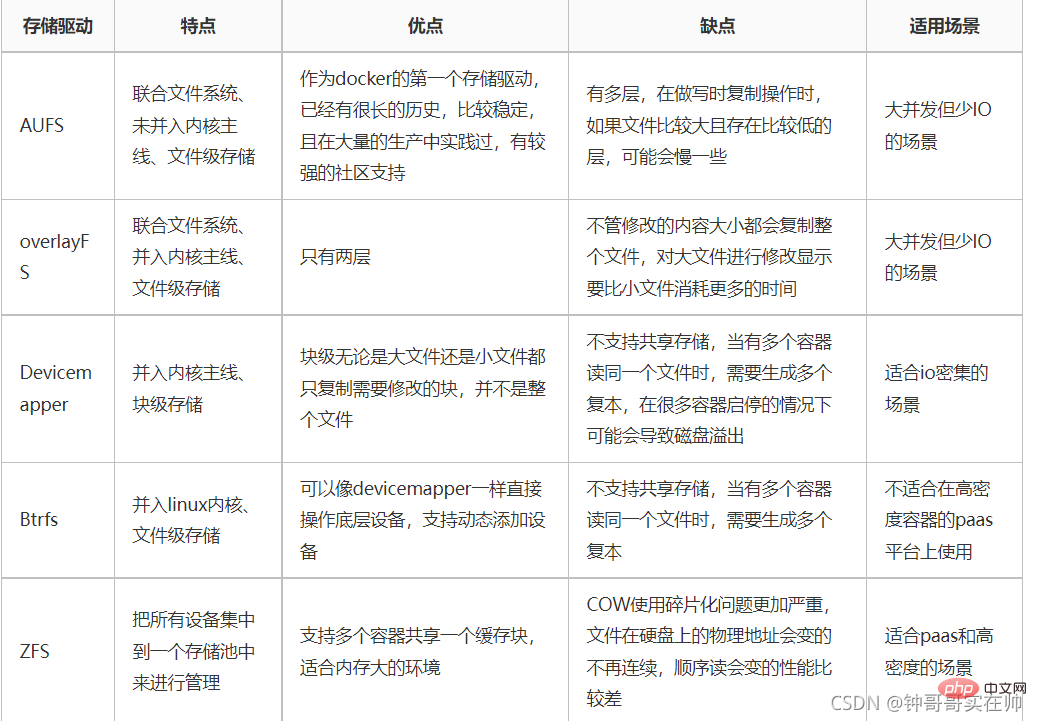
3. Container storage driver
4. Simulate Union FS to better understand the effect

Since the current version of docker uses the overlayFS storage driver, we use the overlay mounting method to conduct experiments. Overlayfs passes through three directories: lower Directory, upper directory, and work directory are implemented. There can be multiple lower directories. The work directory is the basic working directory. After mounting, the content will be cleared and its content will not be visible to the user during use. Finally, the joint mounting is completed. The unified view presented to the user is called the merged directory.
Execute the following command:
mkdir upper lower merged work
echo "lower" > lower/in_lower.txt
echo "from lower" > lower/in_both.txt
echo "from upper" > upper/in_both.txt
echo "upper" > upper/in_upper.txt
path=$(pwd)
mount -t overlay overlay -o lowerdir=${path}/lower,upperdir=${path}/upper,workdir=${path}/work ${path}/merged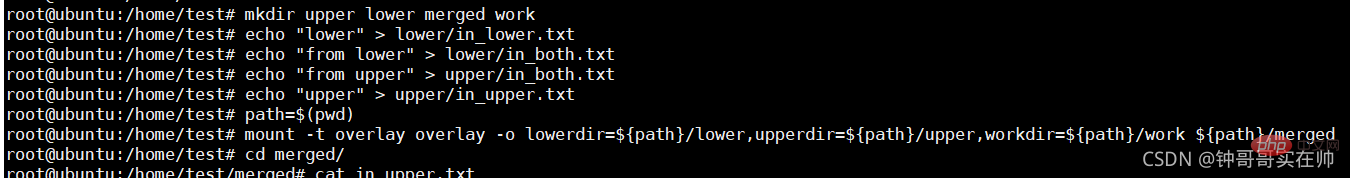
## You can see that the overlay storage driver file is mounted using Effect. After the experiment is completed, you need to restore the environment after umounting the merged directory, and then deleting the four directories. If you delete the others first, rm: cannot remove 'merged/': Device or resource busy may appear, resulting in the merged directory not being deleted. 
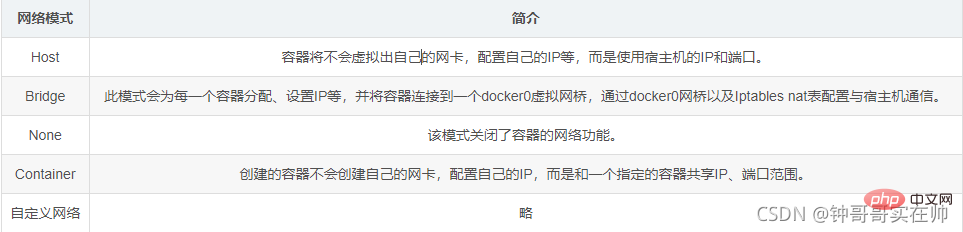
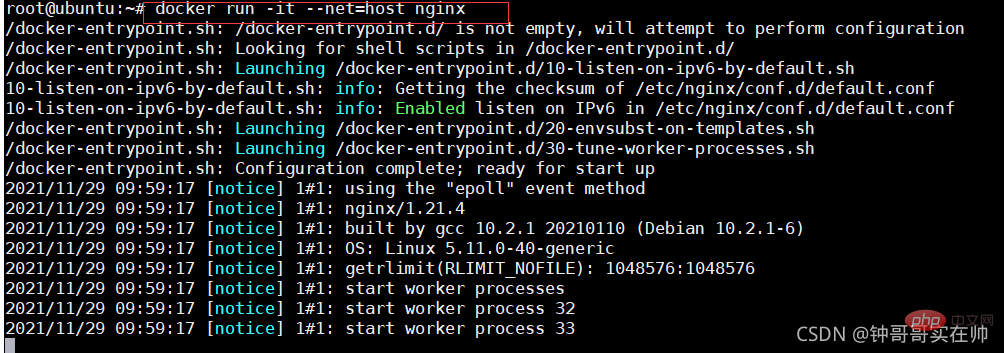
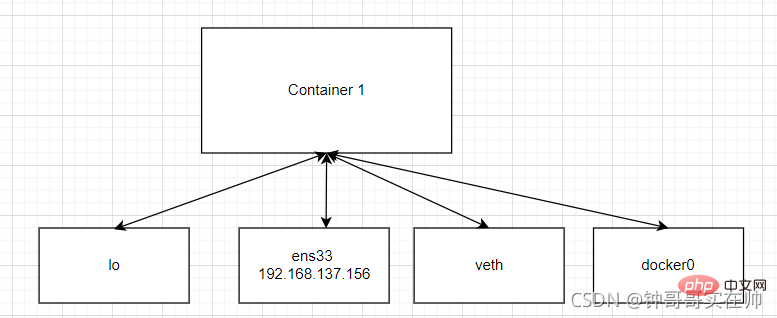
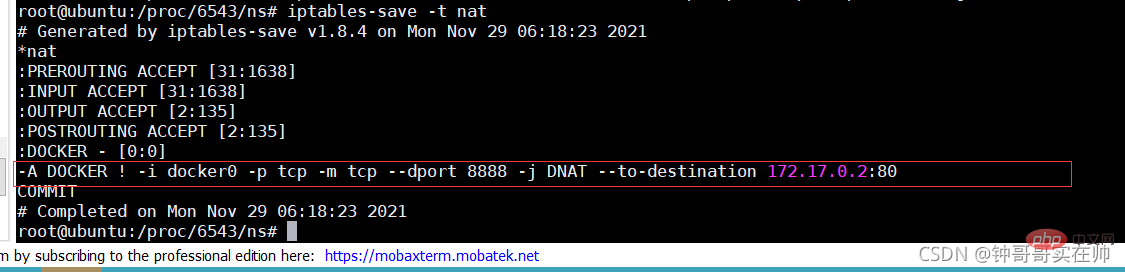
- Query the built-in docker Network mode
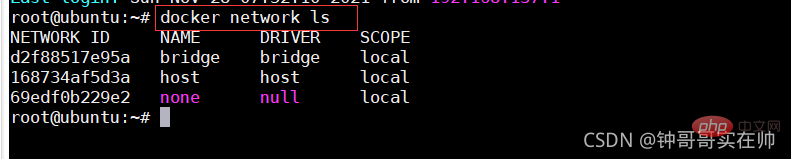
- docker run Select the network mode to run
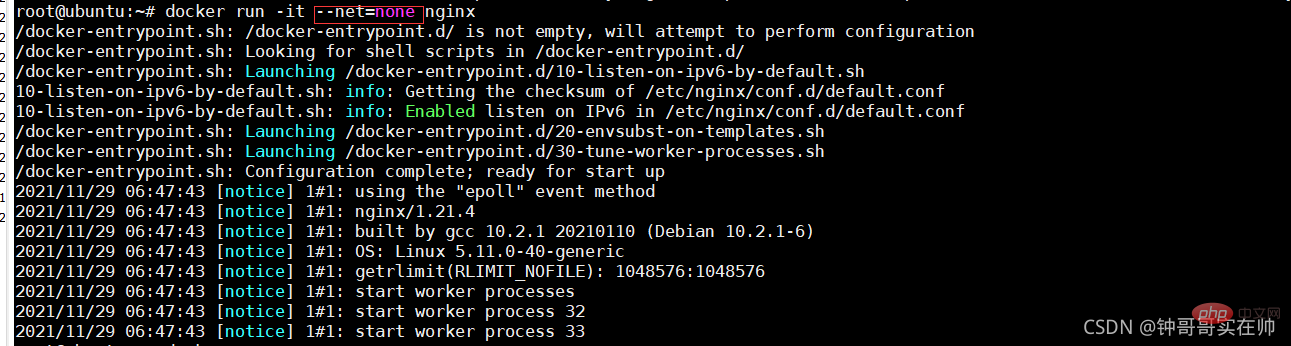
 # 2) none mode: use --net=none specified. The network configuration needs to be configured by yourself
# 2) none mode: use --net=none specified. The network configuration needs to be configured by yourself
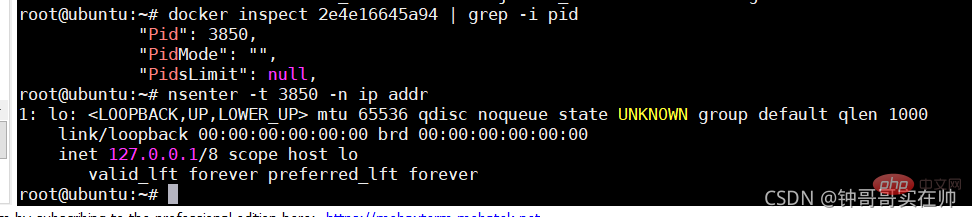 3) Bridge mode: Use --net=bridge to specify, the default setting.
3) Bridge mode: Use --net=bridge to specify, the default setting.
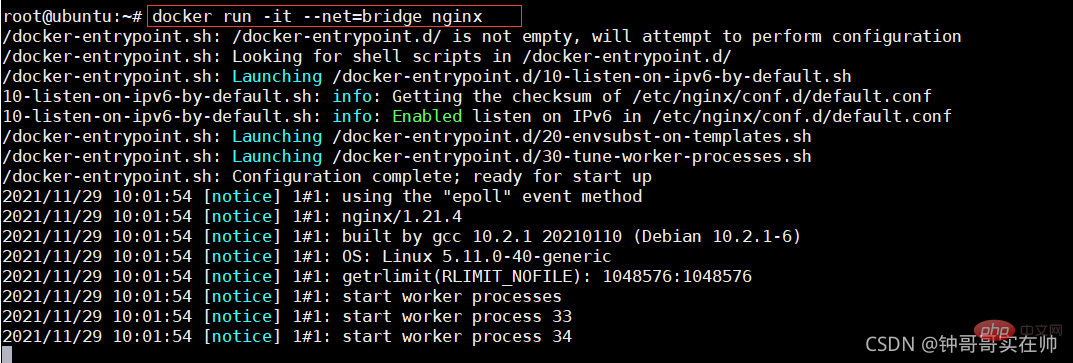
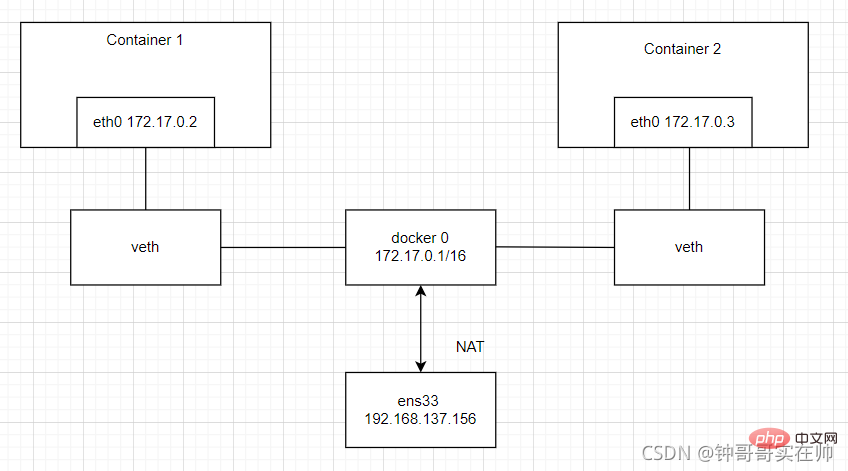
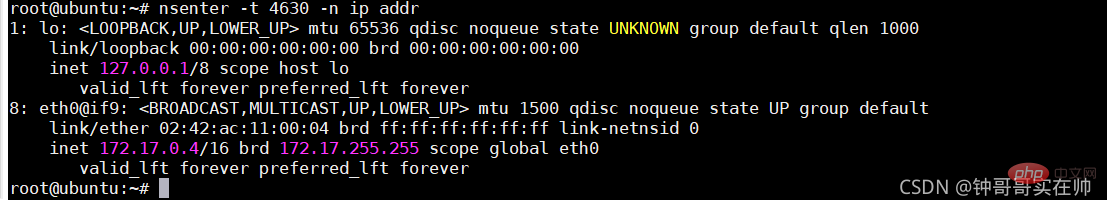 docker network logic diagram bridge and NAT
docker network logic diagram bridge and NAT
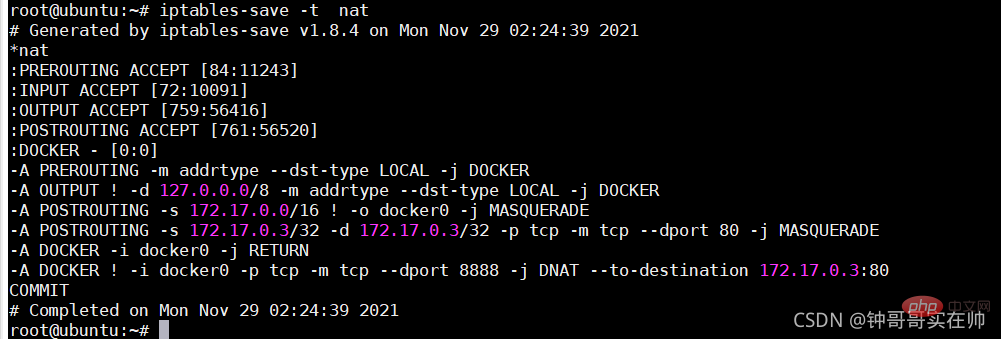
4) Container mode: Use --net=container:NAME_or_ID to specify. Using the network configuration of other containers
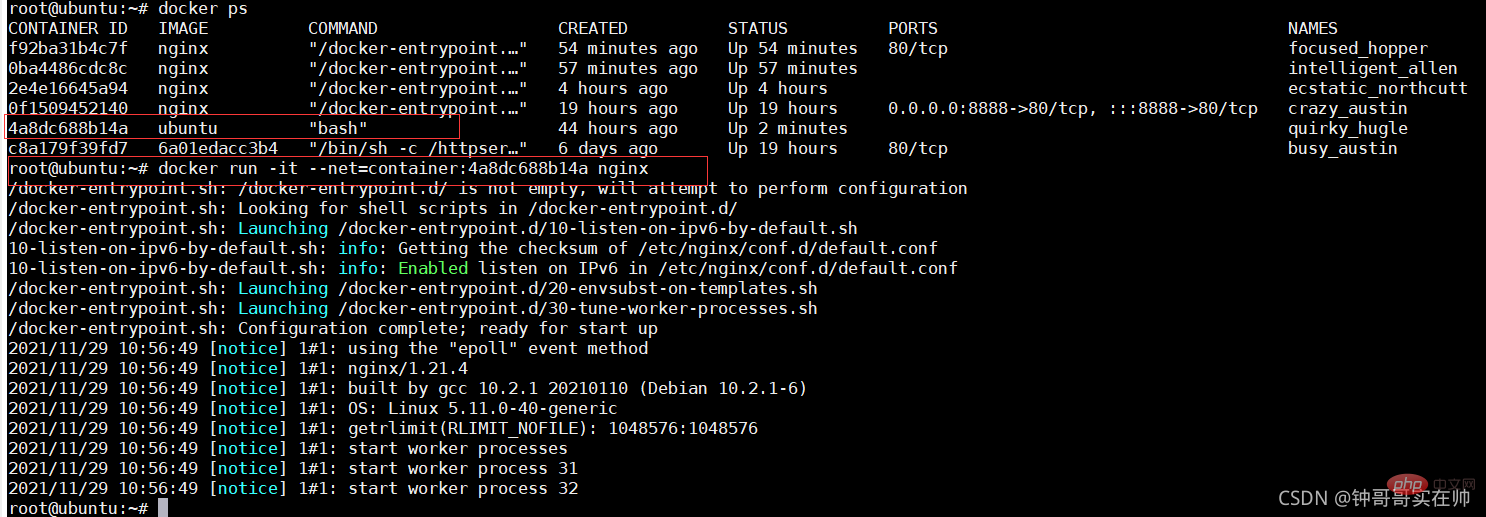
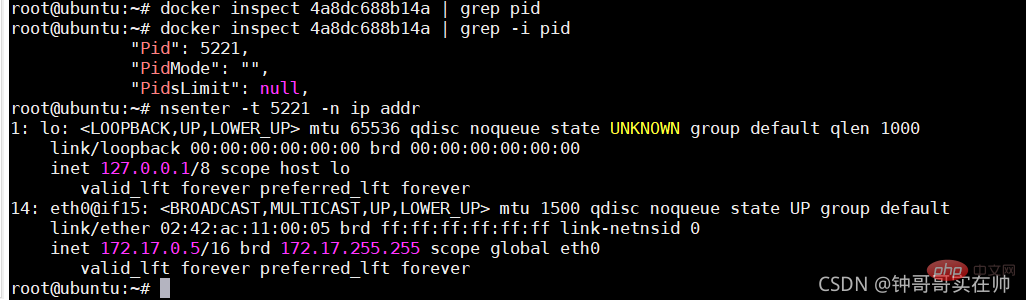
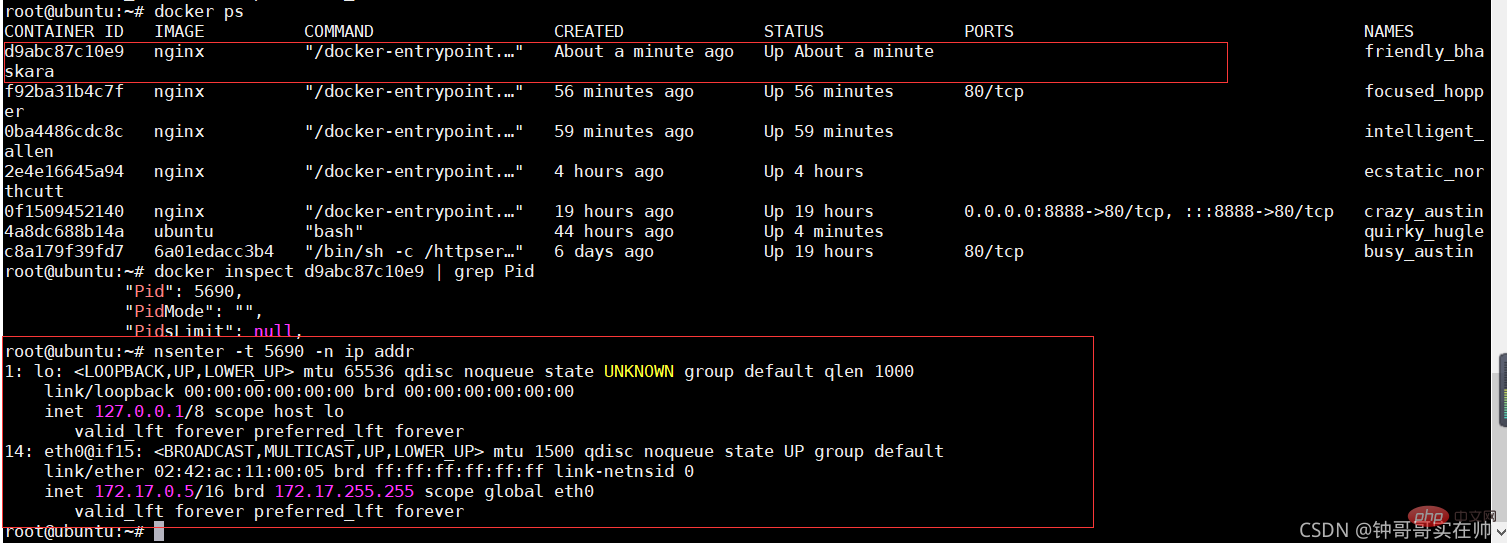
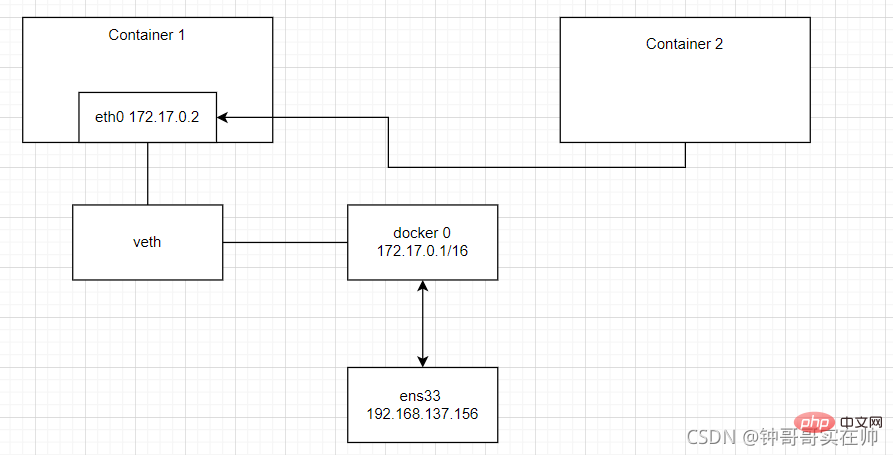
- Create --net=none nginx
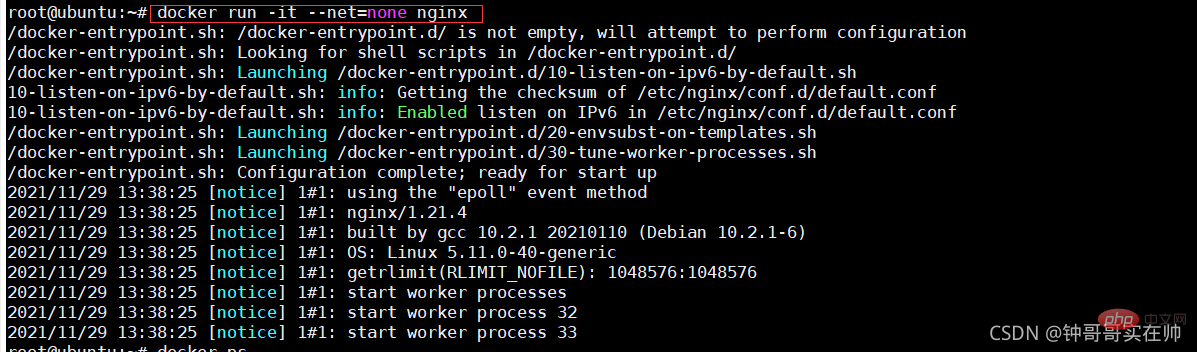
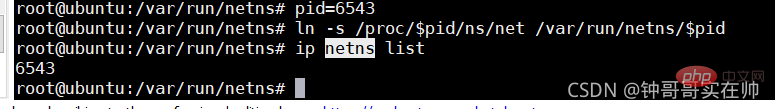
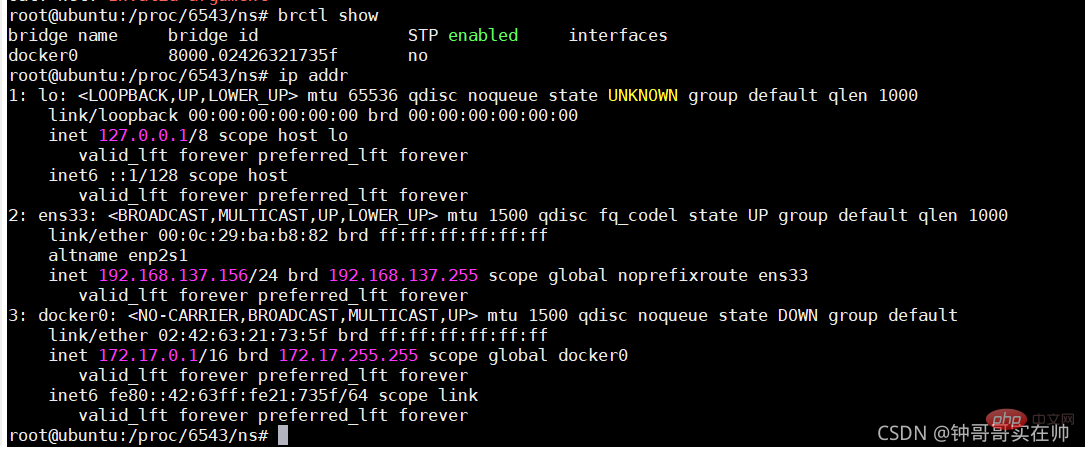
- Create network namespace
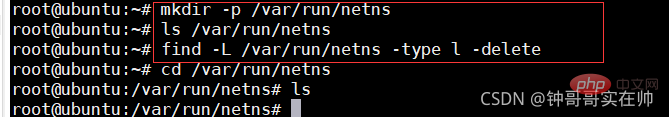
- ## Create network namespace link
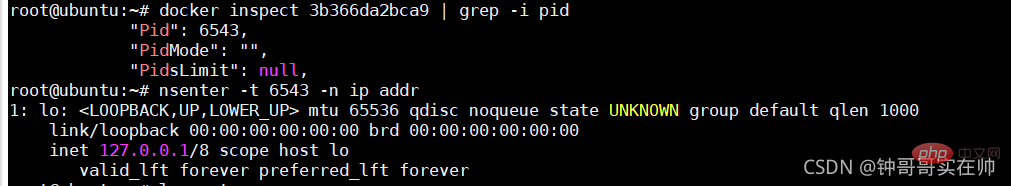
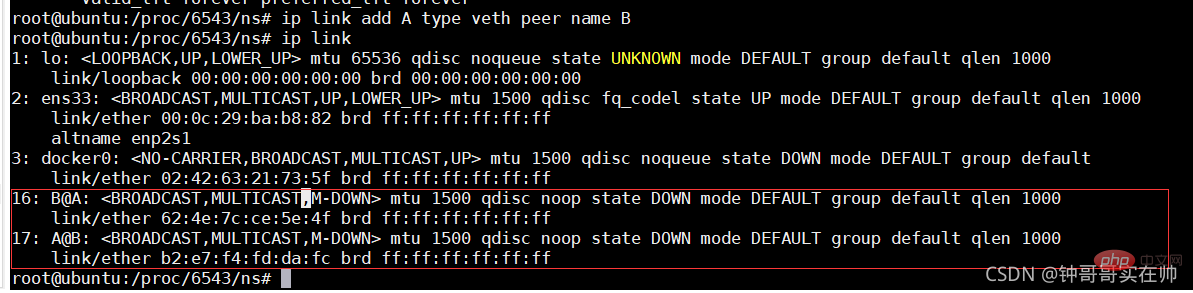
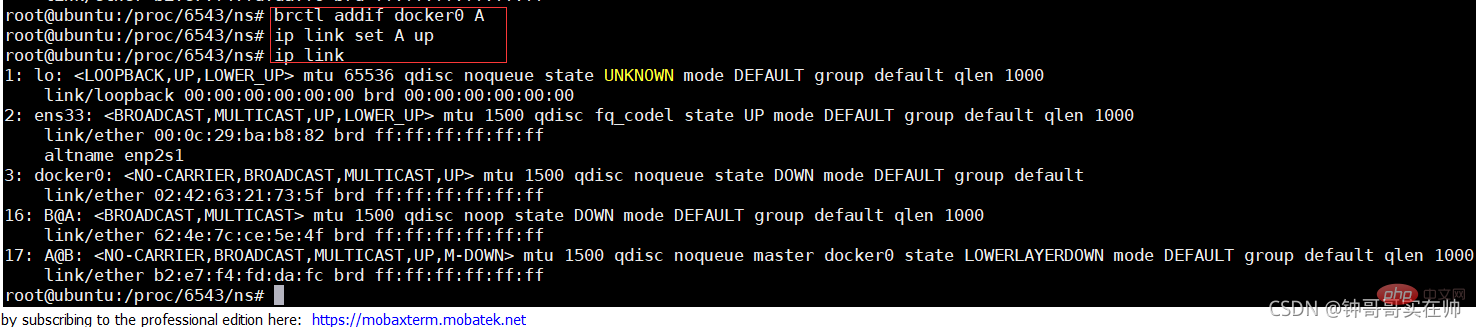
- Generate eth0 network device in nginx docker
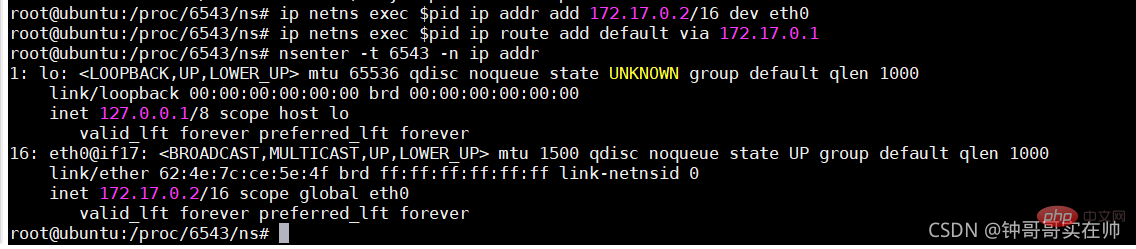
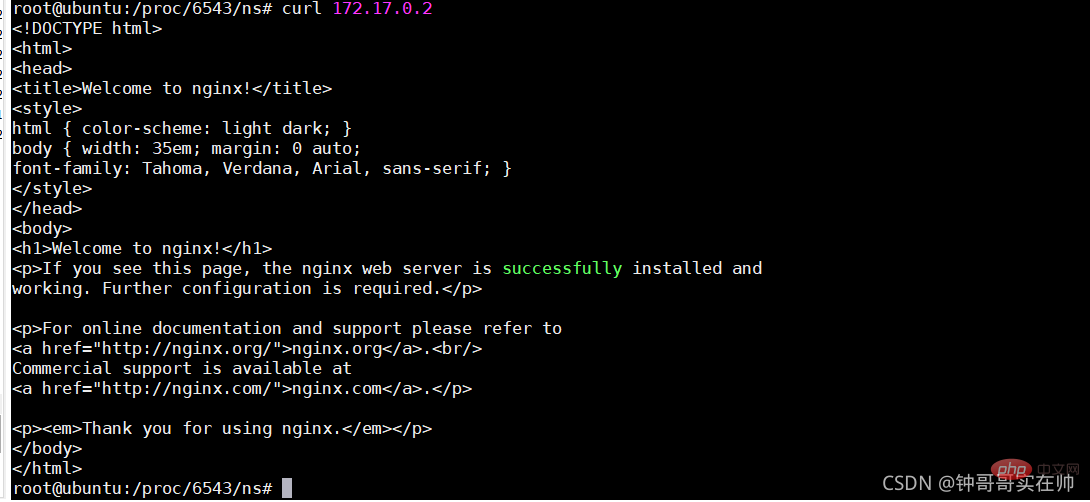
Configure ip gateway for eth0 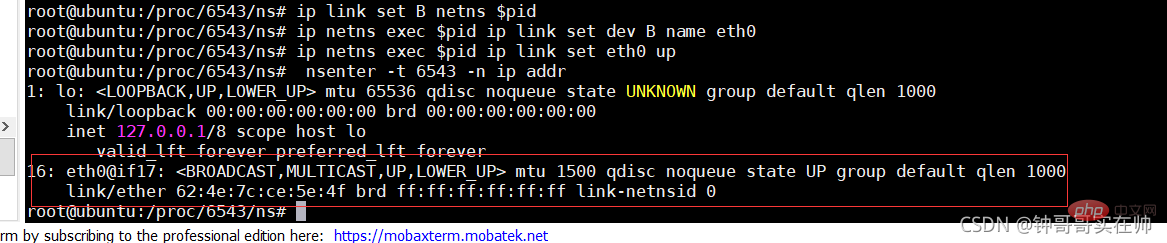

Recommended learning: "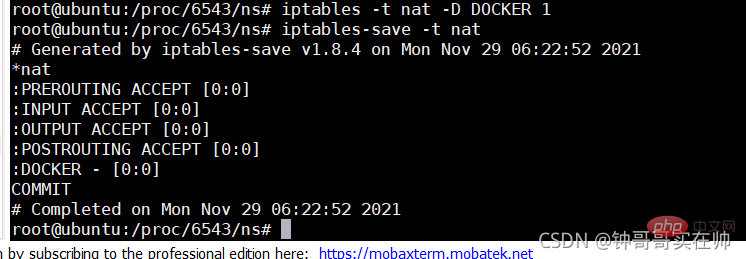 docker video tutorial
docker video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of The most systematic mastery of Docker core technology (summary sharing). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to package project with pycharm
Apr 25, 2024 am 03:54 AM
How to package project with pycharm
Apr 25, 2024 am 03:54 AM
There are four ways to package a project in PyCharm: Package as a separate executable file: Export to EXE single file format. Packaged as an installer: Generate Setuptools Makefile and build. Package as a Docker image: specify an image name, adjust build options, and build. Package as a container: Specify the image to build, adjust runtime options, and start the container.
 Docker completes local deployment of LLama3 open source large model in three minutes
Apr 26, 2024 am 10:19 AM
Docker completes local deployment of LLama3 open source large model in three minutes
Apr 26, 2024 am 10:19 AM
Overview LLaMA-3 (LargeLanguageModelMetaAI3) is a large-scale open source generative artificial intelligence model developed by Meta Company. It has no major changes in model structure compared with the previous generation LLaMA-2. The LLaMA-3 model is divided into different scale versions, including small, medium and large, to suit different application needs and computing resources. The parameter size of small models is 8B, the parameter size of medium models is 70B, and the parameter size of large models reaches 400B. However, during training, the goal is to achieve multi-modal and multi-language functionality, and the results are expected to be comparable to GPT4/GPT4V. Install OllamaOllama is an open source large language model (LL
 Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Detailed explanation and installation guide for PiNetwork nodes This article will introduce the PiNetwork ecosystem in detail - Pi nodes, a key role in the PiNetwork ecosystem, and provide complete steps for installation and configuration. After the launch of the PiNetwork blockchain test network, Pi nodes have become an important part of many pioneers actively participating in the testing, preparing for the upcoming main network release. If you don’t know PiNetwork yet, please refer to what is Picoin? What is the price for listing? Pi usage, mining and security analysis. What is PiNetwork? The PiNetwork project started in 2019 and owns its exclusive cryptocurrency Pi Coin. The project aims to create a one that everyone can participate
 Agile development and operation of PHP microservice containerization
May 08, 2024 pm 02:21 PM
Agile development and operation of PHP microservice containerization
May 08, 2024 pm 02:21 PM
Answer: PHP microservices are deployed with HelmCharts for agile development and containerized with DockerContainer for isolation and scalability. Detailed description: Use HelmCharts to automatically deploy PHP microservices to achieve agile development. Docker images allow for rapid iteration and version control of microservices. The DockerContainer standard isolates microservices, and Kubernetes manages the availability and scalability of the containers. Use Prometheus and Grafana to monitor microservice performance and health, and create alarms and automatic repair mechanisms.
 PHP distributed system architecture and practice
May 04, 2024 am 10:33 AM
PHP distributed system architecture and practice
May 04, 2024 am 10:33 AM
PHP distributed system architecture achieves scalability, performance, and fault tolerance by distributing different components across network-connected machines. The architecture includes application servers, message queues, databases, caches, and load balancers. The steps for migrating PHP applications to a distributed architecture include: Identifying service boundaries Selecting a message queue system Adopting a microservices framework Deployment to container management Service discovery
 How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
There are many ways to install DeepSeek, including: compile from source (for experienced developers) using precompiled packages (for Windows users) using Docker containers (for most convenient, no need to worry about compatibility) No matter which method you choose, Please read the official documents carefully and prepare them fully to avoid unnecessary trouble.
 How to optimize the performance of Java functions through containerization?
Apr 29, 2024 pm 03:09 PM
How to optimize the performance of Java functions through containerization?
Apr 29, 2024 pm 03:09 PM
Containerization improves Java function performance in the following ways: Resource isolation - ensuring an isolated computing environment and avoiding resource contention. Lightweight - takes up less system resources and improves runtime performance. Fast startup - reduces function execution delays. Consistency - Decouple applications and infrastructure to ensure consistent behavior across environments.
 Deploy JavaEE applications using Docker Containers
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:29 PM
Deploy JavaEE applications using Docker Containers
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:29 PM
Deploy Java EE applications using Docker containers: Create a Dockerfile to define the image, build the image, run the container and map the port, and then access the application in the browser. Sample JavaEE application: REST API interacts with database, accessible on localhost after deployment via Docker.