 Development Tools
Development Tools
 composer
composer
 Detailed explanation of how Composer+Git creates a 'service class library'
Detailed explanation of how Composer+Git creates a 'service class library'
Detailed explanation of how Composer+Git creates a 'service class library'
Introduction
I always think that now PHP has progressed into the field of engineering. In the past, PHP developers regarded speed as beauty, and speed and scale were always contradictory. Today's PHP projects, especially larger projects, have gradually evolved to a level that requires both engineering and scale. Engineering a code means evolving into an increasingly complex architecture. For complex architectures, microservices are often a good choice.
I needed this question in a recent project. I need to develop a map service. This service is of course not in the form of a simple class library, but has its own database and its own service interface. In this case, the best option is servitization. Of course, there are many ways to service, such as Thrift, HTTP, etc. But I evaluated the current department environment. PHP is the mainstream language, and the progress of my project is also relatively tight. In my eyes, Thrift, HTTP and other methods all use network protocols to achieve service decoupling. It seems to be a serious solution. I think this approach is not necessary when the project is not clearly in critical condition. The disadvantage of using network protocol servitization is that it introduces significant complexity. This complexity often means investment in manpower, material resources, and time. So I hope to be able to provide a "service class library" in the PHP language for development.
What I am thinking of is PHP’s Composer.
Modification of Composer
Create service class library
First, I need to change my "service class library" from My application (named xxx/main1) is independent. For this independence, I did not choose to create a directory in the application (in fact, I thought about creating a directory such as Services). However, if the code is coupled with the business program, I feel that due to human laziness, it is difficult to control oneself from beginning to end and insist on not using various convenient functions in the application. So my choice is to create a new project in the Git repository and name it xxx/mapService.
composer.json
Now there are two Git projects (xxx/main1 and xxx/mapService). I added the following statement to the composer.json file in main1:

The composer.json in mapService is as follows:

This configuration tells the main1 project that the Git address of mapService needs to be used version of.
Of course you need to pay attention to the following points:
- dev-master means directly using the master branch of mapService. If mapService has other tags, you can use the tag information here
- repositories is the address of the project
- The service I have here is placed on the GitLab built by our company
- mapService The namespace of the src folder below is xxxx\\xxxx\\MapService\\ and supports PSR-4
- mapService uses illuminate/database
Last use composer update -vvv can download the mapService we need and put it in the vendor directory.
Update and modification
Our editor is now in the main1 project. If we have edited and modified the mapService project, and want to merge it into the master branch of mapService , directly enter the vender/xxx/mapService directory and perform Git corresponding operations. This allows direct code modifications.
Independent configuration
The combination of this structure is only the first step in completing the long march of thousands of miles. What is more important later is that when writing this service, I need to always remember not to use everything in main1, so as to maintain the independence of mapService (independence is one of the necessary conditions for servitization). For example, the first problem I encountered was that the configuration file needs to be independent.
My implementation method is to create a Config class directly in mapService, and the configuration is directly written in this class.
I have always felt that the implementation of this configuration file is a bit frustrating, because in this way, this configuration file enters the Git library. But I really can't think of a better solution. There is a way in Laravel to create Config in Laravel's config folder by implementing ServiceProvider, but this method only applies to Laravel. There is no universality. On the other hand, I think which database the service uses is itself part of the service, and it seems to have nothing to do with putting it in the Git library of the service.
Directory structure
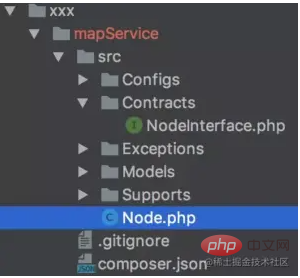
The directory structure is as above
- Configs provides configuration files
- Contracts provides interface protocols
- Exceptions provides exceptions
- Supports provides third-party methods or class libraries
- Models provides interaction with the database
- Node.php implementation Specific interface
The most important thing about the service is the interface protocol. So create a Contracts folder and interface the provided services.
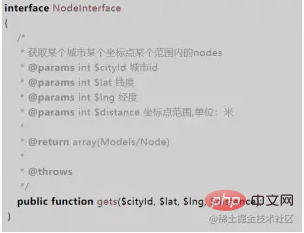
# The exception handling of the interface should try to use exceptions instead of error codes for interaction. And these exceptions should be customized as much as possible. In this way, there is the possibility of unified processing at the upper level.
Thinking
I position this architectural model as a service-oriented model at the PHP code level. Applicable scenarios should be:
- Later planning service-oriented
- Scenarios where both manpower and thinking in the early stage hope to maintain rapid development
and Git The difference between SubTree and SubModule
In fact, these three methods all use one project as the class library of another project. SubTree and SubModule are Git solutions. Composer is a solution for the PHP language. In addition to the function of adding a project to another project, it also provides solutions such as adding versions and dependency solutions. If your project is in PHP, then using Composer is undoubtedly a better choice.
Later protocol serviceization
If my mapService wants to be protocol service-oriented later, then the mapService project can be simplified into an SDK. For the upper-layer business logic, Just use composer update to update.
Service registration and discovery
The so-called "service class library" I call here does not solve the problem of service registration. I have no way of knowing how many projects use me. services. This may require additional process work.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of how Composer+Git creates a 'service class library'. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1379
1379
 52
52
 HadiDB: A lightweight, horizontally scalable database in Python
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
HadiDB: A lightweight, horizontally scalable database in Python
Apr 08, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
HadiDB: A lightweight, high-level scalable Python database HadiDB (hadidb) is a lightweight database written in Python, with a high level of scalability. Install HadiDB using pip installation: pipinstallhadidb User Management Create user: createuser() method to create a new user. The authentication() method authenticates the user's identity. fromhadidb.operationimportuseruser_obj=user("admin","admin")user_obj.
 How to view the results after Bootstrap is modified
Apr 07, 2025 am 10:03 AM
How to view the results after Bootstrap is modified
Apr 07, 2025 am 10:03 AM
Steps to view modified Bootstrap results: Open the HTML file directly in the browser to ensure that the Bootstrap file is referenced correctly. Clear the browser cache (Ctrl Shift R). If you use CDN, you can directly modify CSS in the developer tool to view the effects in real time. If you modify the Bootstrap source code, download and replace the local file, or rerun the build command using a build tool such as Webpack.
 How to use vue pagination
Apr 08, 2025 am 06:45 AM
How to use vue pagination
Apr 08, 2025 am 06:45 AM
Pagination is a technology that splits large data sets into small pages to improve performance and user experience. In Vue, you can use the following built-in method to paging: Calculate the total number of pages: totalPages() traversal page number: v-for directive to set the current page: currentPage Get the current page data: currentPageData()
 Monitor MySQL and MariaDB Droplets with Prometheus MySQL Exporter
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Monitor MySQL and MariaDB Droplets with Prometheus MySQL Exporter
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Effective monitoring of MySQL and MariaDB databases is critical to maintaining optimal performance, identifying potential bottlenecks, and ensuring overall system reliability. Prometheus MySQL Exporter is a powerful tool that provides detailed insights into database metrics that are critical for proactive management and troubleshooting.
 How to view the JavaScript behavior of Bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 am 10:33 AM
How to view the JavaScript behavior of Bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 am 10:33 AM
The JavaScript section of Bootstrap provides interactive components that give static pages vitality. By looking at the open source code, you can understand how it works: Event binding triggers DOM operations and style changes. Basic usage includes the introduction of JavaScript files and the use of APIs, and advanced usage involves custom events and extension capabilities. Frequently asked questions include version conflicts and CSS style conflicts, which can be resolved by double-checking the code. Performance optimization tips include on-demand loading and code compression. The key to mastering Bootstrap JavaScript is to understand its design concepts, combine practical applications, and use developer tools to debug and explore.
 How to build a bootstrap framework
Apr 07, 2025 pm 02:54 PM
How to build a bootstrap framework
Apr 07, 2025 pm 02:54 PM
Bootstrap framework building guide: Download Bootstrap and link it to your project. Create an HTML file to add the necessary elements. Create a responsive layout using the Bootstrap mesh system. Add Bootstrap components such as buttons and forms. Decide yourself whether to customize Bootstrap and compile stylesheets if necessary. Use the version control system to track your code.
 Is Git the same as GitHub?
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:13 AM
Is Git the same as GitHub?
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:13 AM
Git and GitHub are not the same thing. Git is a version control system, and GitHub is a Git-based code hosting platform. Git is used to manage code versions, and GitHub provides an online collaboration environment.
 Password policy strengthening and regular script replacement implementation
Apr 08, 2025 am 10:06 AM
Password policy strengthening and regular script replacement implementation
Apr 08, 2025 am 10:06 AM
This article describes how to use Python scripts to strengthen password policies and change passwords regularly. The steps are as follows: 1. Use Python's random and string modules to generate random passwords that meet the complexity requirements; 2. Use the subprocess module to call system commands (such as Linux's passwd command) to change the password to avoid hard-code the password directly; 3. Use crontab or task scheduler to execute scripts regularly. This script needs to handle errors carefully and add logs, and update regularly to deal with security vulnerabilities. Multi-level security protection can ensure system security.



