A brief analysis of what is a decorator? How to use decorators in Vue?
What is a decorator? This article will introduce you to decorators and briefly introduce how to use decorators in js and vue. I hope it will be helpful to you!

# I believe that you must have encountered the need for secondary pop-up confirmation during development. Whether you are using the secondary pop-up component of the UI framework or your own encapsulated pop-up component. All of them cannot avoid the problem of a large amount of repeated code when used multiple times. The accumulation of these codes results in poor readability of the project. The code quality of the project has also become very poor. So how do we solve the problem of duplicate pop-up codes? Using Decorators
What are decorators?
Decorator is a new syntax for ES7. DecoratorDecorate classes, objects, methods, and properties. Add some additional behavior to it. In layman's terms: it is a secondary packaging of a piece of code.
The use of decorators
The method of use is very simple. We define a function
const decorator = (target, name, descriptor) => {
var oldValue = descriptor.value;
descriptor.value = function(){
alert('哈哈')
return oldValue.apply(this,agruments)
}
return descriptor
}
// 然后直接@decorator到函数、类或者对象上即可。The purpose of the decorator is to reuse the code. Let's take a small example first to see
Using decorators in js
//定义一个装饰器
const log = (target, name, descriptor) => {
var oldValue = descriptor.value;
descriptor.value = function() {
console.log(`Calling ${name} with`, arguments);
return oldValue.apply(this, arguments);
};
return descriptor;
}
//计算类
class Calculate {
//使用装饰器
@log()
function subtraction(a,b){
return a - b
}
}
const operate = new Calculate()
operate.subtraction(5,2)Not using decorators
const log = (func) => {
if(typeof(func) !== 'function') {
throw new Error(`the param must be a function`);
}
return (...arguments) => {
console.info(`${func.name} invoke with ${arguments.join(',')}`);
func(...arguments);
}
}
const subtraction = (a, b) => a + b;
const subtractionLog = log(subtraction);
subtractionLog(10,3);In this comparison, you will find that the code after using decorators Readability has become stronger. Decorators don't care about the implementation of your inner code.
Using decorators in vue
If your project is built with vue-cli and the version of vue-cli is greater than 2.5, you can use it without any configuration. If your project also contains eslit, then you need to enable support for decorator-related syntax detection in eslit. [Related recommendations: vue.js video tutorial]
//在 eslintignore中添加或者修改如下代码:
parserOptions: {
ecmaFeatures:{
// 支持装饰器
legacyDecorators: true
}
}After adding this code, eslit will support decorator syntax.
Usually in projects, we often use secondary pop-up boxes for deletion operations:
//decorator.js
//假设项目中已经安装了 element-ui
import { MessageBox, Message } from 'element-ui'
/**
* 确认框
* @param {String} title - 标题
* @param {String} content - 内容
* @param {String} confirmButtonText - 确认按钮名称
* @param {Function} callback - 确认按钮名称
* @returns
**/
export function confirm(title, content, confirmButtonText = '确定') {
return function(target, name, descriptor) {
const originValue = descriptor.value
descriptor.value = function(...args) {
MessageBox.confirm(content, title, {
dangerouslyUseHTMLString: true,
distinguishCancelAndClose: true,
confirmButtonText: confirmButtonText
}).then(originValue.bind(this, ...args)).catch(error => {
if (error === 'close' || error === 'cancel') {
Message.info('用户取消操作'))
} else {
Message.info(error)
}
})
}
return descriptor
}
}The above code confirm method executes a MessageBox component in element-ui When the user cancels, the Message component will prompt the user to cancel the operation.
Let’s decorate the test() method with a decorator
import { confirm } from '@/util/decorator'
import axios form 'axios'
export default {
name:'test',
data(){
return {
delList: '/merchant/storeList/commitStore'
}
}
},
methods:{
@confirm('删除门店','请确认是否删除门店?')
test(id){
const {res,data} = axios.post(this.delList,{id})
if(res.rspCd + '' === '00000') this.$message.info('操作成功!')
}
}At this time, the user clicks on a store to delete it. The decorator will work. The pop-up is as shown below:
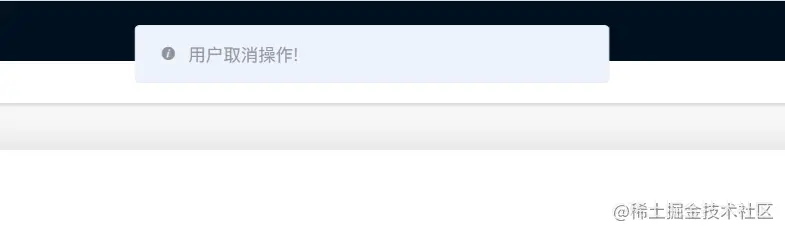
When I click cancel:

tips: The user canceled Operation. The modified test method will not execute .
When we click OK:
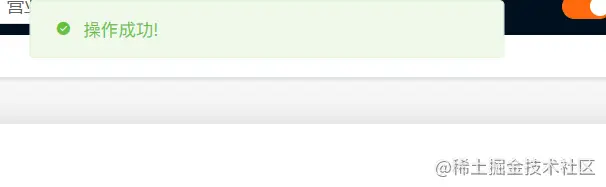
The interface is called and the message pops up
Summary
The decorator is used To repackage a piece of code. Add some behavioral operations and attributes to the code. Using decorators can greatly reduce code duplication. Improve code readability.
Finally
If there are any shortcomings in the article, please criticize and point it out.
For more programming-related knowledge, please visit: Introduction to Programming! !
The above is the detailed content of A brief analysis of what is a decorator? How to use decorators in Vue?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use echarts in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 04:24 PM
How to use echarts in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 04:24 PM
Using ECharts in Vue makes it easy to add data visualization capabilities to your application. Specific steps include: installing ECharts and Vue ECharts packages, introducing ECharts, creating chart components, configuring options, using chart components, making charts responsive to Vue data, adding interactive features, and using advanced usage.
 The role of export default in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:48 PM
The role of export default in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:48 PM
Question: What is the role of export default in Vue? Detailed description: export default defines the default export of the component. When importing, components are automatically imported. Simplify the import process, improve clarity and prevent conflicts. Commonly used for exporting individual components, using both named and default exports, and registering global components.
 How to use map function in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:54 PM
How to use map function in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:54 PM
The Vue.js map function is a built-in higher-order function that creates a new array where each element is the transformed result of each element in the original array. The syntax is map(callbackFn), where callbackFn receives each element in the array as the first argument, optionally the index as the second argument, and returns a value. The map function does not change the original array.
 What are hooks in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:33 PM
What are hooks in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 06:33 PM
Vue hooks are callback functions that perform actions on specific events or lifecycle stages. They include life cycle hooks (such as beforeCreate, mounted, beforeDestroy), event handling hooks (such as click, input, keydown) and custom hooks. Hooks enhance component control, respond to component life cycles, handle user interactions and improve component reusability. To use hooks, just define the hook function, execute the logic and return an optional value.
 validator method in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 04:09 PM
validator method in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 04:09 PM
The Validator method is the built-in validation method of Vue.js and is used to write custom form validation rules. The usage steps include: importing the Validator library; creating validation rules; instantiating Validator; adding validation rules; validating input; and obtaining validation results.
 How to disable the change event in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 07:21 PM
How to disable the change event in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 07:21 PM
In Vue, the change event can be disabled in the following five ways: use the .disabled modifier to set the disabled element attribute using the v-on directive and preventDefault using the methods attribute and disableChange using the v-bind directive and :disabled
 How to introduce echarts in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 04:39 PM
How to introduce echarts in vue
May 09, 2024 pm 04:39 PM
There are three ways to introduce ECharts into Vue.js: Install through npm Introduce through CDN Use the Vue ECharts plug-in Detailed steps: Create a chart container Introduce ECharts Initialize the chart instance Set chart options and data destroy chart instance (optional)
 Can calculated properties in Vue have parameters?
May 09, 2024 pm 06:24 PM
Can calculated properties in Vue have parameters?
May 09, 2024 pm 06:24 PM
Computed properties in Vue can have parameters, which are used to customize calculation behavior and transfer data. The syntax is computedPropertyWithArgs(arg1, arg2) { }. Parameters can be passed when used in templates, but the parameters must be responsive and cannot modify the internal state. .






