What should I do if centos cannot be shut down?
Solution to the problem that centos cannot be shut down: 1. Use the command "ps -aux" to check whether there is a background process running; 2. Shut down through the shutdown, halt or poweroff commands.

The operating environment of this article: centOS7 system, DELL G3 computer
What should I do if centos cannot be shut down?
CentOS 7 Correct shutdown and restart
Linux is mainly used in the server field, and executing a service on the server is never-ending unless it encounters Special circumstances, otherwise it will not shut down. Unlike Windows, under Linux systems, many processes are executed in the background. Behind the screen, there may be many people working at the same time. If you press the power button directly, other people's data may be interrupted. What's more serious is that if you shut down improperly, in serious cases, the file system may be damaged, resulting in data loss.
If you want to shut down, you must ensure that no other users in the current system are logging in to the system. We can use the who command to see if there are other people logged in, or use the command ps -aux to see if there are any background processes running. Shutdown, halt, and poweroff are all shutdown commands. We can use the command man shutdown to view its help documentation. For example, we run the following command to shut down.
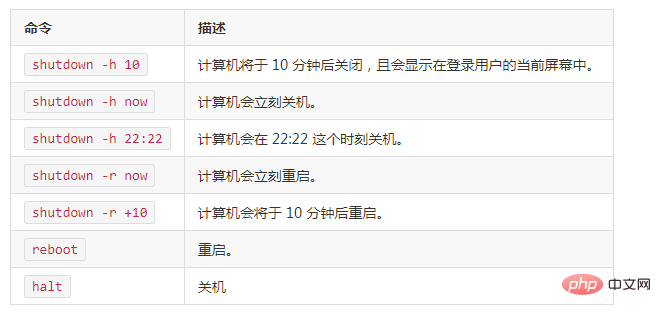
Of course, if you learned it from CentOS 6.5, init 0 and init 6 are applicable to CentOS 7.
Init is divided into 7 levels. The meanings of these 7 levels are as follows.

The default startup runlevel is configured in /etc/inittab. The default value depends on the system release version: Debian and Ubuntu use runlevel 2, Red Hat and Fedora use runlevel 3 or 5, CentOS and Gentoo use runlevel 3
For each runlevel, there is a separate directory rc0.d ... rc6.d in the /etc directory, which contains many points to the /etc/init.d directory Symbolic link, so the service startup script is placed in the /etc/init.d directory.
Recommended: "centos usage tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What should I do if centos cannot be shut down?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 CentOS Stream 8 troubleshooting methods
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:33 PM
CentOS Stream 8 troubleshooting methods
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:33 PM
CentOSStream8 system troubleshooting guide This article provides systematic steps to help you effectively troubleshoot CentOSStream8 system failures. Please try the following methods in order: 1. Network connection testing: Use the ping command to test network connectivity (for example: pinggoogle.com). Use the curl command to check the HTTP request response (for example: curlgoogle.com). Use the iplink command to view the status of the network interface and confirm whether the network interface is operating normally and is connected. 2. IP address and gateway configuration verification: Use ipaddr or ifconfi
 How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
Improve HDFS performance on CentOS: A comprehensive optimization guide to optimize HDFS (Hadoop distributed file system) on CentOS requires comprehensive consideration of hardware, system configuration and network settings. This article provides a series of optimization strategies to help you improve HDFS performance. 1. Hardware upgrade and selection resource expansion: Increase the CPU, memory and storage capacity of the server as much as possible. High-performance hardware: adopts high-performance network cards and switches to improve network throughput. 2. System configuration fine-tuning kernel parameter adjustment: Modify /etc/sysctl.conf file to optimize kernel parameters such as TCP connection number, file handle number and memory management. For example, adjust TCP connection status and buffer size
 What files do you need to modify in HDFS configuration CentOS?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
What files do you need to modify in HDFS configuration CentOS?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:27 PM
When configuring Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) on CentOS, the following key configuration files need to be modified: core-site.xml: fs.defaultFS: Specifies the default file system address of HDFS, such as hdfs://localhost:9000. hadoop.tmp.dir: Specifies the storage directory for Hadoop temporary files. hadoop.proxyuser.root.hosts and hadoop.proxyuser.ro
 Troubleshooting methods for Zookeeper on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:30 PM
Troubleshooting methods for Zookeeper on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:30 PM
ZooKeeper troubleshooting guide for CentOS Systems This article provides a step-by-step guide to help you effectively troubleshoot ZooKeeper faults on CentOS systems. 1. Verify the status of ZooKeeper service: First, use the following command to check the status of ZooKeeper service: sudosystemctlstatuszookeeper If the service is not running, use the following command to start: sudosystemctlstartzookeeper To enable it to start by starting: sudosystemctlenablezookeeper2. Analyze the ZooKeeper log to check Z
 What is the CentOS MongoDB backup strategy?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
What is the CentOS MongoDB backup strategy?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:51 PM
Detailed explanation of MongoDB efficient backup strategy under CentOS system This article will introduce in detail the various strategies for implementing MongoDB backup on CentOS system to ensure data security and business continuity. We will cover manual backups, timed backups, automated script backups, and backup methods in Docker container environments, and provide best practices for backup file management. Manual backup: Use the mongodump command to perform manual full backup, for example: mongodump-hlocalhost:27017-u username-p password-d database name-o/backup directory This command will export the data and metadata of the specified database to the specified backup directory.
 How to configure slow query log in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
How to configure slow query log in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
Enable Redis slow query logs on CentOS system to improve performance diagnostic efficiency. The following steps will guide you through the configuration: Step 1: Locate and edit the Redis configuration file First, find the Redis configuration file, usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Open the configuration file with the following command: sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Step 2: Adjust the slow query log parameters in the configuration file, find and modify the following parameters: #slow query threshold (ms)slowlog-log-slower-than10000#Maximum number of entries for slow query log slowlog-max-len
 CentOS HDFS performance tuning tips
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:00 PM
CentOS HDFS performance tuning tips
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:00 PM
CentOS Platform Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) Performance Optimization Guide Optimizing HDFS Performance is a multi-faceted issue, and multiple parameters need to be adjusted for specific situations. The following are some key optimization strategies: 1. Memory management adjusts the NameNode and DataNode memory configuration: reasonably configure the HADOOP_NAMENODE_OPTS and HADOOP_DATANODE_OPTS environment variables according to the actual memory size of the server to optimize memory utilization. Enable large page memory: For high memory consumption applications (such as HDFS), enabling large page memory can reduce memory page allocation and management overhead and improve efficiency. 2. Disk I/O optimization uses high-speed storage
 Redis configuration steps on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:12 PM
Redis configuration steps on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 04:12 PM
Installation and Configuration Guide for Redis under CentOS System This guide details how to install and configure the Redis database on CentOS system. Step 1: Install the dependencies First, make sure that the system has the necessary compilation tools installed. Open the terminal and execute the following command: sudoyumininstall-ygccmake Step 2: Download the Redis source code Download the latest version of the source code package from the Redis official website. For example, download Redis6.2.6 version: wgethttp://download.redis.io/releases/redis-6.2.6.tar.gz``` (Please replace it with the latest version chain




