Let's talk about the various I/O models in Node
This article will talk about the various I/O models in Node, and introduce the blocking I/O model, non-blocking I/O model and non-blocking asynchronous I/O. I hope to be helpful!

Let’s take network request IO as an example. First, we will introduce the typical process of the server processing a complete network IO request:
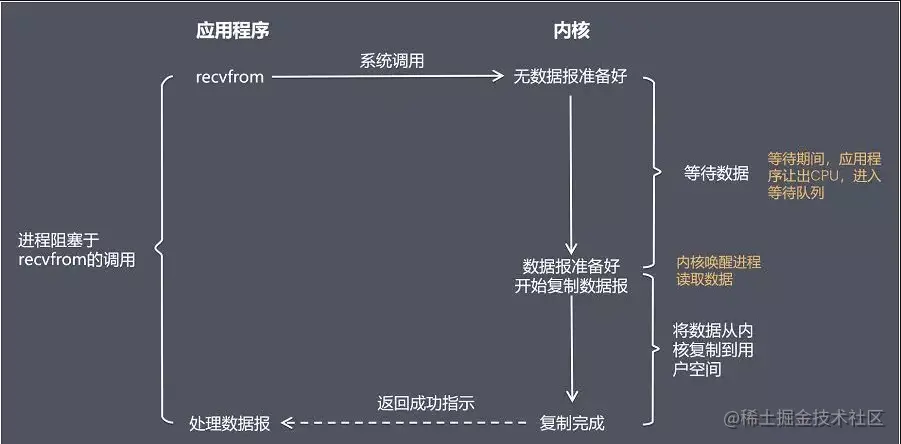
The application obtains the result of an operation, which usually includes two different stages:
Waiting for the data to be ready
- Copying data from the kernel to the process
Below, we take the recvfrom function as an example to explain various IO models
Blocking I/O Model (blocking I/O)
Blocking call means that before the call result is returned, the current thread will be suspended, and the calling thread can only wait for all operations at the system kernel level The call will not end until it is completed.
Blocking I/O causes the CPU to wait for I/O and wastes CPU time slices.

Non-blocking I/O model (non-blocking I/O)
Compared with the former, non-blocking I/O Return directly without data. To obtain the data, you need to try to read the data again through the file descriptor
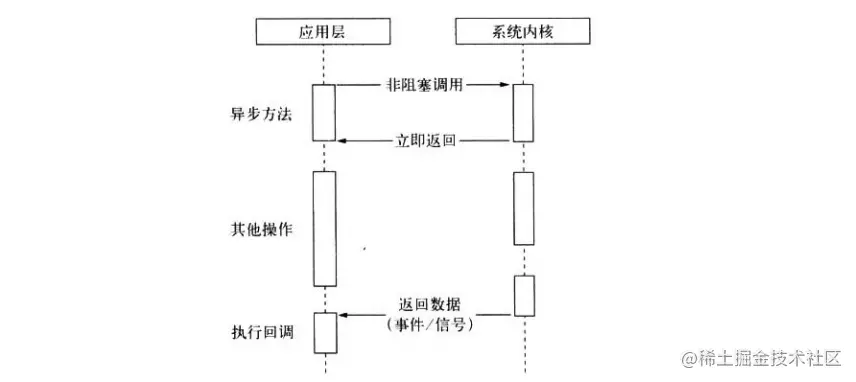
Non-Blocking callGet returned ( Not the actual expected data), the CPU time slice can be used to process other things, which can significantly improve performance.
But the problem that comes with it is that the previous operation was not a complete I/O, and the returned result was not the expected business data, but only the asynchronous call status.
In order to obtain complete data, the application needs to repeatedly call the IO operation to confirm whether the operation has been completed. This operation is called Polling. Several common polling strategies are as follows
Busy Polling
This is the most primitive and lowest performance way. It checks the I/O status through repeated calls to obtain complete data

Advantages: Simple programming
Disadvantages: The CPU is always consumed in polling, which also affects server performance, because the server still has to respond after you poll
I/O multiplexing model (I/O multiplexing)

In the I/O multiplexing model, it will be used Select or Poll function or Epoll function (supported by the kernel after Linux 2.6), these two functions will also cause the process to block, but they are different from blocking I/O.
These three functions can block multiple I/O operations at the same time, and can detect the I/O functions of multiple read operations and multiple write operations at the same time until data is readable or writable. , the I/O operation function is actually called.
The differences between the three I/O multiplexing mechanisms are as follows
select
Due to select A 1024-length array is used to store file status, so up to 1024 file descriptors can be detected simultaneously
poll
Slightly improved compared to select. The use of linked lists avoids the length limit of 1024 and avoids unnecessary traversal checks. The performance is slightly improved compared to select.
##epoll/ kqueue
sleep, until the event occurs and the thread is awakened. It truly utilizes event notifications and executes callbacks instead of traversing (file descriptor) queries, so it does not waste CPU

Polling is still a synchronous operation because the application is still waiting for the I/O to return completely. During the waiting period, it either traverses the file description state or sleeps to wait for the event to occur.
Signal-driven I/O model In the signal-driven I/O model In , the application uses signals to drive I/O and installs a signal processing function. The process continues to run without blocking.
In the signal-driven I/O model In , the application uses signals to drive I/O and installs a signal processing function. The process continues to run without blocking.
When the data is ready, the program will receive a SIGIO signal and can call the I/O operation function in the signal processing function to process the data.
Summary: So far, the signal-driven I/O model is more in line with our asynchronous needs. The program will execute other business logic asynchronously while waiting for data.
but! ! ! It is still blocked during the process of copying data from the kernel to user space, which is not a complete revolution (asynchronous).
Ideal (Node) non-blocking asynchronous I/O
Our ideal asynchronous I/O should be a non-blocking call initiated by the application, without the need to obtain data through polling , there is no need to wait needlessly during the data copy phase, but after the I/O is completed, it can be passed to the application through a signal or callback function, during which the application can execute other business logic.

Actual asynchronous I/O
In fact, the Linux platform natively supports asynchronous I/O (AIO), but currently AIO is not perfect. , so when implementing high-concurrency network programming under Linux, the I/O multiplexing model is mainly used.
Under Windows, true asynchronous I/O is implemented through IOCP.
Multi-threaded simulation of asynchronous I/O
Under the Linux platform, Node uses the thread pool to allow some threads to perform blocking I/O or non-blocking I/O rounds Data acquisition is completed by querying, allowing a separate thread to perform calculations, and passing the I/O results through communication between threads, thus realizing the simulation of asynchronous I/O.
In fact, the bottom layer of the IOCP asynchronous asynchronous solution under the Windows platform is also implemented using a thread pool. The difference is that the latter thread pool is hosted by the system kernel.
We often say that Node is single-threaded, but in fact it can only be said that JS is executed in a single thread, whether it is *nix or windows platform , the bottom layer uses the thread pool to complete I/O operations.
For more node-related knowledge, please visit: nodejs tutorial!
The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about the various I/O models in Node. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to use express to handle file upload in node project
Mar 28, 2023 pm 07:28 PM
How to use express to handle file upload in node project
Mar 28, 2023 pm 07:28 PM
How to handle file upload? The following article will introduce to you how to use express to handle file uploads in the node project. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 How to delete node in nvm
Dec 29, 2022 am 10:07 AM
How to delete node in nvm
Dec 29, 2022 am 10:07 AM
How to delete node with nvm: 1. Download "nvm-setup.zip" and install it on the C drive; 2. Configure environment variables and check the version number through the "nvm -v" command; 3. Use the "nvm install" command Install node; 4. Delete the installed node through the "nvm uninstall" command.
 How to do Docker mirroring of Node service? Detailed explanation of extreme optimization
Oct 19, 2022 pm 07:38 PM
How to do Docker mirroring of Node service? Detailed explanation of extreme optimization
Oct 19, 2022 pm 07:38 PM
During this period, I was developing a HTML dynamic service that is common to all categories of Tencent documents. In order to facilitate the generation and deployment of access to various categories, and to follow the trend of cloud migration, I considered using Docker to fix service content and manage product versions in a unified manner. . This article will share the optimization experience I accumulated in the process of serving Docker for your reference.
 An in-depth analysis of Node's process management tool 'pm2”
Apr 03, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
An in-depth analysis of Node's process management tool 'pm2”
Apr 03, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
This article will share with you Node's process management tool "pm2", and talk about why pm2 is needed, how to install and use pm2, I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Detailed explanation and installation guide for PiNetwork nodes This article will introduce the PiNetwork ecosystem in detail - Pi nodes, a key role in the PiNetwork ecosystem, and provide complete steps for installation and configuration. After the launch of the PiNetwork blockchain test network, Pi nodes have become an important part of many pioneers actively participating in the testing, preparing for the upcoming main network release. If you don’t know PiNetwork yet, please refer to what is Picoin? What is the price for listing? Pi usage, mining and security analysis. What is PiNetwork? The PiNetwork project started in 2019 and owns its exclusive cryptocurrency Pi Coin. The project aims to create a one that everyone can participate
 Let's talk about how to use pkg to package Node.js projects into executable files.
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:06 PM
Let's talk about how to use pkg to package Node.js projects into executable files.
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:06 PM
How to package nodejs executable file with pkg? The following article will introduce to you how to use pkg to package a Node project into an executable file. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 What to do if npm node gyp fails
Dec 29, 2022 pm 02:42 PM
What to do if npm node gyp fails
Dec 29, 2022 pm 02:42 PM
npm node gyp fails because "node-gyp.js" does not match the version of "Node.js". The solution is: 1. Clear the node cache through "npm cache clean -f"; 2. Through "npm install -g n" Install the n module; 3. Install the "node v12.21.0" version through the "n v12.21.0" command.
 Token-based authentication with Angular and Node
Sep 01, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Token-based authentication with Angular and Node
Sep 01, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Authentication is one of the most important parts of any web application. This tutorial discusses token-based authentication systems and how they differ from traditional login systems. By the end of this tutorial, you will see a fully working demo written in Angular and Node.js. Traditional Authentication Systems Before moving on to token-based authentication systems, let’s take a look at traditional authentication systems. The user provides their username and password in the login form and clicks Login. After making the request, authenticate the user on the backend by querying the database. If the request is valid, a session is created using the user information obtained from the database, and the session information is returned in the response header so that the session ID is stored in the browser. Provides access to applications subject to




