PHP Framework
PHP Framework
 ThinkPHP
ThinkPHP
 An article explaining in detail how to add, delete, modify and query the database in Thinkphp5
An article explaining in detail how to add, delete, modify and query the database in Thinkphp5
An article explaining in detail how to add, delete, modify and query the database in Thinkphp5
How to operate the database in Thinkphp5 and perform addition, deletion, modification and query? The following article will give you a detailed understanding of the methods of adding, deleting, modifying and querying the database in Thinkphp5. I hope it will be helpful to you!

##[Related tutorial recommendations:thinkphp standard data table design:
Create time field: create_time
Update time field :update_time
Delete time field: delete_time
Select int as the type, as shown below:
thinkphp framework】
1. Create a model folderCreate a new folder named model in the secondary object directory under the application folder. This folder is the same as The corresponding controller and view directories are at the same level, as shown below: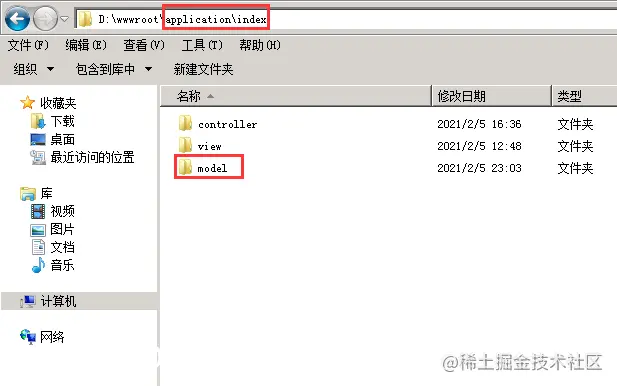
表名 pre_user ---------------> 模型名 User.php 表名 pre_user_info ---------------> 模型名 UserInfo.php
<?php
namespace app\index\model;
use think\Model;
use think\Db;
class User extends Model{
/**
* 定义变量
* 1.变量名称应与数据表中的字段名相同
* 2.此处可根据需求省略,因为如果没有,thinkphp会自动在数据表中寻找的对应字段名
*/
public $username;
public $password;
}
?><?php
namespace app\index\model;
use think\Model;
use think\Db;
class User extends Model
{
protected $table = "admin_user";//指定数据表名
protected $pk = 'id'; //指定主键的字段
}
?>//导入定义的数据模型类
use \app\index\model\User;
//方法一:
$res = User::get(1);
//方法二:
$user = new User;
$res = $user::get(1);
//方法三:
use think\Loader;
$user = Loader::model("User");
$res = $user::get(1);
//方法四:
$user = model("User");
$res = $user::get(1);Copy after login
4. Query operation//导入定义的数据模型类
use \app\index\model\User;
//方法一:
$res = User::get(1);
//方法二:
$user = new User;
$res = $user::get(1);
//方法三:
use think\Loader;
$user = Loader::model("User");
$res = $user::get(1);
//方法四:
$user = model("User");
$res = $user::get(1);get Get a record
$res = User::get(1);
all Get multiple records
1. No parameters are passed$result = User::all(); //查询出所有记录
$result = User::all(1); //查询出id为1的记录
$result = User::all('7, 8, 9, 10'); //查询出id为7、8、9、10的4条记录
$result = User::all([7, 8, 9, 10]); //查询出id为7、8、9、10的4条记录
find Query a certain item
$res = User::where('id','1')->field('name')->find();
Not equal to->where('id','neq',1)##select multiple queries
$res = User::where('id','1')->field('name')->limit(2)->order('id DESC')->select();
$res = User::where('id','1')->value('name');
$res = $res->toArray();
//查询总条数
$res = User::count();
//按条件统计条数
$res = User::where('id','>',3)->count();
1. Get today’s information
db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'today')->select(); //也可以简化为下面方式 db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'd')->select();
2. Get yesterday’s information
db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'yesterday')->select();
3. Get this Weekly information
db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'week')->select(); //也可以简化为下面方式 db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'w')->select();
4. Get this month’s information
db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'month')->select(); //也可以简化为下面方式 db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'm')->select();
5. Get last month’s information
db('table')->whereTime('c_time','last month')->select();
6. Get this year’s information
db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'year')->select(); //也可以简化为下面方式 db('table')->whereTime('c_time', 'y')->select();
7. Get last year’s information
db('table')->whereTime('c_time','last year')->select();
8. Date interval query
//根据时间戳查询今天到后天 db('table')->whereTime('time', 'between', [strtotime(date('Y-m-d')), strtotime(date('Y-m-d', strtotime('+2 day')))])->select(); 根据日期查询今天到后天 db('table')->whereTime('time', 'between', ['2020-3-28', '2020-3-30'])->select();
5. Add operation
1. Use the create() method to add
$res = User::create([
'name' => '安阳',
'age' => 23,
'sex' => 1,
'password' => '123456'
]);2. Add data and return the added primary key
$uid=UserModel::create([
'name' => '安阳',
'age' => 23,
'sex' => 1,
'password' => '123456'
])->id;You can also use the insertGetId method of the DB class, as follows:
$uid = User::insertGetId([
'name' => '安阳',
'age' => 23,
'sex' => 1,
'password' => '123456'
]);3. Add by instantiation
$user = new User; $user->name = '安阳'; $user->age = 23; $user->save();
4 , Filter the inserted fields by instantiation and return the number of inserted rows
$user = new User;
$data = [
'name' => '安阳',
'age' => 23,
'email' => '123456@qq.com'
];
//只有name和age字段会写入
$res = $user->allowField(['name', 'age'])->save($data);5. The model uses allowField() to filter the data of non-data table fields
//定义模型对象,并传入post数据 $user = new User($_POST); //过滤post数组中的非数据表字段数据 $user->allowField(true)->save();
6. The model uses allowField() to specify certain Field writing
$user = new User; // post数组中只有name和email字段会写入 $user->allowField(['name','email'])->save($_POST, ['id' => 1]);
7. Use saveAll() for batch addition
user = new User;
$list = [
['name'=>'安阳','email'=>'thinkphp@qq.com'],
['name'=>'小柒','email'=>'12345678@qq.com']
];
$user->saveAll($list);You can also use the insertAll() method of the DB class to return the number of successfully added items
$res = User::insertAll([
'name' => '安阳',
'age' => 23,
'sex' => 1,
'password' => '123456'
]);Supplementary, other methods of filtering fields:1. In DB operations, you can use strict to turn off strict field checking
Db::name(‘user’)->strict(false)->insert($data);Copy after login2. Use php's unset( ) method destroys variables
6. saveAll adds multiple pieces of data and returns the object listunset($data[‘file’]);Copy after login
$user = new User;
$data = [
[
'name' => '安阳',
'age' => 20,
'email' => '123456@qq.com'
],
[
'name' => '小柒',
'age' => 25,
'email' => 'ap555@qq.com'
]
];
$res = $user->allowField(['name', 'age'])->saveAll($data);6. Update operation
1. update returns the number of affected rows
$res = User::where(['id'=>1])->update(['name'=>'安阳']);
2. setField updates a field individually
User::where('id',1)->setField('name','安阳');
3. setInc
//setInc('money',10)表示将money字段加上10 User::where(['id'=>1])->setInc('money', 10);
4. setDec
//setDec('money',10)表示将money字段减去10 User::where(['id'=>1])->setDec('money', 10);
5. Batch update requires the data to contain Primary key, return the update object list
$user = new User;
$res = $user->saveAll([
['id'=>1, 'name' => '安阳'],
['id'=>2, 'name' => '小柒']
]);7. Delete operation
1. Pass in the primary key, return the number of affected rows
$res = User::destroy(1);
2. Pass in the condition, return the number of affected rows
$res = User::destroy(['name'=>'安阳']);
3. Conditional deletion returns the number of affected rows
$res = User::where(['id'=>1])->delete();
8. Transaction
1. Automatically control transaction processing
Db::transaction(function(){
Db::table('order')->where(['id'=>1])->delete();
Db::table('user')->where('id'=>1)->setInc('money',10);
});2. Manually control transaction
Db::startTrans();//启动事务
try {
Order::where(['id'=>1])->delete();
User::where('id'=>1)->setInc('money',10);
Db::commit();//提交事务
} catch (Exception $e) {
Db::rollback(); //回滚
}9. Model model getter
The naming convention of the reader is:->get the camel case name of the attribute name AttrAdditional explanation: strtotime() parses the date and time description of any English text into a Unix timestamp, and returns the timestamp if successful, otherwise it returns FALSE (before PHP 5.1.0, this function returned -1 on failure )<?php namespace app\index\model; use think\Model; class User extends Model { //获取器:将性别的012修改为男、女、未知 返回 public function getSexAttr($val) { switch ($val) { case 1: return '男'; case 2: return '女'; default: return '未知'; } } //获取器:格式化时间戳后返回 public function getUpdateTimeAttr($val){ if(!empty($val)){ //如果是时间戳,就格式化 if(!strtotime($val)) { return date('Y-m-d H:i:s',$val); }else{ return $val; } }else{ return ''; } } }Copy after login
十、model模型的修改器
<?php
namespace app\index\model;
use think\Model;
class User extends Model
{
//修改器
public function setTimeAttr()
{
return time();
}
/** 修改器:对密码字段加密之后存储
* $val 第一个参数是密码
* $data 第二个参数是添加的数据(可选)
*/
public function setPasswordAttr($val,$data){
if($val === '') {
return $val;
}else{
return md5($val.$data['email']);
}
}
}十一、model模型的自动完成
auto 新增及更新的时候,自动完成的属性数组
insert 仅新增的时候,自动完成的属性数组
update 仅更新的时候,自动完成的属性数组
1、自动完成
<?php
namespace app\index\model;
use think\Model;
class User extends Model
{
//添加和修改时,都会自动完成的字段
protected $auto = ['addtime'];
public function setAddtimeAttr(){
return time();
}
}2、添加数据时,自动完成
<?php
namespace app\index\model;
use think\Model;
class User extends Model
{
// 新增 自动完成
protected $insert = ['addtime'];
public function setAddtimeAttr(){
return time();
}
}3、更新数据时,自动完成:
<?php
namespace app\index\model;
use think\Model;
class User extends Model
{
// 更新 自动完成
protected $update = ['addtime'];
public function setAddtimeAttr(){
return time();
}
}十二、自动完成时间戳
在数据库配置文件database.php中,有下列这项配置:
//自动写入时间戳字段 'auto_timestamp' => false, //如果开启(设置为true),则会自动完成所有表的时间戳,但是不建议这样,只在需要的地方设置更安全。
例如对用户表的时间戳自动完成,就在User的model中设置:
<?php
namespace app\index\model;
use think\Model;
class User extends Model{
//开启自动完成时间戳功能
protected $autoWriteTimestamp = true;
//开启后,
//添加数据时,默认自动完成的字段是:create_time和update_time
//修改数据时,默认自动完成的字段是:update_time
//如果数据表里不是这两个字段,则会报错。需要进行如下修改:
protected $createTime = 'addtime';//修改默认的添加时间字段
protected $updateTime = 'updtime';//修改默认的修改时间字段
protected $updateTime = false;//当不需要这个字段时设置为false
}Thinkphp更新时,自动更新update_time字段时间戳的方法:
1、使用update
User::update(['name'=>'安阳'],['id'=>1]);Copy after loginThinkphp中update方法的源代码如下:
/** * 更新数据 * @access public * @param array $data 数据数组 * @param array $where 更新条件 * @param array|true $field 允许字段 * @return $this */ public static function update($data = [], $where = [], $field = null) { $model = new static(); if (!empty($field)) { $model->allowField($field); } $result = $model->isUpdate(true)->save($data, $where); return $model; }Copy after login2、使用save
$user=new User; $user->isUpdate(true)->save(['name'=>'安阳'],['id'=>1]);Copy after login
十三、软删除
什么是软删除?
当删除某些记录时,有时我们需要假删除,只通过修改某个字段状态来标记该记录已删除,但实际上,数据库中还是存在这些记录的。假删除的应用场景还是比较多的,例如支付宝的收款记录,我们在APP上删除后,就不会再显示出来,你是不是以为真的删掉了,不会再留下任何痕迹?非也,非也,删除支付宝收款记录只是软删除,在支付宝的数据库中,实际上还保留有这些收款记录,如果你的收款涉嫌违规或者触犯法律,警方还是能通过支付宝的网警后台查看到的。
1、开启软删除
<?php
namespace app\index\model;
use think\Model;
use traits\model\SoftDelete;//引入软删除的类
class Order extends Model{
//使用软删除
//删除时,默认更新的字段是delete_time
use SoftDelete;
//如果数据表里不是delete_time这个字段,则会报错。需要进行如下修改:
protected $deleteTime = 'deltime';
}2、 控制器里软删除,返回影响的行数
$res = Order::destroy(1);
执行删除后,就会更新delete_time字段,如果update_time字段也开启了自动完成,也会更新update_time字段。
3、如果开启了软删除,需要真正地删除数据,而不做软删除,用下面的方法
//destory()第二个参数传递true $res = Order::destroy(1,true); //delete()参数传递true $orderData = Order::get(1); $orderData ->delete(true);
4、查询已软删除的数据
$res = Order::withTrashed(true)->find(1);
5、查询仅包含已软删除的数据
$res = Order::onlyTrashed()->select();
推荐学习:《PHP视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of An article explaining in detail how to add, delete, modify and query the database in Thinkphp5. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 How to use CodeIgniter4 framework in php?
May 31, 2023 pm 02:51 PM
How to use CodeIgniter4 framework in php?
May 31, 2023 pm 02:51 PM
PHP is a very popular programming language, and CodeIgniter4 is a commonly used PHP framework. When developing web applications, using frameworks is very helpful. It can speed up the development process, improve code quality, and reduce maintenance costs. This article will introduce how to use the CodeIgniter4 framework. Installing the CodeIgniter4 framework The CodeIgniter4 framework can be downloaded from the official website (https://codeigniter.com/). Down
 How to use PHP scripts to perform database operations in Linux environment
Oct 05, 2023 pm 03:48 PM
How to use PHP scripts to perform database operations in Linux environment
Oct 05, 2023 pm 03:48 PM
How to use PHP to perform database operations in a Linux environment. In modern web applications, the database is an essential component. PHP is a popular server-side scripting language that can interact with various databases. This article will introduce how to use PHP scripts for database operations in a Linux environment and provide some specific code examples. Step 1: Install the Necessary Software and Dependencies Before starting, we need to ensure that PHP and related dependencies are installed in the Linux environment. usually
 How to use Pagoda Panel for MySQL management
Jun 21, 2023 am 09:44 AM
How to use Pagoda Panel for MySQL management
Jun 21, 2023 am 09:44 AM
Pagoda Panel is a powerful panel software that can help us quickly deploy, manage and monitor servers, especially small businesses or individual users who often need to build websites, database management and server maintenance. Among these tasks, MySQL database management is an important job in many cases. So how to use the Pagoda panel for MySQL management? Next, we will introduce it step by step. Step 1: Install Pagoda Panel. Before starting to use Pagoda Panel for MySQL management, you first need to install Pagoda Panel.
 How to use thinkorm to improve database operation efficiency
Jul 28, 2023 pm 03:21 PM
How to use thinkorm to improve database operation efficiency
Jul 28, 2023 pm 03:21 PM
How to use thinkorm to improve database operation efficiency With the rapid development of the Internet, more and more applications require a large number of database operations. In this process, the efficiency of database operations becomes particularly important. In order to improve the efficiency of database operations, we can use thinkorm, a powerful ORM framework, to perform database operations. This article will introduce how to use thinkorm to improve the efficiency of database operations and illustrate it through code examples. 1. What is thinkormthi?
 Using PDO for Database Operations: A Better Way with PHP
Jun 21, 2023 pm 01:36 PM
Using PDO for Database Operations: A Better Way with PHP
Jun 21, 2023 pm 01:36 PM
Using PDO for database operations: A better way with PHP In web development, it is very common to use databases for data storage, management, and query. As a language widely used in Web development, PHP naturally provides a wealth of database operation methods. In PHP, you can use MySQLi, PDO and other extension libraries to perform database operations. Among them, PDO is a very commonly used database operation method and has more advantages than other methods. This article will introduce what PDO is to
 How to use Doctrine ORM for database operations in Symfony framework
Jul 29, 2023 pm 04:13 PM
How to use Doctrine ORM for database operations in Symfony framework
Jul 29, 2023 pm 04:13 PM
How to use DoctrineORM in Symfony framework for database operations Introduction: Symfony framework is a popular PHP framework that provides many powerful tools and components for building web applications quickly and easily. One of the key components is DoctrineORM, which provides an elegant way to handle database operations. This article will introduce in detail how to use DoctrineORM to perform database operations in the Symfony framework. we will
 How to use the FULL OUTER JOIN function in MySQL to obtain the union of two tables
Jul 26, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
How to use the FULL OUTER JOIN function in MySQL to obtain the union of two tables
Jul 26, 2023 pm 05:45 PM
How to use the FULLOUTERJOIN function in MySQL to obtain the union of two tables. In MySQL, the FULLOUTERJOIN function is a powerful join operation that combines inner joins and outer joins. It can be used to get the union of two tables, that is, combine all the data in the two tables into a single result set. This article will introduce the usage of the FULLOUTERJOIN function and provide some sample code to help readers better understand. FULLOUTERJOIN function
 PHP backend design: database operation and data interaction practice
Jan 19, 2024 am 10:31 AM
PHP backend design: database operation and data interaction practice
Jan 19, 2024 am 10:31 AM
When developing a website, application or system, database operations and data interaction are essential. As a commonly used backend development language, PHP's database operation and data interaction capabilities are also very powerful. This article will introduce some commonly used database operation functions and data interaction practices in PHP. At the same time, we will explain these operations and practices with code examples to facilitate readers to better understand and apply them. 1. Database connection Before performing database operations, you first need to connect to the database. In PHP we can use