What are the disk partition forms?
There are two forms of disk partitioning: 1. MBR (Master Boot Record) form, which is a special boot sector that exists at the beginning of the disk drive; 2. GPT (GUID Partition Table) form, which It is a disk organization method that uses UEFI boot.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
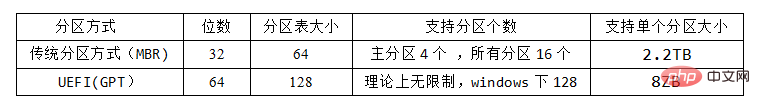
There are two types of disk partitions: MBR and GPT.
When you buy a new hard drive and set the partition, the system will ask you whether you want to use the MBR partition format or the GPT partition format (some hard drives are defaulted when shipped from the factory. The partition format is set for you). MBR is the previous partition form, and GPT is a new partition form, which is now gradually replacing the MBR partition form.
MBR partition
MBR means "Master Boot Record", which was proposed by IBM in the early years. It is a special boot sector that exists at the beginning of the disk drive. This sector contains system information about the installed operating system and a small piece of code to boot the system. If you installed Windows, its startup information is placed in this piece of code - if the MBR information is damaged or accidentally deleted, Windows cannot be started normally. At this time, you need to find a boot repair software tool to repair it. In Linux systems, MBR is usually the GRUB loader. MBR. When a computer starts up, it will first start the BIOS system that comes with the motherboard. The bios loads MBR, and then MBR starts Windows. This is the startup process of mbr.
GPT Partition
GPT means GUID Partition Table, which is "Globally Unique Identification Disk Partition Table". It is another more advanced and novel disk organization method, a disk organization method that uses UEFI boot. Initially it was for better compatibility, but later it was widely used because of its larger supported memory (mbr partition supports up to 2T disks) and more compatibility, especially since all Apple MAC systems use gpt partitions. gtp no longer has the concept of partitions, and all CDEF disks are stored in a piece of information. It can be simply understood as a technology that is more advanced but not widely used enough.
GPT brings many new features, but MBR still has the best compatibility. GPT is not a new standard specific to Windows—Mac OS X, Linux, and other operating systems also use GPT. Before you can use your new disk, you must partition it. MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table) are two different ways of storing partition information on disk. This partition information includes where the partition starts, so that the operating system knows which sector belongs to which partition and which partition can be booted. When creating a partition on a disk, you have to choose between MBR and GPT. Currently, there are only two types of partitioning.
Limitations of MBR
MBR means "Master Boot Record" and was first proposed in IBM PC DOS 2.0 in 1983. It is called the "master boot record" because it is a special boot sector that exists at the beginning of the drive. This sector contains the drive's partition information (64 bytes, fixed size, a partition is recorded in 16 bytes) and the installed operating system's boot loader (446 bytes) and a 2-byte end flag , so the size of this sector is 512 bytes. . The so-called boot loader is a small piece of code used to load larger loaders on other partitions on the drive. If you installed Windows, the initial information of the Windows boot loader is placed in this area - if the MBR information is overwritten and Windows cannot start, you need to use the MBR repair function of Windows to restore it to normal. If you have installed Linux, the GRUB loader will usually be located in the MBR. MBR supports disks up to 2TB, it cannot handle disks with a capacity larger than 2TB. MBR also only supports up to 4 primary partitions - if you want more partitions, you need to create so-called "extended partitions" and create logical partitions within them. MBR has become the industry standard for disk partitioning and booting.
Advantages of GPT
GPT means GUID partition table. (GUID means Globally Unique Identifier). This is a new standard that is gradually replacing MBR. It and UEFI complement each other - UEFI is used to replace the old BIOS, while GPT replaces the old MBR. It’s called a “GUID Partition Table” because each partition on your drive has a globally unique identifier (GUID)—a randomly generated string that’s guaranteed to be Every GPT partition on a GPT partition is assigned a completely unique identifier. This standard does not have the limitations of MBR. Disk drives can be much larger than the operating system and file system can support. It also supports an almost unlimited number of partitions. The limitation is only in the operating system - Windows supports up to 128 GPT partitions. There is no concept of primary partitions and extended partitions on GPT hard disks. All partitions are called partitions. On MBR disks, partition and boot information are saved together. If this part of the data is overwritten or corrupted, things could be in trouble. In contrast, GPT saves multiple copies of this part of the information on the entire disk, so it is more robust and can recover this part of the information if it is damaged. GPT also stores a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) for this information to ensure that it is complete and correct - if the data is corrupted, GPT will detect the corruption and restore it from elsewhere on the disk. MBR is powerless to deal with these problems - only after the problem occurs, you will find that the computer cannot start, or the disk partitions are gone.
GPT compatibility
As you can see, there is also a mark similar to MBR (Master Boot Record) in the first data block of the GTP disk. It's called PMBR (Protected MBR). The function of PMBR is that when using a partitioning tool that does not support GPT, the entire hard disk will appear as a protected partition to prevent the partition table and hard disk data from being damaged. UEFI does not obtain the partition information of the GPT disk from PMBR. It has its own partition table, the GPT partition table.
Primary partition, extended partition and logical partition
These terms are only available in MBR because GPT supports unlimited primary partitions. If you are using the MBR partition format, then you will have at least one and at most four primary partitions; if you want to have more partitions, then you will need to create an extended partition and then create a new one in the extended partition. Multiple logical partitions. And the number of primary partitions and extended partitions shall not exceed four; extended partitions may have none or at most one; logical partitions may have none or multiple logical partitions. Extended partitions cannot be enclosed between primary partitions.
The activated primary partition is the boot partition of the hard disk. It is independent and is also the first partition of the hard disk. If it is divided normally, it is the C drive. After the primary partition is divided, the remaining part can be divided into extended partitions. Generally, the remaining part is divided into extended partitions, or not completely. Then the remaining part is wasted. But the extension cannot be used directly. It is used in the form of logical partitions, so the extended partition can be divided into several logical partitions. Their relationship is an inclusive relationship, and all logical partitions are part of the extended partition. Equivalent to hda partition in Linux.
The capacity of the hard disk = the capacity of the primary partition and the capacity of the extended partition
The capacity of the extended partition = the sum of the capacities of each logical partition
Up to 4 in the MBR partition table Primary partition or 3 primary partitions and 1 extended partition, which means there can only be one extended partition, and then it can be subdivided into multiple logical partitions.
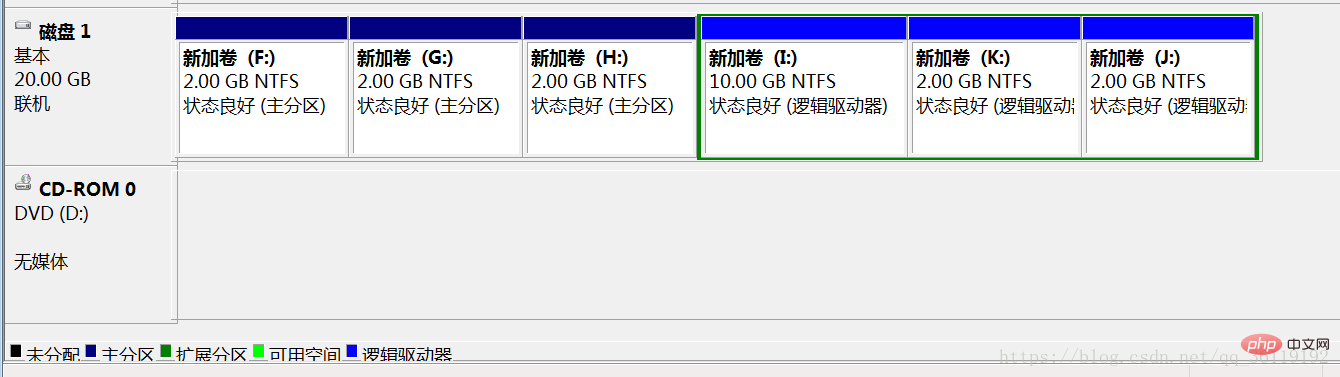
In the Linux system, the hard disk partitions are named sda1~sda4 or hda1~hda4 (sd represents SCSI hard disk, hd represents IDE hard disk, where a represents the hard disk number, and if there are multiple hard disks, they are b and c , d; 1 represents the first partition, 2 represents the second partition, and so on). In an MBR hard disk, partition numbers 1-4 are primary partitions (or extended partitions), and logical partition numbers can only start from 5.
As shown in the figure, the F, G, and H disks in disk 1 are primary partitions, I K J is an extended partition, and I, K, and J are logical partitions.

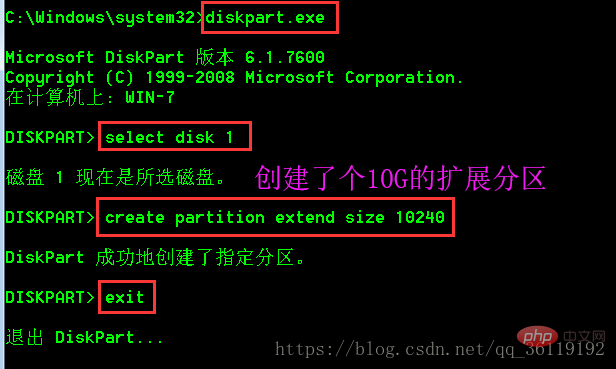
In Windows, by default, an extended partition will be created only after you have created 3 primary partitions. If we want to create an extended partition directly, we can use the command
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What are the disk partition forms?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 win11 disk partition tutorial
Jan 10, 2024 am 08:57 AM
win11 disk partition tutorial
Jan 10, 2024 am 08:57 AM
Sometimes the system's default partition cannot meet our needs. At this time, we need to manually partition the win11 disk. We only need to open the disk manager to easily modify the partition. How to partition a win11 disk: 1. First, right-click "This Computer" and open Computer "Management" 2. Then enter "Disk Management" under the storage option on the left 3. Then check the disk status on the right to see if there is available space. (If there is free space, skip to step 6) 4. If there is no free space, right-click the disk with space and select "Compress Volume" 5. Then select the amount of space that needs to be freed and click "Compress" 6. When the compression is completed The available space will appear. Right-click it and select "New Simple Volume" 7. Then enter the desired simple volume size and click "Next Page" 8.
 Ubuntu system disk partition scheme design and practical experience sharing
Feb 12, 2024 pm 02:54 PM
Ubuntu system disk partition scheme design and practical experience sharing
Feb 12, 2024 pm 02:54 PM
As an open source operating system, Ubuntu is very popular on both servers and personal computers. Disk partitioning is a very important step when installing Ubuntu. A reasonable disk partitioning scheme can improve the performance and stability of the system, and at the same time To better manage data and files, this article will share some experience in the design and practice of Ubuntu system disk partitioning scheme, and how to partition the disk on Ubuntu20.04. Ubuntu20.04 disk partition Ubuntu20.04 is the latest long-term support version, which introduces many new features and improvements. Before doing disk partitioning, we first need to understand some basic concepts. 1. Primary partition and extended partition: The primary partition is used to install
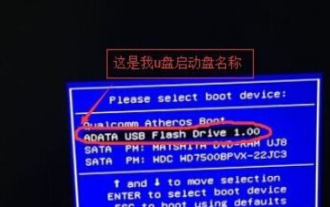 How to partition a disk with the partition tool diskgenius - How to partition a disk with the partition tool diskgenius
Mar 06, 2024 am 10:16 AM
How to partition a disk with the partition tool diskgenius - How to partition a disk with the partition tool diskgenius
Mar 06, 2024 am 10:16 AM
I believe that all the users here are familiar with the partitioning tool diskgenius, but do you know how to partition the disk with the partitioning tool diskgenius? The following article will bring you the method of partitioning the disk with the partitioning tool diskgenius. Let us take a look below. Insert the USB boot disk into the USB interface of the computer, restart the computer, and then continue to press the corresponding computer startup shortcut key (the startup shortcut keys of different computers may be different, you can check according to the keys prompted by the computer's normal startup or the official website) . Then select the USB boot disk in the startup options and press the Enter key to confirm the selection. The steps are as above. 2. Select [02] on the u start main menu interface to run u start win8pe defense.
 How to partition on Debian 12
Mar 21, 2024 pm 10:01 PM
How to partition on Debian 12
Mar 21, 2024 pm 10:01 PM
In Debian12, there are various graphical and command line tools available for partitioning disks. This article will introduce some common tools that you can use to partition storage devices (such as hard drives/SSDs) on Debian12. These tools provide flexibility and control, allowing you to easily manage disk space according to your needs. With these tools, you can effectively divide disk space, create partitions for different purposes, and ensure the security and reliability of your data. Whether you prefer graphical interface or command line operation, Debian12 provides suitable tools to allow you to perform disk partitioning operations according to your preferences and needs. Content topic: Debian12’s common disk partitioning program uses GNOME Disk
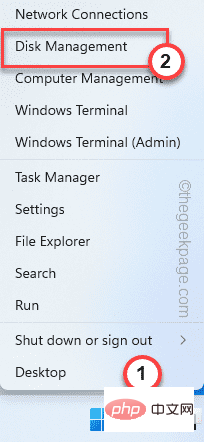
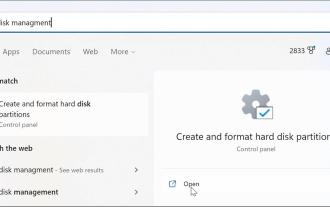 6 Ways to Turn on Disk Management on Windows 11
May 02, 2023 pm 04:25 PM
6 Ways to Turn on Disk Management on Windows 11
May 02, 2023 pm 04:25 PM
Need to quickly partition a new drive or change a drive letter on Windows 11? You need to use disk management. Here's how to launch it on a Windows 11 PC. If you want to create and resize partitions, initialize hard drives, change drive letters, etc. on Windows 11, you need to use the Disk Management tool. You can use this tool in a variety of ways, as well as open it. If you want to speed up your workflow, here are six different ways to turn on Disk Management in Windows 11. 1. Search for Disk Management To avoid clicking through menus, you can search for Disk Management and open it directly. To open Disk Management using the search bar in the Start menu, use the following steps: Click Start
![System Reserved Partition Not Showing in Disk Management [Quick Recovery]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/465/014/168376632735495.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) System Reserved Partition Not Showing in Disk Management [Quick Recovery]
May 11, 2023 am 08:52 AM
System Reserved Partition Not Showing in Disk Management [Quick Recovery]
May 11, 2023 am 08:52 AM
Is the system reserved partition not showing up in Disk Management on Windows 10/11 devices? The System Reserved Partition, or SRP, is a small partition on your hard drive that stores Windows startup information. If the files are deleted in some way, operating system startup problems may occur. Usually, this problem occurs if the partition size is less than 600MB. The system reserved partition is available in Disk Management because Windows does not assign a drive letter to it. Therefore, unlike other drives, it will not be visible in File Explorer. Things can get serious if you delete the system reserved partition from Disk Management. If this happens, users may be unable to update Windows to
 Fix: New SSD not showing up in Windows 11, 10
Apr 14, 2023 pm 02:52 PM
Fix: New SSD not showing up in Windows 11, 10
Apr 14, 2023 pm 02:52 PM
SSDs have revolutionized the world of technology. These data storage solutions, with their ultra-fast and unparalleled read/write speeds, make every user eager to install their system operating system in them. But what if your new SSD doesn’t show up on your Windows device? This is a typical issue you might face with a brand new SSD plugged into your system. Don't worry. We just got the right solution, all you have to do is follow these steps and your SSD will be back in your File Explorer in no time. Solution - 1. Check the SSD connection. If you are using a USB hub, connect the SSD directly to your system. Check the SSD's connectors for any physical defects.
 Linux disk partitioning and mounting
Aug 01, 2023 pm 05:19 PM
Linux disk partitioning and mounting
Aug 01, 2023 pm 05:19 PM
For Linux, wulun has several partitions, which directory is assigned to them. In the final analysis, it has only one root directory, an independent and unique file structure. Each partition in Linux is used to form part of the entire file system.



