what is orm in thinkphp
In thinkphp, ORM refers to "object relational mapping", which is a storage access layer to facilitate developers to use database development; the main purpose of ORM is to map objects represented by the object model to SQL-based relational model database structure.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, thinkphp v5.1 version, Dell G3 computer.
orm in thinkphp
The full name of ORM is Object Relational Mapping, that is, object relational mapping
O (Object) Object is the entity in the project. To be more precise, it is the data Model, which can also be said to be the persistence class.
R (Relation) Relational data
M (Mapping) mapping, mapping objects to relational data, mapping relational data to objects process.
A more intuitive understanding is that ORM uses OOP thinking to generate add, delete, modify and query SQL statements.
ThinkPHP's ORM is a storage access layer for developers to use database development. The framework design picture is as follows:
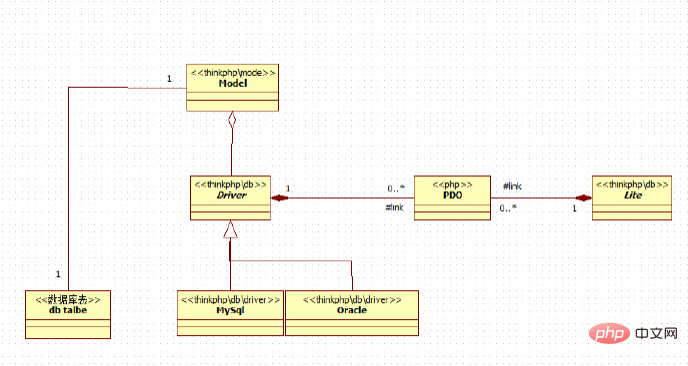
The main purpose is: to convert the object model The represented objects are mapped to the SQL-based relational model database structure.
When changing the properties of the object itself or calling the method of the object, the corresponding execution of certain SQL statements is.
In this way, people who write code can better write business logic instead of repeatedly writing add, delete, modify and query SQL statements.
Application examples in thinkphp
There are two modules for database operations in the TP framework:
Database
Model
Database module in tp
Quote the characteristics of a document Description
Split into Connection/Query/Builder(SQL generator)
Connection connector main It is used to connect to the database. You can use different drivers to connect to different types of databases.
Query query is used to run sql statements, process the results, and map them to the data set.
The Builder generator is used to convert the conditions, sorting, etc. we pass in into SQL statements.
In these 3 steps, we can know that if there is an abstract mapping of ORM ideas used, it can only be the Query query module, but we can carefully check the TP document Description of the data set.
It is more about encapsulating and providing data processing methods, such as:
(The following is a small part copied from the document)
toArray 将数据集的数据转为数组 merge 合并其它数据 diff 比较数组,返回差集 flip 交换数据中的键和值 intersect 比较数组,返回交集 keys 返回数据中的所有键名 pop 删除数据中的最后一个元素 shift 删除数据中的第一个元素 unshift 在数据开头插入一个元素 reduce 通过使用用户自定义函数,以字符串返回数组
But it is not provided Reverse mapping relational operations, such as when we operate a data set, automatically update the data in the database.
So in my understanding, there are not many ORM ideas in the database module. The focus is still on understanding and applying the model
The model in tp
Define model file
namespace app\index\model;
use think\Model;
// 设置类名 需要遵循转换规则,蛇形转为大驼峰
class User extends Model
{
// 设置主键字段名
protected $pk = 'u_id';
// 开启自动维护时间戳字段 (什么时间插入 什么时间更新)
protected $autoWriteTimestamp = true;
// 软删除 开启之后 删除数据只是用一个字段来标识为删除状态 方便查询、备份等
use SoftDelete;
protected $deleteTime = 'delete_time';
}The above code has more content than the model initialization in the first chapter of the document. This is to highlight that the model can complete many functions
This is also the reason for the emergence of ORM : Abstractly map the execution of SQL to objects in object-oriented programming.
We can understand it as: a row of data in the table represents a new object in our code. If the object is changed, the corresponding row in the table will be automatically updated.
Using the model
The code demonstrated is relatively simple, but in reality it can be very flexible
For example, the query uses non-primary key conditions to query, Querying multi-line records, etc.
<?php // *******快速查询、更新******* // 查询主键=1的数据 $user = User::get(1); // 然后更改它的name字段为新的值 $user->name = 'thinkphp'; // 保存,自己去数据库给我更新吧~ $user->save(); // *******插入新的一行数据******* // 新建一个对象(相对应的操作就是新创建一行) $user = new User; // 设置字段的值 有多个字段就多个设置 $user->name= 'thinkphp'; // 保存,自己去插入吧~ $user->save();
Misunderstanding
After seeing how to use it, many beginners start to write code, but they use incorrect methods.
① The model should only be used for the Db class
Although the model can be regarded as a superset of the db class, if you just use it as a simple DB class, rather than using ORM ideas to write it . Then there is no need to use it. .
If you use it incorrectly, it will not only fail to improve efficiency, but will affect yourself. (For example, code specifications are not unified, new tables need to be added with corresponding model files, etc.)
Code demonstration:
<?php $userModel = new User(); // 这里就相当于初始化Db类 $userOneInfo = $userModel->where(['u_id' => 1])->find(); $userTwoInfo = $userModel->where(['u_id' => 2])->find(); // ... 执行其他逻辑 比如判断上下级 操作权限等等 // 业务需求不只是读取用户的数据这么简单 // 还要扣除余额(就是更新数据库) $userOneRes = $userModel->where(['u_id' => 1])->update(['u_balance' => 'xxxx']); // ... 执行其他逻辑
When you see this, stop and think about it. . Has your code ever looked like this?
I believe some people still use it like this! Because I used to use it this way.
Then let’s take a look at the correct way to use it (in my opinion, if you think it’s wrong or have a better one, please comment and exchange)
<?php
$userOneInfo = User::get(1);
// 这里演示使用非主键条件查询的情况!!
// 查询一个1用户的下级出来
$userTwoInfo = User::get(function($query){
$query->where(['p_uid' => 1]);
});
// ... 执行其他逻辑 比如判断上下级 操作权限等等
// 业务需求不只是读取用户的数据这么简单
// 还要扣除余额(就是更新数据库)
$userOneInfo->u_balance = 0;
$userOneRes = $userOneInfo->save();
$userTwoInfo->u_balance = 0;
$userTwoRes = $userTwoInfo->save();
// ... 执行其他逻辑Because an object maps a piece of data, we are operating For data with the same where condition, just operate the object directly. There is no need to repeatedly write where u_id =1 update, u_id = 1 to delete the
usage model, there are many uses, (thanks to the dedication of the open source team, which encapsulates a large number of functions for us)
for example:
– When a new piece of data is added to the user table, another subsidiary table must also initialize a row with the user ID.
– Automatically convert the data format (save the timestamp, and the query will be in 2019-7-13 19:53:04 format).
– Automatically verify data and automatically complete data (the operator’s IP permissions, etc. are stored by default during operation).
– Related query (a very powerful function in TP. The relationship with another model is defined in the model. For example, the u_id in the store table can be used to query the information of the user who belongs to the store. It is equivalent to the store model and Association of user model Automatically join data merge and return to us)
– etc.
Summary
ORM is a An idea and concept that represents object-relational mapping (database-object mapping) ORM abstracts operations on data into operations on objects. Learn to change your thinking, make good use of the features provided by the framework, and write better code. The model in TP is very powerful and encapsulates a lot of logic.
[Related tutorial recommendations: thinkphp framework]
The above is the detailed content of what is orm in thinkphp. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to run thinkphp project
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:33 PM
How to run thinkphp project
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:33 PM
To run the ThinkPHP project, you need to: install Composer; use Composer to create the project; enter the project directory and execute php bin/console serve; visit http://localhost:8000 to view the welcome page.
 There are several versions of thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 06:09 PM
There are several versions of thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 06:09 PM
ThinkPHP has multiple versions designed for different PHP versions. Major versions include 3.2, 5.0, 5.1, and 6.0, while minor versions are used to fix bugs and provide new features. The latest stable version is ThinkPHP 6.0.16. When choosing a version, consider the PHP version, feature requirements, and community support. It is recommended to use the latest stable version for best performance and support.
 How to run thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
How to run thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
Steps to run ThinkPHP Framework locally: Download and unzip ThinkPHP Framework to a local directory. Create a virtual host (optional) pointing to the ThinkPHP root directory. Configure database connection parameters. Start the web server. Initialize the ThinkPHP application. Access the ThinkPHP application URL and run it.
 How to use object-relational mapping (ORM) in PHP to simplify database operations?
May 07, 2024 am 08:39 AM
How to use object-relational mapping (ORM) in PHP to simplify database operations?
May 07, 2024 am 08:39 AM
Database operations in PHP are simplified using ORM, which maps objects into relational databases. EloquentORM in Laravel allows you to interact with the database using object-oriented syntax. You can use ORM by defining model classes, using Eloquent methods, or building a blog system in practice.
 Which one is better, laravel or thinkphp?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
Which one is better, laravel or thinkphp?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 03:18 PM
Performance comparison of Laravel and ThinkPHP frameworks: ThinkPHP generally performs better than Laravel, focusing on optimization and caching. Laravel performs well, but for complex applications, ThinkPHP may be a better fit.
 How to install thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
How to install thinkphp
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:42 PM
ThinkPHP installation steps: Prepare PHP, Composer, and MySQL environments. Create projects using Composer. Install the ThinkPHP framework and dependencies. Configure database connection. Generate application code. Launch the application and visit http://localhost:8000.
 How does Hibernate implement polymorphic mapping?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
How does Hibernate implement polymorphic mapping?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
Hibernate polymorphic mapping can map inherited classes to the database and provides the following mapping types: joined-subclass: Create a separate table for the subclass, including all columns of the parent class. table-per-class: Create a separate table for subclasses, containing only subclass-specific columns. union-subclass: similar to joined-subclass, but the parent class table unions all subclass columns.
 How is the performance of thinkphp?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:24 PM
How is the performance of thinkphp?
Apr 09, 2024 pm 05:24 PM
ThinkPHP is a high-performance PHP framework with advantages such as caching mechanism, code optimization, parallel processing and database optimization. Official performance tests show that it can handle more than 10,000 requests per second and is widely used in large-scale websites and enterprise systems such as JD.com and Ctrip in actual applications.






