What file is mysql frm?
在mysql中,frm的意思为“表定义”,是描述数据表结构的文件。frm文件是用来保存每个数据表的元数据信息,包括表结构的定义等。frm文件跟数据库存储引擎无关,也就是任何存储引擎的数据表都必须有frm文件,命名方式为“数据表名.frm”。

本教程操作环境:windows7系统、mysql8版本、Dell G3电脑。
在mysql中,frm的意思为“表定义”,是描述数据表结构的文件。
在MYSQL中建立任何一张数据表,在其数据目录对应的数据库目录下都有对应表的.frm文件,.frm文件是用来保存每个数据表的元数据(meta)信息,包括表结构的定义等。
.frm文件跟数据库存储引擎无关,也就是任何存储引擎的数据表都必须有.frm文件,命名方式为数据表名.frm,如user.frm. .frm文件可以用来在数据库崩溃时恢复表结构。
通常frm文件是不会损坏的,但是如果出现特殊情况出现frm文件损坏也不要放弃希望,例如下面报错:
1 |
|
当修复MyISAM和InnoDB表时,MySQL服务会首先去调用frm文件,所以我们只能通过修复frm文件进行后面的数据恢复。
MySQL通过sql/table.cc的create_frm()函数创建frm文件,创建出来的frm文件是二进制文件,需要通过hexdump解析成16进制来分析。
create_frm()函数对frm文件头部定义的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 |
|
open_binary_frm()函数对对frm索引部分定义的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 |
|
hexdump是Linux下的一个二进制文件查看工具,可以将二进制文件转换为ASCII、10进制、16进制或8进制进行查看。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
|
实例版本与表字符集:
参考:https://www.percona.com/blog/2015/07/09/obtain-mysql-version-frm-file/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
|
frm列属性:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
|
字段类型(注意5.6版本字段类型有不同,会影响数据恢复):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
|
表中所含索引:
1 2 3 4 |
|
表:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
|
十六进制文件打开:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
|
通过上面的颜色区分,圈出的黄色部分是索引属性,下面红蓝绿三色是三列属性。
列属性结构:
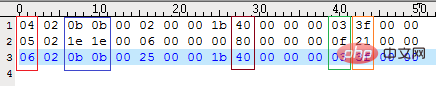
红色部分:字段序号(4开始,4、5、6就是字段第一第二第三)
蓝色部分:字段长度
棕色部分:是否为空
绿色部分:字段类型
黄色部分:字符集
索引属性结构:
索引头部:
淡蓝色部分:索引统计数
粉色部分:索引总共有多少列
索引主体:
棕色部分:是否唯一索引
红色部分:表中列的序号
绿色部分:表中对应列的属性
字段默认值:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
|
【相关推荐:mysql视频教程】
The above is the detailed content of What file is mysql frm?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1392
1392
 52
52
 36
36
 110
110
 How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
How to open phpmyadmin
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
You can open phpMyAdmin through the following steps: 1. Log in to the website control panel; 2. Find and click the phpMyAdmin icon; 3. Enter MySQL credentials; 4. Click "Login".
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.
 How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
How to use single threaded redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Redis uses a single threaded architecture to provide high performance, simplicity, and consistency. It utilizes I/O multiplexing, event loops, non-blocking I/O, and shared memory to improve concurrency, but with limitations of concurrency limitations, single point of failure, and unsuitable for write-intensive workloads.
 MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's position in databases and programming is very important. It is an open source relational database management system that is widely used in various application scenarios. 1) MySQL provides efficient data storage, organization and retrieval functions, supporting Web, mobile and enterprise-level systems. 2) It uses a client-server architecture, supports multiple storage engines and index optimization. 3) Basic usages include creating tables and inserting data, and advanced usages involve multi-table JOINs and complex queries. 4) Frequently asked questions such as SQL syntax errors and performance issues can be debugged through the EXPLAIN command and slow query log. 5) Performance optimization methods include rational use of indexes, optimized query and use of caches. Best practices include using transactions and PreparedStatemen
 Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL is chosen for its performance, reliability, ease of use, and community support. 1.MySQL provides efficient data storage and retrieval functions, supporting multiple data types and advanced query operations. 2. Adopt client-server architecture and multiple storage engines to support transaction and query optimization. 3. Easy to use, supports a variety of operating systems and programming languages. 4. Have strong community support and provide rich resources and solutions.
 How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Apache connects to a database requires the following steps: Install the database driver. Configure the web.xml file to create a connection pool. Create a JDBC data source and specify the connection settings. Use the JDBC API to access the database from Java code, including getting connections, creating statements, binding parameters, executing queries or updates, and processing results.
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 phpMyAdmin comprehensive use guide
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
phpMyAdmin comprehensive use guide
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
phpMyAdmin is not just a database management tool, it can give you a deep understanding of MySQL and improve programming skills. Core functions include CRUD and SQL query execution, and it is crucial to understand the principles of SQL statements. Advanced tips include exporting/importing data and permission management, requiring a deep security understanding. Potential issues include SQL injection, and the solution is parameterized queries and backups. Performance optimization involves SQL statement optimization and index usage. Best practices emphasize code specifications, security practices, and regular backups.





