This article will help you understand what Git version management is
This article brings you relevant knowledge about Git version management. The version management tool can record each modification. As long as it is submitted to the version repository, you can find the status at any previous time. ,I hope everyone has to help.

Git is a "distributed version management tool".
The version management tool can record every modification. As long as it is submitted to the version warehouse, the status at any previous time can be found.
We have all used the undo function when writing, but undo can only go back a limited number of steps. Usually, the editing software is closed and then reopened. At this time, the undo record has been cleared. The "version management tool" is different. It can record every modification. As long as it is submitted to the version warehouse, you can find the status at any previous time.
Create warehouse
After installing the git software, create a new folder in any directory, open it, and then execute git init to create a new git warehouse (this command A hidden subdirectory named .git will be created).
Check out the warehouse
Execute the command git clone remote project address to clone the warehouse on the remote server.
Git status
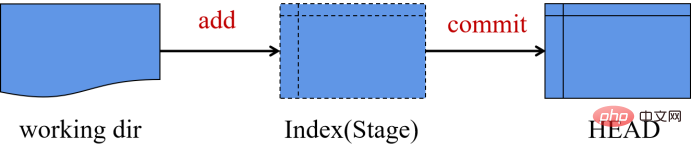
Git has three states, namely committed, modified, and staged.
- Modified: Modified means that the file has been modified but has not been saved to the database.
- Staged (staged): Indicates that the current version of a modified file has been marked so that it will be included in the next submitted snapshot.
- Committed: The data has been safely saved in the local database.
The three states of Git correspond to the three workflows of the local warehouse. This low warehouse is composed of three trees maintained by git.
- The first one is the working directory, which holds the actual files, additions and deletions of files and content;
- The second one is the temporary storage area (Index), which is like a cache area and is temporarily saved. change. Enter git add filename, and the changes will be placed in the temporary storage area.
- The third one is HEAD, pointing to the last submitted result. Enter the git commit command, and the changes will be placed in the local warehouse. What comes after the commit can be called a version.

Basic git workflow:
- Propose changes (add to staging area)
Use the command git add (for a specific file) or git add * (for all files) can propose changes (add them to the staging area). - Submit changes
Use the command git commit -m "code submission information" to actually submit the changes. After execution, the changes are submitted to HEAD, but have not yet reached the remote warehouse. - Push changes
Use the command git push origin master to submit the changes to the remote warehouse master branch (usually not submitted directly to the master branch, but pushed to your own branch, and then merge after verification ).
Branch
The master branch was mentioned earlier, so how to understand the branch intuitively?
Branches are used to insulate feature development. When creating a repository, master is the "default" branch. Develop on other branches and merge them into the master branch when finished. 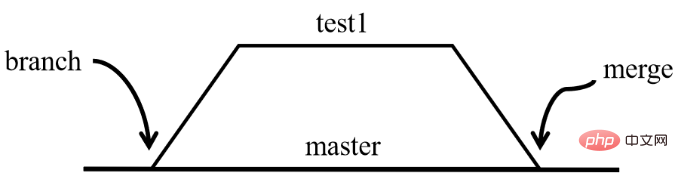
| git branch test1 | Create a branch named test1. |
|---|---|
| git checkout test1 | Switch the current branch to test1 |
| git checkout -b test1 | Create a branch called "test1" and switch to it. |
| git checkout master | Switch back to the master branch. |
| git branch -d test1 | Delete the newly created branch. |
| git push origin | Push the branch to the remote warehouse. |
| git merge test | Merge branches. |
Update and merge
Use the command git pull "remote branch name" to get the code from the remote and merge it into this lower version (get (fetch) in the working directory and merge ( merge) Remote changes)
Use the command git merge "branch name" to merge other branches into the current branch.
In the first two cases, git will try to automatically merge the changes. However, conflicts may occur during merging, and you need to manually modify the files to merge these conflicts. After making changes, execute git add to mark them as merged successfully. Before merging changes, you can use git diff
Replace local changes
If you make a mistake, you can use the command git checkout - to replace the local changes. This command will replace the files in the working directory with the latest content in HEAD (changes and new files that have been added to the staging area will not be affected)
Removal and reinstallation of remote warehouses Naming
Rename test to test1: git remote rename test test1
Remove remote warehouse test1: git remote rm test1
Undo operation
Cancel the temporary file: git reset filename
Undo the modification to the file: git checkout –filename
History record
Use git log You can get the history of the local warehouse.
Use the command git log --author=bob to view only the commit records of a certain person. Add some parameters to modify the output to get the results you want.
Check which files have changed: git log --name-status
Recommended study: "Git Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of This article will help you understand what Git version management is. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
There are many ways to install DeepSeek, including: compile from source (for experienced developers) using precompiled packages (for Windows users) using Docker containers (for most convenient, no need to worry about compatibility) No matter which method you choose, Please read the official documents carefully and prepare them fully to avoid unnecessary trouble.
 Summary of FAQs for DeepSeek usage
Feb 19, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
Summary of FAQs for DeepSeek usage
Feb 19, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
DeepSeekAI Tool User Guide and FAQ DeepSeek is a powerful AI intelligent tool. This article will answer some common usage questions to help you get started quickly. FAQ: The difference between different access methods: There is no difference in function between web version, App version and API calls, and App is just a wrapper for web version. The local deployment uses a distillation model, which is slightly inferior to the full version of DeepSeek-R1, but the 32-bit model theoretically has 90% full version capability. What is a tavern? SillyTavern is a front-end interface that requires calling the AI model through API or Ollama. What is breaking limit
 What are the Grayscale Encryption Trust Funds? Common Grayscale Encryption Trust Funds Inventory
Mar 05, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
What are the Grayscale Encryption Trust Funds? Common Grayscale Encryption Trust Funds Inventory
Mar 05, 2025 pm 12:33 PM
Grayscale Investment: The channel for institutional investors to enter the cryptocurrency market. Grayscale Investment Company provides digital currency investment services to institutions and investors. It allows investors to indirectly participate in cryptocurrency investment through the form of trust funds. The company has launched several crypto trusts, which has attracted widespread market attention, but the impact of these funds on token prices varies significantly. This article will introduce in detail some of Grayscale's major crypto trust funds. Grayscale Major Crypto Trust Funds Available at a glance Grayscale Investment (founded by DigitalCurrencyGroup in 2013) manages a variety of crypto asset trust funds, providing institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals with compliant investment channels. Its main funds include: Zcash (ZEC), SOL,
 Delphi Digital: How to change the new AI economy by parsing the new ElizaOS v2 architecture?
Mar 04, 2025 pm 07:00 PM
Delphi Digital: How to change the new AI economy by parsing the new ElizaOS v2 architecture?
Mar 04, 2025 pm 07:00 PM
ElizaOSv2: Empowering AI and leading the new economy of Web3. AI is evolving from auxiliary tools to independent entities. ElizaOSv2 plays a key role in it, which gives AI the ability to manage funds and operate Web3 businesses. This article will dive into the key innovations of ElizaOSv2 and how it shapes an AI-driven future economy. AI Automation: Going to independently operate ElizaOS was originally an AI framework focusing on Web3 automation. v1 version allows AI to interact with smart contracts and blockchain data, while v2 version achieves significant performance improvements. Instead of just executing simple instructions, AI can independently manage workflows, operate business and develop financial strategies. Architecture upgrade: Enhanced A
 As top market makers enter the crypto market, what impact will Castle Securities have on the industry?
Mar 04, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
As top market makers enter the crypto market, what impact will Castle Securities have on the industry?
Mar 04, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
The entry of top market maker Castle Securities into Bitcoin market maker is a symbol of the maturity of the Bitcoin market and a key step for traditional financial forces to compete for future asset pricing power. At the same time, for retail investors, it may mean the gradual weakening of their voice. On February 25, according to Bloomberg, Citadel Securities is seeking to become a liquidity provider for cryptocurrencies. The company aims to join the list of market makers on various exchanges, including exchanges operated by CoinbaseGlobal, BinanceHoldings and Crypto.com, people familiar with the matter said. Once approved by the exchange, the company initially planned to set up a market maker team outside the United States. This move is not only a sign
 Significantly surpassing SFT, the secret behind o1/DeepSeek-R1 can also be used in multimodal large models
Mar 12, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Significantly surpassing SFT, the secret behind o1/DeepSeek-R1 can also be used in multimodal large models
Mar 12, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Researchers from Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai AILab and the Chinese University of Hong Kong have launched the Visual-RFT (Visual Enhancement Fine Tuning) open source project, which requires only a small amount of data to significantly improve the performance of visual language big model (LVLM). Visual-RFT cleverly combines DeepSeek-R1's rule-based reinforcement learning approach with OpenAI's reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT) paradigm, successfully extending this approach from the text field to the visual field. By designing corresponding rule rewards for tasks such as visual subcategorization and object detection, Visual-RFT overcomes the limitations of the DeepSeek-R1 method being limited to text, mathematical reasoning and other fields, providing a new way for LVLM training. Vis
 Bitwise: Businesses Buy Bitcoin A Neglected Big Trend
Mar 05, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Bitwise: Businesses Buy Bitcoin A Neglected Big Trend
Mar 05, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
Weekly Observation: Businesses Hoarding Bitcoin – A Brewing Change I often point out some overlooked market trends in weekly memos. MicroStrategy's move is a stark example. Many people may say, "MicroStrategy and MichaelSaylor are already well-known, what are you going to pay attention to?" This is true, but many investors regard it as a special case and ignore the deeper market forces behind it. This view is one-sided. In-depth research on the adoption of Bitcoin as a reserve asset in recent months shows that this is not an isolated case, but a major trend that is emerging. I predict that in the next 12-18 months, hundreds of companies will follow suit and buy large quantities of Bitcoin
 The latest tutorial on how to install the ios version installation package of Ouyi
Feb 21, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
The latest tutorial on how to install the ios version installation package of Ouyi
Feb 21, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of how to install the latest installation packages from EV Exchange on iOS devices. Ouyi Exchange is a leading cryptocurrency trading platform that provides a wide range of cryptocurrency trading, asset management and investment services. By following the step-by-step instructions provided in this guide, users can easily and easily install the Euyi Exchange app on their iPhone or iPad. This guide is suitable for all iOS devices, from older models to the latest generation, and includes clear screenshots and detailed instructions to ensure a seamless installation process.