There are several ways to create a Docker image
There are two ways to create a Docker image: 1. Use the "docker commit" command to manually build the image based on the existing container; 2. Use Dockerfile to automatically build the image. The Docker program will read the instructions in the Dockerfile build file. Automatically generate images.

The operating environment of this tutorial: linux5.9.8 system, docker-1.13.1 version, Dell G3 computer.
Sometimes the image downloaded from the Docker image warehouse cannot meet the requirements. We can build an own image based on a basic image.
Introduction to image construction
Under what circumstances Next we need to build the image ourselves?
(1) When we cannot find an existing image, such as an application developed by ourselves
(2) We need to add specific functions to the image
docker build There are two ways to image: docker commitcommand and DockerfileBuild file
docker commit build image
Building an image based on an existing container is mainly done through docker commit command to build a new image.
There are three main steps for dockercommit construction:
- Run the container
- Modify the container
- Save the container as a new image
For example, install the vim editor in the centos image and save it as a new image
(1) Run the container
[root@ken1 docker]# docker run -it centos Unable to find image 'centos:latest' locally latest: Pulling from library/centos a02a4930cb5d: Pull complete Digest: sha256:184e5f35598e333bfa7de10d8fb1cebb5ee4df5bc0f970bf2b1e7c7345136426 Status: Downloaded newer image for centos:latest
(2) Install the vim editor
vim The editor confirms that it is not installed
[root@69f501e858a6 /]# vim bash: vim: command not found
Install it
[root@69f501e858a6 /]# yum install vim -y
(3) Save it as a new image
First check the currently running image
[root@ken1 ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 69f501e858a6 centos "/bin/bash" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes quizzical_torvalds
Use commit Save as a new image
[root@ken1 ~]# docker commit 69f501e858a6 centos-vim sha256:42083b89a179368bc29a8f40d14f8824990183c8e4b28fd84411d440c26342e5
69f501e858a6 is the ID of the running container. You can also use the name below name.
centos-vim is the name of the new image.
Check to see if centos-vim is available. Mirror
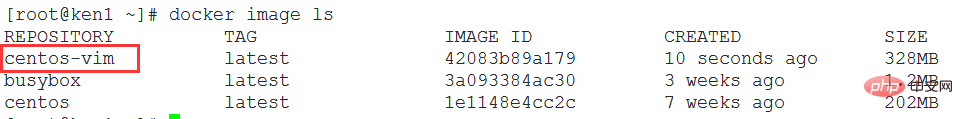

Restart the new mirror and verify whether the vim editor can be used
You can find that the new mirror can be used with the vim editor
[root@ken1 ~]# docker run -it centos-vim [root@61d090898bad /]# vim [root@61d090898bad /]# vim test
The above demonstrates how to use commit to create a new image, but docker does not recommend using this method to create an image for the following reasons:
- This is a manual way to create an image. , the container is wrong, and the efficiency is low and the repeatability is weak
- More importantly. The user does not know how the image is created. Is there any malicious program inside?
Dockerfile builds the image
Dockerfile is a file composed of a set of instructions. Each instruction corresponds to a command in Linux. The Docker program reads the Dockerfile The instructions in ultimately generate the image.
The first Dockerfike
Step one: Create a new directory
[root@ken1 ~]# mkdir /test
Step two: Write a Dockerfile
The name is Dockerfile, and The first D needs to be capitalized
[root@ken1 ~]# cat Dockerfile FROM centos RUN yum install vim -y
FROMcentos means using the centos basic image
RUN means installing the vim editor on centos
Step 3: Build the image
[root@ken1 ~]# docker build -t centos-vim2 .
-t is followed by specifying the tag name (tag) of the new image
. The last dot indicates that the docker context is the current directory. Docker will search for the Dockerfile file from the build context by default. We can also specify the location of the Dockerfile through the -f parameter
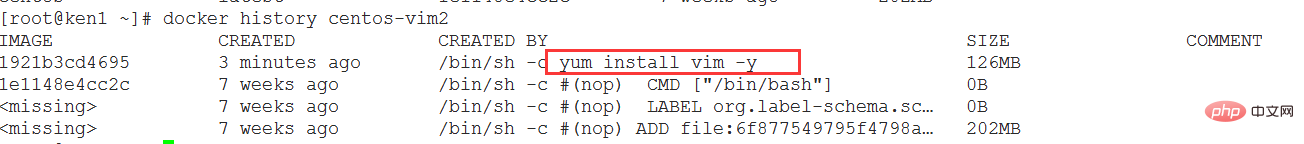
Step 4: View the image
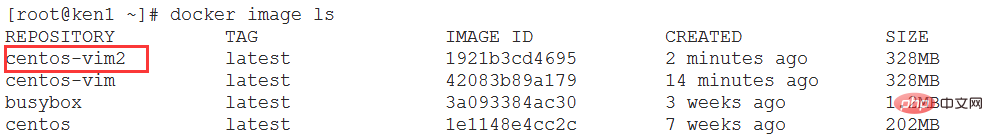
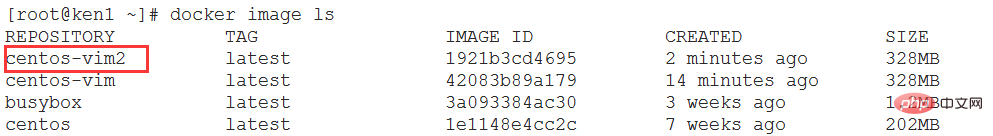
View the image hierarchical structure
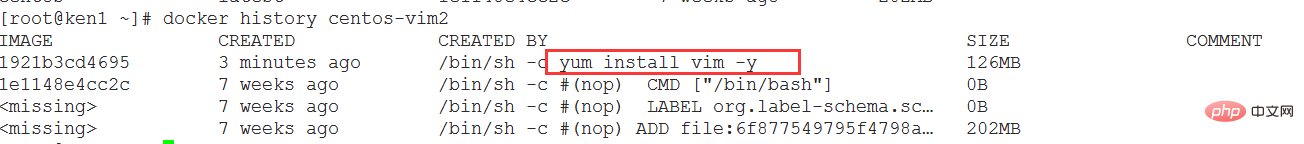
10.CMD
容器启动时运行指定的命令
dockerfile中可以多个CMD指令,但是只要最后一个生效。CMD可以被docker run之后的参数替换
11.ENTRYPOINT
设置容器启东市的命令
dockerfile中可以有多个ENTRYPOINT,但是只有最后一个生效。
CMD或者docker run之后的参数会被当做参数传递给ENTERYPOINT.
Dockerfile演示
下面演示一个比较全面的dockerfile
[root@ken1 test]# cat Dockerfile #my Dockerfile FROM busybox MAINTAINER ken WORKDIR /ken RUN touch test COPY ["ken1","."] ADD ["wordpress.tar.gz","."] ENV name "ken"
注意:Dockerfile支持以#开头的注释
构建镜像
[root@ken1 test]# docker build -t myimage . Sending build context to Docker daemon 4.281MB Step 1/7 : FROM busybox ---> 3a093384ac30 Step 2/7 : MAINTAINER ken ---> Running in 2a73a83507ce Removing intermediate container 2a73a83507ce ---> 8c3df9b3d823 Step 3/7 : WORKDIR /ken ---> Running in 31c6f9fe2195 Removing intermediate container 31c6f9fe2195 ---> a458cf986072 Step 4/7 : RUN touch test ---> Running in e1b08ebd363c Removing intermediate container e1b08ebd363c ---> 41601920009a Step 5/7 : COPY ["ken1","."] ---> 2ebfa0933fca Step 6/7 : ADD ["wordpress.tar.gz","."] ---> d0ad29d3aa34 Step 7/7 : ENV name "ken" ---> Running in fceae6e20e63 Removing intermediate container fceae6e20e63 ---> 7efe0600e48f Successfully built 7efe0600e48f Successfully tagged myimage:latest
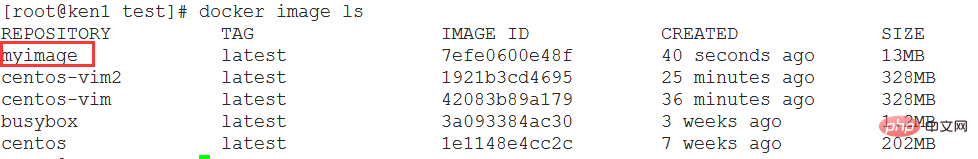
查看镜像

运行该镜像
[root@ken1 test]# docker run -it myimage /ken # ls ken1 test wordpress /ken # echo $name ken
- 可以发现当前工作目录为/ken,且自动创建
- ken1是我们从docker context目录中复制过去的
- test是使用touch创建的
- wordpres压缩包已经被自动解压
- $name为变量值为ken
推荐学习:《docker视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of There are several ways to create a Docker image. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
The steps to update a Docker image are as follows: Pull the latest image tag New image Delete the old image for a specific tag (optional) Restart the container (if needed)
 How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use Docker Desktop? Docker Desktop is a tool for running Docker containers on local machines. The steps to use include: 1. Install Docker Desktop; 2. Start Docker Desktop; 3. Create Docker image (using Dockerfile); 4. Build Docker image (using docker build); 5. Run Docker container (using docker run).
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to view the docker process
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:48 AM
How to view the docker process
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Docker process viewing method: 1. Docker CLI command: docker ps; 2. Systemd CLI command: systemctl status docker; 3. Docker Compose CLI command: docker-compose ps; 4. Process Explorer (Windows); 5. /proc directory (Linux).
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to save docker image
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:54 AM
How to save docker image
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:54 AM
To save the image in Docker, you can use the docker commit command to create a new image, containing the current state of the specified container, syntax: docker commit [Options] Container ID Image name. To save the image to the repository, you can use the docker push command, syntax: docker push image name [: tag]. To import saved images, you can use the docker pull command, syntax: docker pull image name [: tag].
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database




