What is the difference between 5.6 and 5.5 in mysql
Differences: 1. In version 5.5, the binlog and POS parameters cannot be omitted in the master-slave configuration, but in version 5.6, these two parameters can be omitted; 2. In version 5.5, multi-thread replication is not supported. Synchronous replication is single-threaded and queued, while multi-threaded replication is supported in version 5.6.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows10 system, mysql8.0.22 version, Dell G3 computer.
What are the differences between 5.6 and 5.5 in mysql?
Improvements of 5.6:
1. In 5.5 and previous versions of mysql, the master-slave configuration must be done in the slave Node configuration change master to specify binlog and POS. In 5.6 and later
, these two parameters can be omitted. MySQL can automatically find synchronization points through the internal GTID mechanism. We only need to specify the master's IP, username and password, and port.
2. 5.6 supports multi-threaded replication
In 5.5, synchronous replication is single-threaded and queued, and can only be executed one by one. In 5.6, multiple libraries can be copied at the same time (note: multi-threading is still not allowed in the same library).
5.6 will involve the UUID parameter
MySQL [(none)]>show variables like '%uuid%'; +---------------+--------------------------------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +---------------+--------------------------------------+ | server_uuid | ca910cf0-3aec-11e6-9319-b888e3dcfeb8 | +---------------+--------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Note: This UIID will be automatically generated when mysql is first started and written to auto.cnf. Officials do not recommend modifying this value. And server_uuid and GTID are closely related.
GTID: Global Transaction Identifier
When using this function, each transaction submission will generate a unique identifier in the binlog, which consists of UUID and transaction ID. The transaction ID submitted for the first time is 1, and it increases sequentially thereafter.
When GTID is turned on, there is no need to find the binlog log and POS point when the slave performs synchronous replication. Direct
GTID writing method:
change master to master_HOST=192.168.2.100, master_PORT=2206, master_USER=repluser, master_PASSWORD='123456', master_AUTO_POSITION=1; 另外传统的写法: CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='master2.mycompany.com', MASTER_USER='replication', MASTER_PASSWORD='bigs3cret', MASTER_PORT=3306, MASTER_LOG_FILE='master2-bin.001', MASTER_LOG_POS=4, MASTER_CONNECT_RETRY=10;
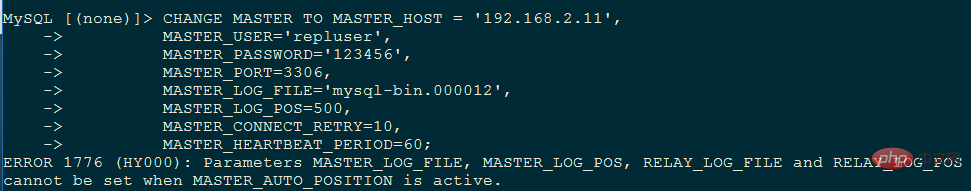
If GTID has been enabled before, then you can no longer use the traditional change master to method, and an error will be reported, as follows:
ERROR 1776 (HY000): Parameters MASTER_LOG_FILE, MASTER_LOG_POS, RELAY_LOG_FILE and RELAY_LOG_POS cannot be set when MASTER_AUTO_POSITION is active.
GTID workflow:
1, Submit a transaction on the master and write it to binlog
2. The binlog is sent to the slave. The slave receives and writes the relay log. The slave reads the GTID and sets the value of gtid_next. For example:
set @@SESSION.GTID_NEXT='B0869D03-D332223-35454:3';
Then tell the slave that the next transaction must use GTID and write it to its own binlog .
3. The slave checks and confirms that the gtid is not used. If it is not used, then it starts executing the transaction and writes it to its own binlog.
4. Since the value of gtid_next is not empty, the slave will not try to generate a new gtid, but obtain the GTID through master-slave synchronization.
In addition, if you want to use the GTID method for master-slave synchronization, you must also add the following configuration to my.cnf:
[mysqld] log-bin=mysql-bin binlog_format = mixed log_slave_updates = ON gtid-mode = ON enforce_gtid_consistency = ON
Then export mysqldump -uroot -proot -q on the master --single-transaction -R -E --triggers -B hellodb > /root/hello.sql
Import mysql on slave -uroot -proot < /root/hello.sql
Configure the change master to point on the slave (the following 6 lines of code):
change master to master_HOST=192.168.2.100, master_PORT=3306, master_USER=repluser, master_PASSWORD='123456', master_AUTO_POSITION=1;
Limitations of GTID:
1. GTID replication is based on transactions and does not support MyISAM. This May result in multiple GTID allocations for the same transaction.
2. The create table...select statement is not supported. Because this statement will be split into two transactions: create table and insert, and if these two transactions are assigned the same GTID, insert will be ignored by the standby database.
3. Creation and deletion of temporary tables are not supported.
Multi-threaded replication demonstration:
Execute the following commands on the slave:
> stop slave; > set global slave_parallel_workers = 4; > start slave; > show full processlist;可以看到有4个线程 Waitingfor an eventfromCoordinator
If this When there are a large number of insert operations on the master, you can execute > select * from mysql.slave_worker_info\G on the slave. You should be able to see that the worker_id is constantly changing, indicating that multi-thread replication is working.
Description: slave_parallel_workers can achieve multi-threaded concurrent replication on the slave. However, it can only support concurrent replication between multiple databases under one instance, and cannot truly achieve concurrent replication of multiple tables. Therefore, when there is a large concurrent load, the slave still cannot catch up with the master in time, and needs to find ways to optimize (for example: try to split a table in a library into multiple libraries according to business logic to save, so that during write operations, The slave can start multi-thread replication, reducing the synchronization delay.)
In addition, it is recommended to modify my.cnf and add 2 lines (by default, this info_file is a file and is not written to the database)
relay_log_info_repository = table master_info_repository = table
This alone is not enough. By default, these two tables are MyISAM. If it is unsafe, you need to convert them
> alter table slave_master_info engine innodb; > alter table slave_relay_log_info engine innodb; > alter table slave_worker_info engine innodb;
This way, you can prevent table damage and you can repair it yourself after damage.
Master-slave replication in GTID mode, the solution to the error that cannot be skipped during synchronization:
If you see a synchronization error on the slave "The XXX key of the slave node does not exist"
We can try to use the old method on 5.5
> stop slave; > set global sql_slave_skip_counter=1 > start slave;
When executing, you will find an error, the prompt is as follows:

可以看出运行在GTID模式下,不支持sql_slave_skip_counter这种方式跳过的。
那么可以如下方法来跳过:
> show slave status\G查看如下2行的信息:
Retrieved_Gtid_Set: ca910cf0-3aec-11e6-9319-b888e3dcfeb8:1-2 Executed_Gtid_Set: ca910cf0-3aec-11e6-9319-b888e3dcfeb8:1
第一行表示收到的事务,第二行表示已经执行完的事务。也就是说执行到Retrieved_Gtid_Set时候发生错误了。
因此,我们直接单单跳过这个事务即可。
> stop slave; > set GTID_NEXT='ca910cf0-3aec-11e6-9319-b888e3dcfeb8:2'; 就是这种写法,不要加什么1-2这些玩意 > begin; > commit; > set GTID_NEXT="AUTOMATIC"; #把gtid_next设置回来 > start slave; > show slave status\G 验证下是否IO/SQL都是YES状态。
GTID模式转换为传统模式的方法及注意点:
要转换成传统模式,需要在my.cnf里面注释掉下面2行:
# gtid-mode=ON # enforce_gtid_consistency = ON
然后重启MySQL。
登进mysql,执行类似如下命令:
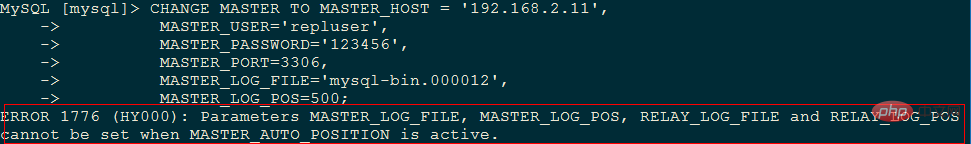
> stop slave; > CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='master2.mycompany.com', MASTER_USER='replication', MASTER_PASSWORD='bigs3cret', MASTER_PORT=3306, MASTER_LOG_FILE='master2-bin.001', MASTER_LOG_POS=4, MASTER_CONNECT_RETRY=10;
结果报错了,如下图:
解决方法:
> change master to MASTER_AUTO_POSITION=0; # 关闭这个参数,这个参数是GTID复制才用到的。 > CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST = '192.168.2.11', MASTER_USER='repluser', MASTER_PASSWORD='123456', MASTER_PORT=3306, MASTER_LOG_FILE='mysql-bin.000012', MASTER_LOG_POS=500, MASTER_CONNECT_RETRY=10; > start slave; > show slave status\G 验证下是否IO/SQL都是YES状态。
推荐学习:mysql视频教程
The above is the detailed content of What is the difference between 5.6 and 5.5 in mysql. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP's big data structure processing skills
May 08, 2024 am 10:24 AM
PHP's big data structure processing skills
May 08, 2024 am 10:24 AM
Big data structure processing skills: Chunking: Break down the data set and process it in chunks to reduce memory consumption. Generator: Generate data items one by one without loading the entire data set, suitable for unlimited data sets. Streaming: Read files or query results line by line, suitable for large files or remote data. External storage: For very large data sets, store the data in a database or NoSQL.
 How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
Backing up and restoring a MySQL database in PHP can be achieved by following these steps: Back up the database: Use the mysqldump command to dump the database into a SQL file. Restore database: Use the mysql command to restore the database from SQL files.
 How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
MySQL query performance can be optimized by building indexes that reduce lookup time from linear complexity to logarithmic complexity. Use PreparedStatements to prevent SQL injection and improve query performance. Limit query results and reduce the amount of data processed by the server. Optimize join queries, including using appropriate join types, creating indexes, and considering using subqueries. Analyze queries to identify bottlenecks; use caching to reduce database load; optimize PHP code to minimize overhead.
 How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into MySQL table? Connect to the database: Use mysqli to establish a connection to the database. Prepare the SQL query: Write an INSERT statement to specify the columns and values to be inserted. Execute query: Use the query() method to execute the insertion query. If successful, a confirmation message will be output.
 How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
Creating a MySQL table using PHP requires the following steps: Connect to the database. Create the database if it does not exist. Select a database. Create table. Execute the query. Close the connection.
 How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
To use MySQL stored procedures in PHP: Use PDO or the MySQLi extension to connect to a MySQL database. Prepare the statement to call the stored procedure. Execute the stored procedure. Process the result set (if the stored procedure returns results). Close the database connection.
 How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
One of the major changes introduced in MySQL 8.4 (the latest LTS release as of 2024) is that the "MySQL Native Password" plugin is no longer enabled by default. Further, MySQL 9.0 removes this plugin completely. This change affects PHP and other app
 The difference between oracle database and mysql
May 10, 2024 am 01:54 AM
The difference between oracle database and mysql
May 10, 2024 am 01:54 AM
Oracle database and MySQL are both databases based on the relational model, but Oracle is superior in terms of compatibility, scalability, data types and security; while MySQL focuses on speed and flexibility and is more suitable for small to medium-sized data sets. . ① Oracle provides a wide range of data types, ② provides advanced security features, ③ is suitable for enterprise-level applications; ① MySQL supports NoSQL data types, ② has fewer security measures, and ③ is suitable for small to medium-sized applications.






