
How to check open ports on Linux: 1. Use the nmap tool to detect open ports; 2. Use the netstat tool to detect open ports; 3. Use the lsof tool to detect open ports; 4. Use telnet to detect open ports; 5. Use the netcat tool to detect open ports.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux5.9.8 system, Dell G3 computer.
In network technology, ports include logical ports and physical ports. Physical ports refer to physically existing ports, such as interfaces on ADSL Modems, hubs, switches, and routers used to connect to other network devices, such as RJ-45 ports, SC ports, etc. Logical port refers to the port used to distinguish services in a logical sense, such as the service port in the TCP/IP protocol. The port number ranges from 0 to 65535, such as port 80 for web browsing services and port 21 for FTP services. wait. Due to the large number of physical ports and logical ports, in order to distinguish the ports, each port is numbered, which is the port number
Ports can be divided into 3 categories according to the port number:
1: Well Known Port
Well-known port numbers range from 0 to 1023. They are closely bound to some common services. For example, the FTP service uses port 21, which you can see in /etc/services. this mapping relationship.
2: Registered Ports:
from 1024 to 49151. They are loosely tied to some services. That is to say, there are many services bound to these ports, and these ports are also used for many other purposes.
3: Dynamic and/or Private Ports
Dynamic ports, That is, private port numbers are the number of ports that can be used by any software to communicate with any other software, using the Internet's Transmission Control Protocol, or User Transport Protocol. Dynamic ports are generally from 49152 to 65535
Linux has a limited port range. If I want to reserve certain ports for my program, then I need to control this port range. /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range defines the local TCP/UDP port range. You can define net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000
[root@localhost ~]# cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range 32768 61000 [root@localhost ~]# echo 1024 65535 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_local_port_range
About ports and services in /etc/sysctl.conf , I once used the analogy of a public toilet. Each toilet in a public toilet is like each port of the system. To provide convenience for people is the so-called service. If you provide these services, then the port (toilet) must be opened. When someone goes to When using the toilet, links are established at these ports. If that toilet is occupied by someone, it means that the port number is occupied by a service. If one day there is no public toilet service here and the public toilet is demolished, naturally there will be no port number. In fact, a more vivid example is like a bank lobby. The port numbers are the counters, and the people who take the numbers to handle business are like various clients linked to the server. They send business contact with the counter through port redirection technology. To give another easy-to-understand example, the port number is like each station on the high-speed rail line. For example, Changsha, Yueyang, etc. each represent a port number. Passengers go to their respective stations through train tickets, which is like each application program sending to the server. Port IP packet.
How to check whether the port is open? In fact, if I don’t sort it out, I don’t know that there are so many methods!
1: nmap tool detects open ports
nmap is a network scanning and host detection tool. Installation of nmap is very simple as shown below for rpm installation.
[root@DB-Server Server]# rpm -ivh nmap-4.11-1.1.x86_64.rpm warning: nmap-4.11-1.1.x86_64.rpm: Header V3 DSA signature: NOKEY, key ID 37017186 Preparing... ########################################### [100%] 1:nmap ########################################### [100%] [root@DB-Server Server]# rpm -ivh nmap-frontend-4.11-1.1.x86_64.rpm warning: nmap-frontend-4.11-1.1.x86_64.rpm: Header V3 DSA signature: NOKEY, key ID 37017186 Preparing... ########################################### [100%] 1:nmap-frontend ########################################### [100%] [root@DB-Server Server]#
Regarding the use of nmap, you can write a long and close-up article, and I will not expand it here. As shown below, nmap 127.0.0.1 checks the open ports of this machine and scans all ports. Of course, other server ports can also be scanned.
[root@DB-Server Server]# nmap 127.0.0.1 Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2016-06-22 15:46 CST Interesting ports on localhost.localdomain (127.0.0.1): Not shown: 1674 closed ports PORT STATE SERVICE 22/tcp open ssh 25/tcp open smtp 111/tcp open rpcbind 631/tcp open ipp 1011/tcp open unknown 3306/tcp open mysql Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.089 seconds You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root [root@DB-Server Server]#
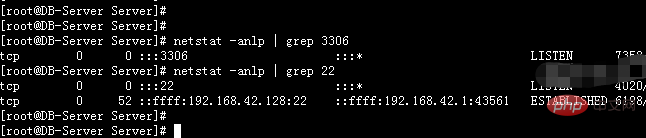
2: The netstat tool detects open ports
[root@DB-Server Server]# netstat -anlp | grep 3306 tcp 0 0 :::3306 :::* LISTEN 7358/mysqld [root@DB-Server Server]# netstat -anlp | grep 22 tcp 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 4020/sshd tcp 0 52 ::ffff:192.168.42.128:22 ::ffff:192.168.42.1:43561 ESTABLISHED 6198/2 [root@DB-Server Server]#

As shown above, this The tool feels less concise and clear than nmap. Of course, it is not as powerful as nmap.
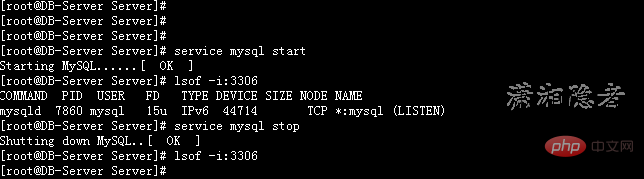
3: lsof tool detects open ports
[root@DB-Server Server]# service mysql start Starting MySQL......[ OK ] [root@DB-Server Server]# lsof -i:3306 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE NODE NAME mysqld 7860 mysql 15u IPv6 44714 TCP *:mysql (LISTEN) [root@DB-Server Server]# service mysql stop Shutting down MySQL..[ OK ] [root@DB-Server Server]# lsof -i:3306 [root@DB-Server Server]#
[root@DB-Server Server]# lsof -i TCP| fgrep LISTEN cupsd 3153 root 4u IPv4 9115 TCP localhost.localdomain:ipp (LISTEN) portmap 3761 rpc 4u IPv4 10284 TCP *:sunrpc (LISTEN) rpc.statd 3797 rpcuser 7u IPv4 10489 TCP *:1011 (LISTEN) sshd 4020 root 3u IPv6 12791 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN) sendmail 4042 root 4u IPv4 12876 TCP localhost.localdomain:smtp (LISTEN)
4: Use telnet to detect whether the port is open
Even if the server port is in the listening state, but the firewall iptables blocks the port, it is impossible to detect whether the port is open through this method.
5: The netcat tool checks whether the port is open.
[root@DB-Server ~]# nc -vv 192.168.42.128 1521 Connection to 192.168.42.128 1521 port [tcp/ncube-lm] succeeded! [root@DB-Server ~]# nc -z 192.168.42.128 1521; echo $? Connection to 192.168.42.128 1521 port [tcp/ncube-lm] succeeded! 0 [root@DB-Server ~]# nc -vv 192.168.42.128 1433 nc: connect to 192.168.42.128 port 1433 (tcp) failed: No route to host
Related recommendations: "Linux Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of How to check which ports are open in Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!