What is centos7 yum
In centos7, the full name of yum is "Yellowdog update Modified", which is a Shell front-end package manager in Fedora, RedHat and SUSE. Yum is based on RPM package management and can automatically download and install RPM packages from designated servers.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: centos7 system, thinkpad t480 computer.
What is yum
Yum is the abbreviation of Yellowdog update Modified. It is a Shell front-end package manager in Fedora, RedHat and SUSE.
Based on RPM package management, it can automatically download and install RPM packages from a designated server. It can automatically handle dependencies and install all dependent software packages at once, without the need to download and install them again and again.
yum provides commands to find, install, and delete a certain, a group, or even all software packages. The commands are concise and easy to remember.
The purpose of yum is to automatically upgrade, install/remove rpm installation packages (that is to say, the yum command operates on RPM packages), collects rmp-related information, checks dependencies, and prompts users solve.
The key to yum is to have a reliable repository. As the name suggests, this is the software warehouse. It can be an http or ftp site, or a local software pool, but it must contain the rpm header and rmp header. The header includes various information about rmp, including description, function, provided files, dependencies, etc. It is by collecting this information that the remaining tasks can be completed automatically.
Yum itself is a system that automatically manages installation packages running on Linux. The idea of yum is to use a central repository (repository) to manage the interrelationships of a part or even a distribution of applications, and perform related upgrades, installations, deletions, etc. based on the calculated software dependencies, reducing the dependencies that Linux users have always had a headache for. question.
At this point, yum and apt are the same. apt was originally used by debian deb type software management, but now it can also be used by rpm under RedHat.
Features of yum
1. Multiple repositories can be configured at the same time
2. Simple configuration file (generally the configuration file is /etc/yum.conf )
3. Automatically solve dependency problems encountered when adding or deleting rpm packages
4. Keep consistent with the rpm database
yum configuration file
yum configuration file, its absolute path is generally: /etc/yum.conf. All configuration information of yum is stored in this file, which is the most important content in the yum system.
Yum.conf is generally divided into two parts: main and repository, but by default there is only the main part. Each yum.conf can only have one main section. The repository section defines the specific configuration of each source/server, which can be one or more. Often located in various files in the /etc/yum.repo.d directory.
Use cat /etc/yum.conf to view the contents of the file.
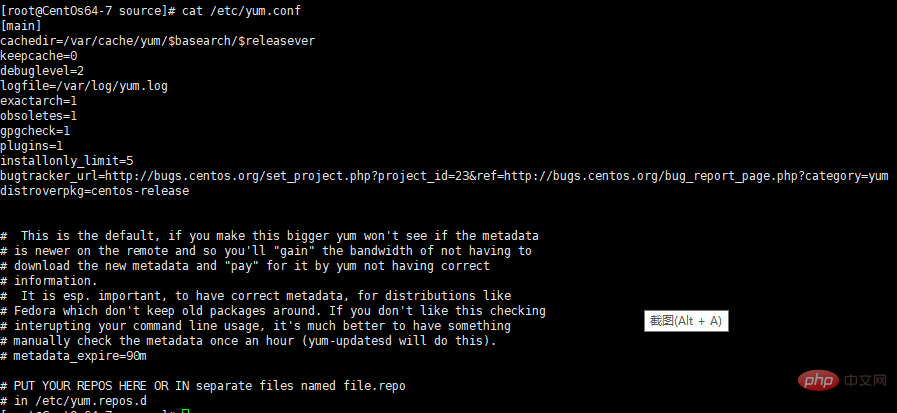
1.cachedir: This item is the cache directory of the RPM package downloaded by yum. yum stores the downloaded rpm package and database here
2.keepcache : Whether the cache is saved, 1 means retaining the software package after installation, 0 means deleting the software package after installation
3.debuglevel: Error log level, the level is 0-10, the default is 2 (only installation and deletion records are kept )
4.logfile: Stores records of system update software. Users can check what updates they have made in the past days in the file configured by this configuration item
5. pkgpolicy: Package policy. There are two options, newest and last. This function is if you set up multiple repositories, and the same software exists in different repositories at the same time, which one yum should install. If it is newest, yum will install the latest version. . If it is last, yum will sort the server IDs alphabetically and select the software installation on the last server.
6.distroverp: Specify a software package. Yum will determine your release version based on this package. The default is RedHat-release, or it can be any rpm installed for your own release. Bag.
7.tolerent: There are also two options, 1 and 0, indicating whether yum tolerates package-related errors on the command line. For example, you want to install three packages 1, 2, and 3. , and 3 of them have been installed before. If you set it to 1, yum will not show an error message. The default is 0.
8.exactarch: There are two options, 1 and 0, which represent whether to only upgrade the package with the same cpu system as the software package you installed. If it is set to 1, it will be as if you installed a i386 rpm, yum will not use the 1686 package to upgrade.
9.retries: The number of retries after a network connection error occurs. If set to 0, it will retry infinitely.
10.obsoletes: This is an update parameter. For details, please refer to yum(8). Simply put, it is equivalent to upgrade and allows updates. Old RPM packages.
11.gpgcheck: Whether to check GPG (GNU Private Guard), a key signature.
12.plugins: Whether to allow the use of plug-ins, the default is 0 not allowed , but we generally use the yum-fastestmirror plug-in.
13.installonly_limit: How many kernel packages are allowed to be retained.
14.exclude: Shield RPM packages that you do not want to update. Wildcards can be used, and spaces are used to separate multiple RPM packages.
15.reposdir: This option allows users to specify the absolute path to the .repo file. The .repo file contains information about the software repository (same as the [repository] section in the /etc/yum.conf file). reposdir=[absolute path to the directory containing the .repo file]
16.bugtracker_url:trackingbugpath
Usage: man 5 yum.conf # Detailed explanation of yum.conf is available
##yum Working principle
#yum’s working mode is C/S architecture:
##ServerEnd(yumwarehouse): Dependency library, original file, verification code file.
Client: yumClient program, configuration file (ConnectionServerPath Information). #
#When executing the yum command, the address of the software warehouse will first be obtained from the many repo files in the "/etc/yum.repo.d" directory and Download "metadata". "Metadata" includes the package names of all software packages registered in the software warehouse and their required dependency environments. After yum obtains this information, it will compare it with the local environment and then list and confirm it. Which packages need to be installed, and the installation will start after the user confirms.
"Metadata" is indexed by repomd.xml located in the repodata directory in the path related to the yum source server.
##yum system workflow:
##Server side: All rpm packages are stored on the server, and then the dependencies of each rpm file are analyzed using related functions, and these data are recorded into files. Stored in a specific directory on the server.
##Client: If you need to install a certain software, first download the dependencies recorded on the server Sexual relationship files (can be through WWW or FTP), by analyzing the record data downloaded from the server, and then obtaining all related software, downloading them all at once for installation. #
#.repo file
What is a repo file? The repo file is the configuration file of the yum source (software warehouse) in Fedora. Usually a repo file defines the details of one or more software warehouses, such as where we will download the software packages that need to be installed or upgraded, and the settings in the repo file. The content will be read and applied by yum!
# Enter the /etc/yum.repos.d/ directory and you can See that there are three files as follows by default:
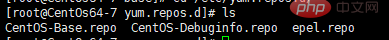 ## Where CentOS-Base.repo is the configuration file of the yum network source (usually this is used) CentOS-Debuginfo .repo debug package, especially kernel-related updates and software installation
## Where CentOS-Base.repo is the configuration file of the yum network source (usually this is used) CentOS-Debuginfo .repo debug package, especially kernel-related updates and software installation
CentOS-Media.repo This is a file that is called after being mounted using a CD (I don’t have it on my machine)
CentOS-Vault. repo This is the old version of yum source configuration added to the latest new version (no...)
epel.repo: EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) is created by the Fedora community and is distributed for RHEL and derivatives Versions such as CentOS and other projects that provide high-quality software packages. After installing EPEL, just like on Fedora, you can use yum install package name to install many software that needed to be compiled and installed before, commonly used software or some more popular software, such as the now popular nginx, htop, ncdu , vnstat, etc., can be easily installed and updated using EPEL. You can install it directly by executing the command:
yum install epel-release. If it cannot be installed, refer to:
yum command formatThe command form of yum is generally as follows :
yum [options] [command] [package ...] The [options] are optional, and the options include -h (help), -y ( When prompted during the installation process, select "yes" for all), -q (do not display the installation process), etc. [command] is the operation to be performed, and [package...] is the object of the operation.
1.OPTIONS
--nogpgcheck: gpg check is prohibited;
-y:
The automatic answer is "yes"; ##, do not output display information;
--disablerepo=repoidglob: Temporarily disable the repo specified here; --enablerepo=repoidglob: Temporarily enable the repo specified here; ; ..com.com #COMMAND (1)Display warehouse list:repolist yum repolist [all|enabled|disabled] [All|available|unavailable] See: https://blog.csdn.net/xmm1981/article/details/ 78258176 Recommended: "centos usage tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What is centos7 yum. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 CentOS7 various version image download addresses and version descriptions (including Everything version)
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:20 AM
CentOS7 various version image download addresses and version descriptions (including Everything version)
Feb 29, 2024 am 09:20 AM
When loading CentOS-7.0-1406, there are many optional versions. For ordinary users, they don’t know which one to choose. Here is a brief introduction: (1) CentOS-xxxx-LiveCD.ios and CentOS-xxxx- What is the difference between bin-DVD.iso? The former only has 700M, and the latter has 3.8G. The difference is not only in size, but the more essential difference is that CentOS-xxxx-LiveCD.ios can only be loaded into the memory and run, and cannot be installed. Only CentOS-xxx-bin-DVD1.iso can be installed on the hard disk. (2) CentOS-xxx-bin-DVD1.iso, Ce
 Detailed explanation of the steps to upgrade gcc using yum on CentOS6.5
Dec 31, 2023 am 10:59 AM
Detailed explanation of the steps to upgrade gcc using yum on CentOS6.5
Dec 31, 2023 am 10:59 AM
Because C++11 needs to be used, but the gcc4.4.7 that comes with CentOS does not support it, I decided to upgrade gcc. The operation is as follows: #Backup mv/etc/yum.repos.d/devtools-2.repo/etc/yum.repos.d/devtools-2.repo.bakwgethttp://people.centos.org/tru/devtools-2 /devtools-2.repo-O/etc/yum.repos.d/devtools-2.repoyuminstalldevtoolset-2-gccdevtoolse
 Steps to enter CentOS 7 emergency repair mode
Jan 13, 2024 am 09:36 AM
Steps to enter CentOS 7 emergency repair mode
Jan 13, 2024 am 09:36 AM
Open the centos7 page and appear: welcome to emergency mode! afterloggingin, type "journalctl -xb" to viewsystemlogs, "systemctlreboot" toreboot, "systemctldefault" to tryagaintobootintodefaultmode. giverootpasswordformaintenance(??Control-D???): Solution: execute r
 How to access and clean junk files in /tmp directory in CentOS 7?
Dec 27, 2023 pm 09:10 PM
How to access and clean junk files in /tmp directory in CentOS 7?
Dec 27, 2023 pm 09:10 PM
There is a lot of garbage in the tmp directory in the centos7 system. If you want to clear the garbage, how should you do it? Let’s take a look at the detailed tutorial below. To view the list of files in the tmp file directory, execute the command cdtmp/ to switch to the current file directory of tmp, and execute the ll command to view the list of files in the current directory. As shown below. Use the rm command to delete files. It should be noted that the rm command deletes files from the system forever. Therefore, it is recommended that when using the rm command, it is best to give a prompt before deleting the file. Use the command rm-i file name, wait for the user to confirm deletion (y) or skip deletion (n), and the system will perform corresponding operations. As shown below.
 How to set password rules in centos7? How to set password rules in centos7
Jan 07, 2024 pm 01:17 PM
How to set password rules in centos7? How to set password rules in centos7
Jan 07, 2024 pm 01:17 PM
Set password rules for security reasons Set the number of days after which passwords expire. User must change password within days. This setting only affects created users, not existing users. If setting to an existing user, run the command "chage -M (days) (user)". PASS_MAX_DAYS60#Password expiration time PASS_MIN_DAYS3#Initial password change time PASS_MIN_LEN8#Minimum password length PASS_WARN_AGE7#Password expiration prompt time Repeat password restriction use [root@linuxprobe~]#vi/etc/pam.d/system-auth#nearline15:
 Centos offline installation of Chinese version of GitLab
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:36 AM
Centos offline installation of Chinese version of GitLab
Feb 19, 2024 am 11:36 AM
1. Download the gitlab installation package. Download the latest Chinese version of the gitlab installation package from [Tsinghua University Open Source Software Mirror Station]. The installation package comes with a simplified Chinese localization package. Download the latest gitlab installation package from [gitlab official website]. 2. Install gitlab, take gitlab-ce-14.9.4-ce.0.el7.x86_64 as an example, upload it to the centos server and use yum to install gitlabyum-yinstallgitlab-ce-14.3.2-ce.0.el7.x86_64. rpm uses yum to install gityum-yinstallgit#Install git and modify the gitlab configuration file vi
 How to install mbstring extension under CENTOS7?
Jan 06, 2024 pm 09:59 PM
How to install mbstring extension under CENTOS7?
Jan 06, 2024 pm 09:59 PM
1.UncaughtError:Calltoundefinedfunctionmb_strlen(); When the above error occurs, it means that we have not installed the mbstring extension; 2. Enter the PHP installation directory cd/temp001/php-7.1.0/ext/mbstring 3. Start phpize(/usr/local/bin /phpize or /usr/local/php7-abel001/bin/phpize) command to install php extension 4../configure--with-php-config=/usr/local/php7-abel
 How to install Mysql in CentOS7 and set it to start automatically at boot
Jun 02, 2023 pm 08:36 PM
How to install Mysql in CentOS7 and set it to start automatically at boot
Jun 02, 2023 pm 08:36 PM
Centos7 does not have a mysql database. The default database is mariadb (a branch of mysql). You can install the mysql database manually by following the steps below. 1. Download the rpm installation file wgethttp://repo.mysql.com/mysql-community-release-el7.rpm 2. Execute rpm to install rpm-ivhmysql-community-release-el7.rpm. After the dependency resolution is completed, the following options appear: dependenciesresolved =================================




